Pain relief through distraction -- it's not all in your head
2012-05-18
(Press-News.org) Mental distractions make pain easier to take, and those pain-relieving effects aren't just in your head, according to a report published online on May 17 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication.
The findings based on high-resolution spinal fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) as people experienced painful levels of heat show that mental distractions actually inhibit the response to incoming pain signals at the earliest stage of central pain processing.
"The results demonstrate that this phenomenon is not just a psychological phenomenon, but an active neuronal mechanism reducing the amount of pain signals ascending from the spinal cord to higher-order brain regions," said Christian Sprenger of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf.
Those effects involve endogenous opioids, which are naturally produced by the brain and play a key role in the relief of pain, the new evidence shows.
The research group asked participants to complete either a hard or an easy memory task, both requiring them to remember letters, while they simultaneously applied a painful level of heat to their arms.
When study participants were more distracted by the harder of the two memory tasks, they did indeed perceive less pain. What's more, their less painful experience was reflected by lower activity in the spinal cord as observed by fMRI scans. (fMRI is often used to measure changes in brain activity, Sprenger explained, and recent advances have made it possible to extend this tool for use in the spinal cord.)
Sprenger and colleagues then repeated the study again, this time giving participants either a drug called naloxone, which blocks the effects of opioids, or a simple saline infusion. The pain-relieving effects of distraction dropped by 40 percent during the application of the opioid antagonist compared to saline, evidence that endogenous opioids play an essential role.
The findings show just how deeply mental processes can go in altering the experience of pain, and that may have clinical importance.
"Our findings strengthen the role of cognitive-behavioral therapeutic approaches in the treatment of pain diseases, as it could be extrapolated that these approaches might also have the potential to alter the underlying neurobiological mechanisms as early as in the spinal cord," the researchers say.
###
Sprenger et al.: "Attention modulates spinal cord responses to pain."
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-05-18
When it comes to weight gain, when you eat might be at least as important as what you eat. That's the conclusion of a study reported in the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism published early online on May 17th.
When mice on a high-fat diet are restricted to eating for eight hours per day, they eat just as much as those who can eat around the clock, yet they are protected against obesity and other metabolic ills, the new study shows. The discovery suggests that the health consequences of a poor diet might result in part from a mismatch between our body clocks and our ...
2012-05-18
Research to be published in Science on May 18, 2012, sheds light on a hot-button political issue: the role and effectiveness of government regulation. Does it kill jobs or protect the public?
The new study, co-authored by Harvard Business School Professor Michael Toffel, Professor David Levine of the Haas School of Business at the University of California, Berkeley, and Boston University doctoral student Matthew Johnson, examines workplace safety inspections conducted by California's Division of Occupational Safety and Health (Cal/OSHA). The authors carried out the first ...
2012-05-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich.--- Across history and cultures, religion increases trust within groups but also may increase conflict with other groups, according to an article in a special issue of Science.
"Moralizing gods, emerging over the last few millennia, have enabled large-scale cooperation and sociopolitical conquest even without war," says University of Michigan anthropologist Scott Atran, lead author of the article with Jeremy Ginges of the New School for Social Research.
"Sacred values sustain intractable conflicts like those between the Israelis and the Palestinians ...
2012-05-18
The strategy used by Google to decide which pages are relevant for a search query can also be used to determine which proteins in a patient's cancer are relevant for the disease progression. Researchers from Dresden University of Technology, Germany, have used a modified version of Google's PageRank algorithm to rank about 20,000 proteins by their genetic relevance to the progression of pancreatic cancer. In their study, published in PLoS Computational Biology, they found seven proteins that can help to assess how aggressive a patient's tumor is and guide the clinician ...
2012-05-18
###
Weill Cornell Medical College
Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University's medical school located in New York City, is committed to excellence in research, teaching, patient care and the advancement of the art and science of medicine, locally, nationally and globally. Physicians and scientists of Weill Cornell Medical College are engaged in cutting-edge research from bench to bedside, aimed at unlocking mysteries of the human body in health and sickness and toward developing new treatments and prevention strategies. In its commitment to global health and ...
2012-05-18
In two back-to-back reports published online on 17 May in Cell, researchers have sequenced the genomes of 21 breast cancers and analysed the mutations that emerged during the tumours' development. The individual results are described below.
Led by researchers from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, the team created a catalogue of all the mutations in the genomes of the 21 cancer genomes and identified the mutational processes that lead to breast cancer. They found that these mutations accumulate in breast cells over many years, initially rather slowly, but picking up ...
2012-05-18
Researchers at the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute have confirmed the long-held conjecture that studying the genes we share with other animals is a viable means of extrapolating information about human biology. The study, published in the open access journal PLoS Computational Biology, shows how bioinformatics makes it possible to test the conjecture.
Scientists have long looked to model species – mice, for example – to understand human biology. This is at the root of what is called the 'ortholog conjecture': the idea ...
2012-05-18
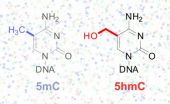
Imagine reading an entire book, but then realizing that your glasses did not allow you to distinguish "g" from "q." What details did you miss?
Geneticists faced a similar problem with the recent discovery of a "sixth nucleotide" in the DNA alphabet. Two modifications of cytosine, one of the four bases that make up DNA, look almost the same but mean different things. But scientists lacked a way of reading DNA, letter by letter, and detecting precisely where these modifications are found in particular tissues or cell types.
Now, a team of scientists from the University ...
2012-05-18
VIDEO:
This is an interview with Dr. Panda.
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA, CA----It turns out that when we eat may be as important as what we eat. Scientists at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies have found that regular eating times and extending the daily fasting period may override the adverse health effects of a high-fat diet and prevent obesity, diabetes and liver disease in mice.
In a paper published May 17 in Cell Metabolism, scientists from Salk's ...
2012-05-18
Researchers at the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute have confirmed the long-held belief that studying the genes we share with other animals is useful. The study, published today in the open access journal PLoS Computational Biology, shows how bioinformatics makes it possible to test the fundamental principles on which life science is built.
Studying genes helps life science researchers understand how our bodies work and how diseases progress. Scientists have long looked to model species – mice, for example – to understand ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pain relief through distraction -- it's not all in your head