(Press-News.org) Toronto, CANADA – A walk in the park may have psychological benefits for people suffering from depression.
In one of the first studies to examine the effect of nature walks on cognition and mood in people with major depression, researchers in Canada and the U.S. have found promising evidence that a walk in the park may provide some cognitive benefits.
The study was led by Marc Berman, a post-doctoral fellow at Baycrest's Rotman Research Institute in Toronto, with partners from the University of Michigan and Stanford University. It is published online this week, ahead of print publication, in the Journal of Affective Disorders.
"Our study showed that participants with clinical depression demonstrated improved memory performance after a walk in nature, compared to a walk in a busy urban environment," said Dr. Berman, who cautioned that such walks are not a replacement for existing and well-validated treatments for clinical depression, such as psychotherapy and drug treatment.
"Walking in nature may act to supplement or enhance existing treatments for clinical depression, but more research is needed to understand just how effective nature walks can be to help improve psychological functioning," he said.
Dr. Berman's research is part of a cognitive science field known as Attention Restoration Theory (ART) which proposes that people concentrate better after spending time in nature or looking at scenes of nature. The reason, according to ART, is that people interacting with peaceful nature settings aren't bombarded with external distractions that relentlessly tax their working memory and attention systems. In nature settings, the brain can relax and enter a state of contemplativeness that helps to restore or refresh those cognitive capacities.
In a research paper he published in 2008 in Psychological Science, Dr. Berman showed that adults who were not diagnosed with any illness received a mental boost after an hour-long walk in a woodland park – improving their performance on memory and attention tests by 20 percent – compared to an hour-long stroll in a noisy urban environment. The findings were reported by The Wall Street Journal, The Boston Globe, The New York Times, and in the Pulitzer Prize finalist book by Nicholas Carr, The Shallows: What the internet is doing to our brains.
In this latest study, Dr. Berman and his research team explored whether a nature walk would provide similar cognitive benefits, and also improve mood for people with clinical depression. Given that individuals with depression are characterized by high levels of rumination and negative thinking, the researchers were skeptical at the outset of the study that a solitary walk in the park would provide any benefit at all and may end up worsening memory and exacerbating depressed mood.
For the study, 20 individuals were recruited from the University of Michigan and surrounding Ann Arbor area; all had a diagnosis of clinical depression. The 12 females and eight males (average age 26) participated in a two-part experiment that involved walking in a quiet nature setting and in a noisy urban setting.
Prior to the walks, participants completed baseline testing to determine their cognitive and mood status. Before beginning a walk, the participants were asked to think about an unresolved, painful autobiographical experience. They were then randomly assigned to go for an hour-long walk in the Ann Arbor Arboretum (woodland park) or traffic heavy portions of downtown Ann Arbor. They followed a prescribed route and wore a GPS watch to ensure compliance.
After completing their walk, they completed a series of mental tests to measure their attention and short-term/working memory and were re-asssessed for mood. A week later the participants repeated the entire procedure, walking in the location that was not visited in the first session.
Participants exhibited a 16 percent increase in attention and working memory after the nature walk relative to the urban walk. Interestingly, interacting with nature did not alleviate depressive mood to any noticeable degree over urban walks, as negative mood decreased and positive mood increased after both walks to a significant and equal extent. Dr. Berman says this suggests that separate brain mechanisms may underlie the cognitive and mood changes of interacting with nature.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health and a private grant from the TKF Foundation.
At Baycrest's Rotman Research Institute, Marc Berman's research explores the brain mechanisms involved in controlling thoughts, feeling and behaviors, and how to improve those abilities. Prior to joining Baycrest in 2011, Dr. Berman received his Ph.D. in Cognitive Neuroscience and Industrial and Operations Engineering at the University of Michigan.
For more information on this press release, please contact:
Kelly Connelly
Senior Media Officer
Rotman Research Institute
Baycrest
416.785.2432
END
A recent CBS report has retailers gearing up for increased sales for this upcoming Mother's Day. Since 1908, Americans have come together every year on this springtime Sunday to honor mothers everywhere. Over one hundred years later, the public continues to show its appreciation of our creation and development without sparing any expense. Twigs Cafe, a quaint, local restaurant tucked away in the charming Tunkhannock, Pennsylvania is just one of the many businesses preparing to help consumers celebrate our treasured female figures.
The report quotes research conducted ...
Reticulated dragonet have been found in Väderöarna – "Weather Islands" – off the west coast of Sweden. It is not often that a new species of fish is discovered in Sweden.
Lars-Ove Loo is the underwater photographer who has captured the fish on film. He saw it while making an inventory ahead of the creation of a new nature reserve in the islands. This was in August 2010, 19 meters below the surface of the sea south of Lyngö in the southern Väderöarna (58° 32.554' N, 11° 05.373' E).
Reticulated dragonet (Callionymus reticulatus) is similar to its more common Swedish relatives ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A study has identified microRNA-3151 as a new independent prognostic marker in certain patients with acute leukemia. The study involves patients with acute myeloid leukemia and normal-looking chromosomes
(CN-AML).
The study by researchers at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James) found that when microRNA-3151 (miR-3151) is overexpressed in CN-AML, the disease responds poorly to treatment and patients experience shorter remissions and survival periods. ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — The sound of silence isn't so golden for consumers, and both marketers and advertisers should take note, says new research from a University of Illinois expert in new product development and marketing.
According to published research from Ravi Mehta, a professor of business administration, ambient background noise turns out to be an important factor affecting creative cognition among consumers.
"We found that ambient noise is an important antecedent for creative cognition," Mehta said. "A moderate level of noise not only enhances creative problem-solving ...
Paediatric brain tumours preserve specific characteristics of the normal cells from which they originate – a previously unknown circumstance with ramifications for how tumour cells respond to treatment. This has been shown by Uppsala researcher Fredrik Swartling together with colleagues in the U.S., Canada and England in a study that was published today in the distinguished journal Cancer Cell.
Every year, 80-90 children in Sweden are afflicted with brain tumours, a serious form of paediatric cancer. Today, three of four children who receive treatment survive.
The ...
VIDEO:
In today's technology-driven world, batteries, especially button batteries, are everywhere. A new study shows that every 90 minutes a child younger than 18 years of age is seen in a...
Click here for more information.
In today's technology-driven world, batteries, especially button batteries, are everywhere. They power countless gadgets and electronic items that we use every day. While they may seem harmless, button batteries can be dangerous if swallowed by children. ...
VIDEO:
Sippy cups, bottles and pacifiers are popular items used by many parents for their kids. However, a new study shows that these items can be dangerous if a child is...
Click here for more information.
A new study by researchers in the Center for Biobehavioral Health and the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children's Hospital examined pediatric injuries associated with baby bottles, pacifiers and sippy cups. Researchers found that from 1991 to 2010, ...
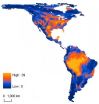
A safe haven could be out of reach for 9 percent of the Western Hemisphere's mammals, and as much as 40 percent in certain regions, because the animals just won't move swiftly enough to outpace climate change.
For the past decade scientists have outlined new areas suitable for mammals likely to be displaced as climate change first makes their current habitat inhospitable, then unlivable. For the first time a new study considers whether mammals will actually be able to move to those new areas before they are overrun by climate change. Carrie Schloss, University of Washington ...
Grand Rapids, Mich. (May 14, 2012) - A team of international scientists has made a significant breakthrough in understanding the cause of bile duct cancer, a deadly type of liver cancer. By identifying several new genes frequently mutated in bile duct cancers, researchers are paving the way for better understanding of how bile duct cancers develop. Their discovery is published online in Nature Genetics.
Bile Duct Cancer, or Cholangiocarcinoma, is a fatal cancer with a poor prognosis. Accounting for 10 to 25 per cent of all primary liver cancers worldwide, bile duct cancer ...
URBANA – A new study that looked at the hunger trends over a 10-year period found that 14.85 percent of seniors in the United States, more than one in seven, face the threat of hunger. This translates into 8.3 million seniors.
"In 2005, we reported that one in nine seniors faced the threat of hunger," said Craig Gundersen, University of Illinois associate professor of agricultural and consumer economics and executive director of the National Soybean Research Laboratory who led the data analysis on the study. "So, unlike the population as a whole, food insecurity among ...