(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
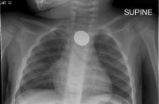
In today's technology-driven world, batteries, especially button batteries, are everywhere. A new study shows that every 90 minutes a child younger than 18 years of age is seen in a...
Click here for more information.
In today's technology-driven world, batteries, especially button batteries, are everywhere. They power countless gadgets and electronic items that we use every day. While they may seem harmless, button batteries can be dangerous if swallowed by children. A new study conducted by researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy of The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital found that the annual number of battery-related emergency department visits among children younger than 18 years of age more than doubled over the 20-year study period, jumping from 2,591 emergency department visits in 1990 to 5,525 emergency department visits in 2009. The number of button batteries swallowed by children also doubled during this period.
The study, being released online May 14, 2012 and appearing in the June 2012 print issue of Pediatrics, found that more than three-fourths of battery-related visits to emergency departments by children were among children 5 years-old or younger, with one-year-olds having the greatest number of emergency department visits. Of the cases where the battery's intended use was mentioned, only 29 percent involved batteries that were used for toys and games. The majority of cases involved batteries from products not intended for use by young children, such as watches (14 percent), calculators (12 percent), flashlights (9 percent) and remote controls (6 percent).
"We live in a world designed by adults for the convenience of adults, and the safety of children is often not considered," said Gary Smith, MD, DrPH, director of the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children's Hospital. "Products with easily-accessible battery compartments are everywhere in our homes today. By making a few simple design changes and strengthening product manufacturing standards, including products not intended for use by young children, we could prevent many of the serious and sometimes fatal injuries that occur when children are able to easily access button batteries in common household products."
Among cases that described the type of battery, 84 percent involved button batteries. Researchers attribute this finding to the increasing number and variety of electronics powered by button batteries and the resulting increased availability of these products in the home. Recent reports suggest that the number of fatal and severe button battery ingestions is on the rise. This trend is associated with the increasing use of the three volt, 20 millimeter, lithium button batteries.
"The increased prevalence of the higher voltage 20mm lithium batteries is concerning because it coincides with an alarming 113 percent increase in battery ingestions and insertions by young children," said Dr. Smith, also a professor of pediatrics at The Ohio State University College of Medicine. "When a button battery is swallowed and gets caught in a child's esophagus, serious, even fatal injuries can occur in less than two hours."
Recommendations to prevent these types of injuries include:
Taping the battery compartments of all household devices shut
Storing batteries and products with batteries out of the reach of young children
Being aware of this potential danger when your child is visiting other homes
Researchers also recommend that manufacturers ensure that packaging for batteries and products containing button batteries is child resistant and that they design all battery compartments to either require a screwdriver to be opened or that they be secured with a child-resistant locking mechanism, regardless of whether the product is intended for use by children or adults. Parents who think that their child may have swallowed a button battery should seek medical attention immediately so that an x-ray can be taken to be sure that the battery is not stuck in the esophagus.
INFORMATION:
Data for this study were obtained from the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS), which is operated by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. The NEISS dataset provides information on consumer product-related and sports and recreation-related injuries treated in hospital emergency departments across the country.
The Center for Injury Research and Policy (CIRP) of The Research Institute at Nationwide
Children's Hospital works globally to reduce injury-related pediatric death and disabilities. With innovative research as its core, CIRP works to continually improve the scientific understanding of the epidemiology, biomechanics, prevention, acute treatment and rehabilitation of injuries. CIRP serves as a pioneer by translating cutting edge injury research into education, policy and advances in clinical care. For related injury prevention materials or to learn more about CIRP visit http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/injury-research-and-policy.
For more information on Dr. Gary Smith, visit http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/gary-a-smith
For more information on The Center for Injury Research and Policy, visit http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/injury-research-and-policy
Study finds number of battery-related emergency department visits by children more than doubles
Every 90 minutes, a child younger than 18 years of age is seen in a US emergency department for a battery-related problem
2012-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study examines injuries with baby bottles, pacifiers and sippy cups in the US
2012-05-15
VIDEO:
Sippy cups, bottles and pacifiers are popular items used by many parents for their kids. However, a new study shows that these items can be dangerous if a child is...
Click here for more information.
A new study by researchers in the Center for Biobehavioral Health and the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children's Hospital examined pediatric injuries associated with baby bottles, pacifiers and sippy cups. Researchers found that from 1991 to 2010, ...
Nearly one-tenth of hemisphere's mammals unlikely to outrun climate change
2012-05-15
A safe haven could be out of reach for 9 percent of the Western Hemisphere's mammals, and as much as 40 percent in certain regions, because the animals just won't move swiftly enough to outpace climate change.
For the past decade scientists have outlined new areas suitable for mammals likely to be displaced as climate change first makes their current habitat inhospitable, then unlivable. For the first time a new study considers whether mammals will actually be able to move to those new areas before they are overrun by climate change. Carrie Schloss, University of Washington ...
Scientists make breakthrough in bile duct cancer with discovery of new gene mutations
2012-05-15
Grand Rapids, Mich. (May 14, 2012) - A team of international scientists has made a significant breakthrough in understanding the cause of bile duct cancer, a deadly type of liver cancer. By identifying several new genes frequently mutated in bile duct cancers, researchers are paving the way for better understanding of how bile duct cancers develop. Their discovery is published online in Nature Genetics.
Bile Duct Cancer, or Cholangiocarcinoma, is a fatal cancer with a poor prognosis. Accounting for 10 to 25 per cent of all primary liver cancers worldwide, bile duct cancer ...
Great recession reflux amounts to more hunger among seniors
2012-05-15
URBANA – A new study that looked at the hunger trends over a 10-year period found that 14.85 percent of seniors in the United States, more than one in seven, face the threat of hunger. This translates into 8.3 million seniors.
"In 2005, we reported that one in nine seniors faced the threat of hunger," said Craig Gundersen, University of Illinois associate professor of agricultural and consumer economics and executive director of the National Soybean Research Laboratory who led the data analysis on the study. "So, unlike the population as a whole, food insecurity among ...
New York Stem Cell Foundation scientist grows bone from human embryonic stem cells
2012-05-15
NEW YORK, NY (May 14, 2012) -- Dr. Darja Marolt, an Investigator at The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Laboratory, is lead author on a study showing that human embryonic stem cells can be used to grow bone tissue grafts for use in research and potential therapeutic application. Dr. Marolt conducted this research as a post-doctoral NYSCF – Druckenmiller Fellow at Columbia University in the laboratory of Dr. Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic.
The study is the first example of using bone cell progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells to grow compact bone tissue ...
Brain circuitry is different for women with anorexia and obesity
2012-05-15
AURORA, Colo. (May 14, 2012) - Why does one person become anorexic and another obese? A study recently published by a University of Colorado School of Medicine researcher shows that reward circuits in the brain are sensitized in anorexic women and desensitized in obese women. The findings also suggest that eating behavior is related to brain dopamine pathways involved in addictions.
Guido Frank, MD, assistant professor director of the Developmental Brain Research Program at the CU School of Medicine and his colleagues used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) ...
Growing risks from hatchery fish
2012-05-15
Portland, Oregon – May 14, 2012 -- A newly published collection of more than 20 studies by leading university scientists and government fishery researchers in Alaska, British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, California, Russia and Japan provides mounting evidence that salmon raised in man-made hatcheries can harm wild salmon through competition for food and habitat.
"The genetic effects of mixing hatchery fish with wild populations have been well-documented," says journal editor David Noakes from Oregon State University. "But until now the ecological effects were largely ...
Genetic test identifies eye cancer tumors likely to spread
2012-05-15
AUDIO:
The most common form of cancer in the eye can be deadly. New treatments have allowed doctors to preserve vision in patients with ocular melanoma, but sometimes the cancer...
Click here for more information.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a genetic test that can accurately predict whether the most common form of eye cancer will spread to other parts of the body, particularly the liver.
In 459 patients with ocular ...
Lawrence Livermore work may improve the efficiency of the biofuel production cycle
2012-05-15
By deciphering the makeup of a bacterium found in the soil of a tropical rain forest, scientists may have a better understanding of how to more efficiently produce biofuels.
The production of liquid fuels derived from plant biomass offers a promising technology for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
While sugars stored within the plant cell wall, known as lignocellulose, are plentiful enough to supply most energy needs on the planet, their extraction is difficult and requires chemical pretreatment followed by enzymatic digestion using ...
Microbe that can handle ionic liquids
2012-05-15
In the search for technology by which economically competitive biofuels can be produced from cellulosic biomass, the combination of sugar-fermenting microbes and ionic liquid solvents looks to be a winner save for one major problem: the ionic liquids used to make cellulosic biomass more digestible for microbes can also be toxic to them. A solution to this conundrum, however, may be in the offing.
Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI), a multi-institutional partnership led by Berkeley Lab, have identified a tropical rainforest ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
[Press-News.org] Study finds number of battery-related emergency department visits by children more than doublesEvery 90 minutes, a child younger than 18 years of age is seen in a US emergency department for a battery-related problem