(Press-News.org) A new technique that converts stem cells into brain cells has been developed by researchers at Lund University. The method is simpler, quicker and safer than previous research has shown and opens the doors to a shorter route to clinical cell transplants.
By adding two different molecules, the researchers have discovered a surprisingly simple way of starting the stem cells' journey to become finished brain cells. The process mimics the brain's natural development by releasing signals that are part of the normal development process. Experiments in animal models have shown that the cells quickly adapt in the brain and behave like normal brain cells.
"This technique allows us to fine-tune our steering of stem cells to different types of brain cells. Previous studies have not always used the signals that are activated during the brain's normal development. This has caused the transplanted cells to develop tumours or function poorly in the brain", says Agnete Kirkeby, one of the authors of the study.
Since the method effectively imitates the brain's own processes, it reduces the risk of tumour formation, one of the most common obstacles in stem cell research. The quick, simple technique makes the cells mature faster, which both makes the transplant safer and helps the cells integrate better into the brain. The results of the study bring stem cell research closer to transplant trials in the human brain.
"We have used the new protocol to make dopamine neurons, the type of neuron that is affected by Parkinson's disease, and for the first time, we are seriously talking about these cells as being good enough to move forward for transplantation in patients. The next step is to test the process on a larger scale and to carry out more pre-clinical safety tests", explains Malin Parmar, research team leader.
###
The research is presented in the report 'Generation of regionally specified neural progenitors and functional neurons from human embryonic stem cells under defined conditions' in the journal Cell Reports.
The study has been conducted as part of the EU 7th Framework Programme project NeuroStemcell.
For more information, please contact:
Malin Parmar +46 709 823901, Malin.Parmar@med.lu.se
Agnete Kirkeby +45 5168 5353, Agnete.Kirkeby@med.lu.se
From stem cell to brain cell – new technique mimics the brain
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Like curry? New biological role identified for compound used in ancient medicine
2012-05-28
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists have just identified a new reason why some curry dishes, made with spices humans have used for thousands of years, might be good for you.
New research at Oregon State University has discovered that curcumin, a compound found in the cooking spice turmeric, can cause a modest but measurable increase in levels of a protein that's known to be important in the "innate" immune system, helping to prevent infection in humans and other animals.
This cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide, or CAMP, is part of what helps our immune system fight off various ...
Phone contact with nurses linked with better outcomes for women with gestational diabetes
2012-05-28
OAKLAND, Calif., May 25, 2012 – Among women with gestational diabetes mellitus, referral to a telephone-based nurse management program was associated with lower risk of high baby birth weight and increased postpartum glucose testing, according to Kaiser Permanente researchers.
Investigators for the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research examined the associations between referral to telephone-based nurse consultation and outcomes in 12 Kaiser Permanente medical centers with variation in the percent of patients referred to telephonic nurse management. ...
A new invading sea crab reaches the Ebro Delta
2012-05-28
Originally endemic to the Atlantic Coast of North America, over the past 30 years Dyspanopeus sayi has been involuntarily introduced in the UK, France, the Netherlands, the Black Sea and the Adriatic Sea. A study shows that in recent years the sea crab has established itself along the Western Mediterranean Coast.
A team of Spanish and German researchers have recorded the first American Dyspanopeus sayi sea crab in the bay of Els Alfacs in the Ebro Delta (Spain). Both sexes were captured along with many ovigerous females (carrying eggs) in different areas and different ...
First study to suggest that the immune system may protect against Alzheimer's changes in humans
2012-05-28
Recent work in mice suggested that the immune system is involved in removing beta-amyloid, the main Alzheimer's-causing substance in the brain. Researchers have now shown for the first time that this may apply in humans.
Researchers at the Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Exeter with colleagues in the National Institute on Aging in the USA and in Italy screened the expression levels of thousands of genes in blood samples from nearly 700 people. The telltale marker of immune system activity against beta-amyloid, a gene called CCR2, emerged as ...
Autopsy of an eruption: Linking crystal growth to volcano seismicity
2012-05-28
How processes below a volcano are linked to seismic signals at the surface is described by scientists from the petrology group of the Ruhr-Universität Bochum and their colleagues from Bristol in a paper published today in Science. They analyzed the growth of crystals in the magma chamber and used results obtained from the monitoring of seismic signals. The research could ultimately help to predict future volcanic eruptions with greater accuracy.
Like tree rings: Crystals in a magma chamber
A few kilometers below the volcano a liquid reservoir exists, the magma chamber, ...
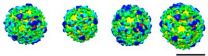
Picture release: More than meets the eye
2012-05-28
VIDEO:
Depicting each copy of COPI as a triangle, the different arrangements of these building blocks become easier to spot.
Click here for more information.
These spheres may look almost identical, but subtle differences between them revealed a molecular version of the robots from Transformers. Each sphere is a vesicle, a pod that cells use to transport materials between different compartments. The images, produced by Marco Faini from John Briggs' lab at the European Molecular ...
Oldest Jewish archaeological evidence on the Iberian Peninsula
2012-05-28
On a marble plate, measuring 40 by 60 centimetres, the name "Yehiel" can be read, followed by further letters which have not yet been deciphered. The Jena Archaeologists believe that the new discovery might be a tomb slab. Antlers, which were found very close to the tomb slab in the rubble gave a clue to the age determination. "The organic material of the antlers could be dated by radiocarbon analysis with certainty to about 390 AD," excavation leader Dr. Dennis Graen of the Jena University explains. "Therefore we have a so-called 'terminus ante quem' for the inscription, ...
70 percent of women use contraceptives during their first sexual encounter
2012-05-28
VIDEO:
Contraceptive use in Spain during the first sexual encounter is similar to other European countries. However, there are some geographical differences between Spanish regions: women in Murcia use contraceptives less...
Click here for more information.
Contraceptive use in Spain during the first sexual encounter is similar to other European countries. However, there are some geographical differences between Spanish regions: women in Murcia use contraceptives less (55.8%) ...
Copy of the genetic makeup travels in a protein suitcase
2012-05-28
The blueprint of all living beings is stored in their genetic material. In higher organisms this is stored in the well-protected cell nucleus. "Here a kind of copier works around the clock to make copies of the information needed at the time," says first author Jan Peter Siebrasse from the Institute for Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Bonn. The copies contain the information which the cells need to produce vital enzymes or other cell building materials. These copies consist of messenger RNA which travels on random paths to the membrane of the cell ...
Inherited DNA change explains overactive leukemia gene
2012-05-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A small inherited change in DNA is largely responsible for overactivating a gene linked to poor treatment response in people with acute leukemia.
The study by researchers at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James) focused on a gene called BAALC. This gene is often overactive, or overexpressed, in people with acute myeloid or acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and it indicates that the disease is likely to respond poorly to standard therapy.
This study ...