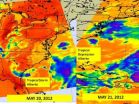
(Press-News.org) Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed Alberto weakened from a tropical storm to a tropical depression as it appears more disorganized. At 10:30 a.m. EDT on May 21, Tropical Storm Alberto weakened to a tropical depression, and has maintained that status today, May 22.
As of 5 a.m. EDT on May 22, Alberto's maximum sustained winds were near 35 mph (55 kph) but he is expected to weaken in 24 hours. Alberto was centered about 220 miles south of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, near 32.0 North and 75.5 West. Alberto was moving to the northeast near 15 mph (24 kph), and had a minimum central pressure of 1008 millibars.
Over two days, NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared images of Alberto and saw it's deterioration from a tropical storm to a tropical depression. The infrared images were captured from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite on May 20 and May 21. The coldest cloud top temperatures were as cold as -63F (-52C) and indicated the strongest thunderstorms with the heaviest rainfall.
On May 22, a visible image from NOAA's GOES-15 satellite showed Alberto off the coast of North Carolina. The depression appeared to look almost wedge-shaped as it continues to weaken and move to the northeast. The image was created by the NASA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
The National Hurricane Center expects Alberto to continue moving northeast and speed up. As Alberto speeds up, it is expected to weaken and could become a post-tropical remnant low pressure area by Wednesday and dissipate by Thursday, May 24.
INFORMATION:
Alberto now a tropical depression, seen by NASA
2012-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cleft lip/palate cause much more than cosmetic problems
2012-05-23
MAYWOOD, Ill. -- Children born with cleft lip, cleft palate and other craniofacial disorders face numerous medical challenges beyond appearance.
Patients can face serious airway, feeding, speech and hearing problems, as well as social and psychological challenges, Laura Swibel Rosenthal, MD, of Loyola University Medical Center and colleagues write in the June 2012 issue of Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America.
"The management of patients with craniofacial syndromes is complex," Rosenthal and colleagues write. "Otolaryngologic [ear-nose-throat] evaluation is of paramount ...
Scientists start explaining Fat Bastard's vicious cycle
2012-05-23
This press release is available in French.
VIDEO:
Stephanie Fulton of Université de Montréal and its affiliated research hospital studies the behavior of mice and their brain chemistry to reveal how humans may act in similar circumstances.
Click here for more information.
Fat Bastard's revelation "I eat because I'm depressed and I'm depressed because I eat" in the Austin Powers ...
Weight loss improves SBD and metabolic dysregulation in obese children
2012-05-23
ATS 2012, SAN FRANCISCO –Weight loss improved both metabolic parameters and sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) in obese children in a new study from researchers in Belgium, confirming links between metabolic dysregulation, SDB and obesity.
"SDB is highly prevalent in childhood obesity, and may be a risk factor for the metabolic syndrome. In our population of 224 obese children and adolescents, 30% had SDB, which was significantly correlated with metabolic parameters, including aspartate aminotransferase (ASAT), alanine aminotransferase (ALAT) and HDL cholesterol at baseline," ...
Severity of sleep disordered breathing predicts glycemic health
2012-05-23
ATS 2012, SAN FRANCISCO –The severity of sleep disordered breathing and nocturnal hypoxemia independently predict both glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), according to a new study.
"Because people with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) are often overweight or obese it has been difficult to interpret earlier studies of the relationship between sleep disordered breathing and metabolic disorders," said Brian Kent, MBBCh, research fellow at St. Vincent's University Hospital in Dublin. "We found that obstructive sleep apnea syndrome ...
Oniqua Announces Major Enhancements to Material and Catalog Standards Database Solution
2012-05-23
Oniqua MRO Analytics (www.oniqua.com), the leading provider of analytics-based MRO optimization solutions for asset-intensive organizations, today announced significant enhancements to its Oniqua Standards Dictionary (OSD) database solution.
Available on an online subscription basis, OSD is a comprehensive material and catalog standards environment specifically designed, built and optimized for asset-intensive industries.
OSD 3.0 maximizes efficiencies in cataloging while minimizing inconsistencies and errors in completed cataloged records. It is designed to assist ...
Viral infections in infancy are not associated with wheezing symptoms in later childhood
2012-05-23
ATS 2012, SAN FRANCISCO – The number of viral infections during infancy is not associated with wheezing later in childhood, according to a new study from researchers in the Netherlands. While viral illnesses with wheezing in infancy predicted wheezing later in childhood, this association was due in part to decreased neonatal lung function.
"Viral infections in infancy, particularly rhinovirus, are thought to be a risk factor for later asthma development, but it is unclear whether this association is due to the viruses themselves or whether rhinovirus-associated wheeze ...
Long-term ICS use reduces pleural effusion in patients with CAP
2012-05-23
ATS 2012, SAN FRANCISCO – Prior treatment with inhaled corticosteroids in patients with respiratory disorders who develop community acquired pneumonia (CAP) is associated with a lower incidence and severity of parapneumonic effusion, according to a new study from researchers in Spain.
A parapneumonic effusion is a type of pleural effusion (excess fluid that accumulates between the two pleural layers, the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs) that arises as a result of a pneumonia, lung abscess, or bronchiectasis.
"Long-term treatment with inhaled corticosteroids ...
Tiny implanted coil improves lung function in patients with severe emphysema
2012-05-23
ATS 2012, SAN FRANCISCO – A tiny, resilient metal wire designed to gather and compress diseased lung tissue may offer relief to patients with severe heterogeneous emphysema, a subtype of the disease that involves specific, usually isolated areas of the lungs, according to the results of a multicenter international trial conducted in the Netherlands, Germany and France. The wire, called a lung volume reduction coil (LVRC), can be easily implanted and is designed to take the place of more invasive procedures used to improve the lung function of emphysema patients.
The study ...
Study shows antibiotic improves respiratory function in lung transplant patients
2012-05-23
ATS 2012, SAN FRANCISCO – Researchers in the United Kingdom have determined that azithromycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic that also has anti-inflammatory properties, can be an effective treatment option for patients suffering from bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS), a life-threatening complication that occurs in the majority of patients following lung transplantation.
BOS is the leading cause of mortality after the first year following transplantation, and occurs in part when the body repeatedly rejects the transplanted lung tissue. The syndrome causes the airways ...
P. aeruginosa bacteria associated with increased hospitalizations in COPD patients
2012-05-23
ATS 2012, SAN FRANCISCO – Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who become infected with the bacterium Pseudomonas aerguinosa are more likely to have worse clinical outcomes and experience more hospitalizations during the course of their disease than COPD patients who are not infected, according to researchers from Buffalo, N.Y.
The study will be presented at the ATS 2012 International Conference in San Francisco.
Bacterial bronchial infection plays a key role in the course of COPD, causing chronic inflammation as well as acute exacerbations of ...