(Press-News.org) Highlights
A minimally invasive procedure called renal denervation, which disrupts certain nerves in the kidneys, lowers blood pressure in patients with chronic kidney disease and hypertension.
The procedure may help protect the kidneys and reduce heart risks in patients with chronic kidney disease.
60 million people globally have chronic kidney disease.
Washington, DC (May 17, 2012) — Disrupting certain nerves in the kidneys can safely and effectively lower blood pressure in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and hypertension, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). The findings indicate that the procedure might improve CKD patients' heart health.
Overactivity of neurons in the sympathetic—or fight or flight—nervous system is very common in patients with CKD. It not only contributes to high blood pressure and heart problems in these patients, but also to worsening of their kidney disease.
A minimally invasive procedure called renal denervation—which uses radiofrequency waves to disrupt the overactive sympathetic nerves running along the arteries in the kidneys—can lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension and normal kidney function. Dagmara Hering, MD, Markus Schlaich, MD (Baker IDI Heart & Diabetes Institute, in Melbourne, Australia) and their colleagues looked to see if the procedure can also safely help CKD patients with hypertension.
The investigators performed renal denervation in 15 patients with hypertension and CKD. Normal blood pressure in the general population is 120/80 mmHg. Patients' average level at the start of the study was 174/91 mmHg despite taking numerous antihypertensive drugs. Patients' blood pressure readings dropped considerably at one, three, six, and 12 months after the procedure (-34/-14, -25/-11, -32/-15, and -33/-19 mmHg, respectively). Renal denervation did not worsen patients' kidney function, indicating that it is safe even when CKD is present.
"These initial findings now open up an entirely new approach to better control blood pressure in CKD and potentially slow down progression of CKD and reduce cardiovascular risk in these patients. said Dr. Schlaich.
Approximately 60 million people globally have CKD. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in these individuals.
###Study co-authors include Felix Mahfoud, MD, Antony Walton, MD, Henry Krum, MBBS, PhD, Gavin W Lambert, PhD, Elisabeth Lambert, PhD, Paul A Sobotka, MD, Michael Böhm, MD, Bodo Cremers, MD, Murray Esler, MBBS, PhD.
Disclosures: This study was funded in part by grants from the National Health and Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) and the Victorian Government's Operational Infrastructure Support Program. Professor Schlaich, Prof Esler, Dr E Lambert, and Dr G Lambert are supported by career fellowships from the NHMRC. Dr Dagmara Hering is currently supported by Research Fellowship from the Foundation for Polish Science KOLUMB/2010-1. Dr Felix Mahfoud is supported by the Deutsche Hochdruckliga. Dres Schlaich, Mahfoud, Walton, Krum, Boehm, Esler are principal investigators in studies sponsored by Medtronic, the company that manufactures the renal deneravtion device and have received consultancy/lecture fees from Medtronic.
The article, entitled "Renal Denervation in Moderate to Severe CKD," will appear online at http://jasn.asnjournals.org/ on May 17, 2012 2012, doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011111062.
The content of this article does not reflect the views or opinions of The American Society of Nephrology (ASN). Responsibility for the information and views expressed therein lies entirely with the author(s). ASN does not offer medical advice. All content in ASN publications is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects. This content should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Please consult your doctor or other qualified health care provider if you have any questions about a medical condition, or before taking any drug, changing your diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment. Do not ignore or delay obtaining professional medical advice because of information accessed through ASN. Call 911 or your doctor for all medical emergencies.
Founded in 1966, and with more than 13,500 members, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) leads the fight against kidney disease by educating health professionals, sharing new knowledge, advancing research, and advocating the highest quality care for patients.
Simple procedure lowers blood pressure in kidney disease patients
Renal denervation may protect the kidneys and reduce heart risks
2012-05-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pain relief through distraction -- it's not all in your head
2012-05-18
Mental distractions make pain easier to take, and those pain-relieving effects aren't just in your head, according to a report published online on May 17 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication.
The findings based on high-resolution spinal fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) as people experienced painful levels of heat show that mental distractions actually inhibit the response to incoming pain signals at the earliest stage of central pain processing.
"The results demonstrate that this phenomenon is not just a psychological phenomenon, but an active neuronal ...
When you eat matters, not just what you eat
2012-05-18
When it comes to weight gain, when you eat might be at least as important as what you eat. That's the conclusion of a study reported in the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism published early online on May 17th.
When mice on a high-fat diet are restricted to eating for eight hours per day, they eat just as much as those who can eat around the clock, yet they are protected against obesity and other metabolic ills, the new study shows. The discovery suggests that the health consequences of a poor diet might result in part from a mismatch between our body clocks and our ...
New study shows that workplace inspections save lives, don't destroy jobs
2012-05-18
Research to be published in Science on May 18, 2012, sheds light on a hot-button political issue: the role and effectiveness of government regulation. Does it kill jobs or protect the public?
The new study, co-authored by Harvard Business School Professor Michael Toffel, Professor David Levine of the Haas School of Business at the University of California, Berkeley, and Boston University doctoral student Matthew Johnson, examines workplace safety inspections conducted by California's Division of Occupational Safety and Health (Cal/OSHA). The authors carried out the first ...
Religion is a potent force for cooperation and conflict, research shows
2012-05-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich.--- Across history and cultures, religion increases trust within groups but also may increase conflict with other groups, according to an article in a special issue of Science.
"Moralizing gods, emerging over the last few millennia, have enabled large-scale cooperation and sociopolitical conquest even without war," says University of Michigan anthropologist Scott Atran, lead author of the article with Jeremy Ginges of the New School for Social Research.
"Sacred values sustain intractable conflicts like those between the Israelis and the Palestinians ...
Google goes cancer: Researchers use search engine algorithm to find cancer biomarkers
2012-05-18
The strategy used by Google to decide which pages are relevant for a search query can also be used to determine which proteins in a patient's cancer are relevant for the disease progression. Researchers from Dresden University of Technology, Germany, have used a modified version of Google's PageRank algorithm to rank about 20,000 proteins by their genetic relevance to the progression of pancreatic cancer. In their study, published in PLoS Computational Biology, they found seven proteins that can help to assess how aggressive a patient's tumor is and guide the clinician ...
Researchers reveal an RNA modification influences thousands of genes
2012-05-18
###
Weill Cornell Medical College
Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University's medical school located in New York City, is committed to excellence in research, teaching, patient care and the advancement of the art and science of medicine, locally, nationally and globally. Physicians and scientists of Weill Cornell Medical College are engaged in cutting-edge research from bench to bedside, aimed at unlocking mysteries of the human body in health and sickness and toward developing new treatments and prevention strategies. In its commitment to global health and ...
Untangling the development of breast cancer
2012-05-18
In two back-to-back reports published online on 17 May in Cell, researchers have sequenced the genomes of 21 breast cancers and analysed the mutations that emerged during the tumours' development. The individual results are described below.
Led by researchers from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, the team created a catalogue of all the mutations in the genomes of the 21 cancer genomes and identified the mutational processes that lead to breast cancer. They found that these mutations accumulate in breast cells over many years, initially rather slowly, but picking up ...
Resolving the ortholog conjecture
2012-05-18
Researchers at the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute have confirmed the long-held conjecture that studying the genes we share with other animals is a viable means of extrapolating information about human biology. The study, published in the open access journal PLoS Computational Biology, shows how bioinformatics makes it possible to test the conjecture.
Scientists have long looked to model species – mice, for example – to understand human biology. This is at the root of what is called the 'ortholog conjecture': the idea ...
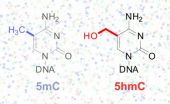
New technique reveals unseen information in DNA code
2012-05-18
Imagine reading an entire book, but then realizing that your glasses did not allow you to distinguish "g" from "q." What details did you miss?
Geneticists faced a similar problem with the recent discovery of a "sixth nucleotide" in the DNA alphabet. Two modifications of cytosine, one of the four bases that make up DNA, look almost the same but mean different things. But scientists lacked a way of reading DNA, letter by letter, and detecting precisely where these modifications are found in particular tissues or cell types.
Now, a team of scientists from the University ...
Salk study may offer drug-free intervention to prevent obesity and diabetes
2012-05-18
VIDEO:
This is an interview with Dr. Panda.
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA, CA----It turns out that when we eat may be as important as what we eat. Scientists at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies have found that regular eating times and extending the daily fasting period may override the adverse health effects of a high-fat diet and prevent obesity, diabetes and liver disease in mice.
In a paper published May 17 in Cell Metabolism, scientists from Salk's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
JMIR Publications’ JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology invites submissions on Bridging Data, AI, and Innovation to Transform Health
Honey bees navigate more precisely than previously thought
Air pollution may directly contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
Study finds early imaging after pediatric UTIs may do more harm than good
UC San Diego Health joins national research for maternal-fetal care
New biomarker predicts chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Treatment algorithms featured in Brain Trauma Foundation’s update of guidelines for care of patients with penetrating traumatic brain injury
Over 40% of musicians experience tinnitus; hearing loss and hyperacusis also significantly elevated
Artificial intelligence predicts colorectal cancer risk in ulcerative colitis patients
Mayo Clinic installs first magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia system for cancer research in the US
[Press-News.org] Simple procedure lowers blood pressure in kidney disease patientsRenal denervation may protect the kidneys and reduce heart risks