(Press-News.org) CARNELIAN BAY, Calif. — Results of a new U.S. Geological Survey study conclude that faults west of Lake Tahoe, Calif., referred to as the Tahoe-Sierra frontal fault zone, pose a substantial increase in the seismic hazard assessment for the Lake Tahoe region of California and Nevada, and could potentially generate earthquakes with magnitudes ranging from 6.3 to 6.9. A close association of landslide deposits and active faults also suggests that there is an earthquake-induced landslide hazard along the steep fault-formed range front west of Lake Tahoe.
Using a new high-resolution imaging technology, known as bare-earth airborne LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging), combined with field observations and modern geochronology, USGS scientists, and their colleagues from the University of Nevada, Reno; the University of California, Berkeley; and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, have confirmed the existence of previously suspected faults.
LiDAR imagery allows scientists to "see" through dense forest cover and recognize earthquake faults that are not detectable with conventional aerial photography.
"This study is yet one more stunning example of how the availability of LiDAR information to precisely and accurately map the shape of the solid Earth surface beneath vegetation is revolutionizing the geosciences," said USGS Director Marcia McNutt. "From investigations of geologic hazards to calculations of carbon stored in the forest canopy to simply making the most accurate maps possible, LiDAR returns its investment many times over."
Motion on the faults has offset linear moraines (the boulders, cobbles, gravel, and sand deposited by an advancing glacier) providing a record of tectonic deformation since the moraines were deposited. The authors developed new three-dimensional techniques to measure the amount of tectonic displacement of moraine crests caused by repeated earthquakes. Dating of the moraines from the last two glaciations in the Tahoe basin, around 21 thousand and 70 thousand years ago, allowed the study authors to calculate the rates of tectonic displacement.
"Although the Tahoe-Sierra frontal fault zone has long been recognized as forming the tectonic boundary between the Sierra Nevada to the west, and the Basin and Range Province to the east, its level of activity and hence seismic hazard was not fully recognized because dense vegetation obscured the surface expressions of the faults," said USGS scientist and lead author, James Howle. "Using the new LiDAR technology has improved and clarified previous field mapping, has provided visualization of the surface expressions of the faults, and has allowed for accurate measurement of the amount of motion that has occurred on the faults. The results of the study demonstrate that the Tahoe-Sierra frontal fault zone is an important seismic source for the region."
###An abstract of the paper, "Airborne LiDAR analysis and geochronology of faulted glacial moraines in the Tahoe-Sierra frontal fault zone reveal substantial seismic hazards in the Lake Tahoe region, California-Nevada USA," published in the "Geological Society of America Bulletin" is available online. Contact GSA for a copy of the full article.
A video is available online showing a visual example of how airborne LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) imagery penetrates dense forest cover to reveal an active fault line not detectable with conventional aerial photography.
Contact Information:
U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey
Office of Communications and Publishing
12201 Sunrise Valley Dr, MS 119
Reston, VA 20192
Paul Laustsen, USGS
Phone: 650-329-4000
Kea Giles, GSA
Phone: 303-357-1057
LiDAR technology reveals faults near Lake Tahoe
Joint GSA-USGS press release
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Device may inject a variety of drugs without using needles
2012-05-28
MIT researchers have engineered a device that delivers a tiny, high-pressure jet of medicine through the skin without the use of a hypodermic needle. The device can be programmed to deliver a range of doses to various depths — an improvement over similar jet-injection systems that are now commercially available.
The researchers say that among other benefits, the technology may help reduce the potential for needle-stick injuries; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that hospital-based health care workers accidentally prick themselves with needles ...
Positive words: The glue to social interaction
2012-05-28
Scientists at ETH Zurich have studied the use of language, finding that words with a positive emotional content are more frequently used in written communication. This result supports the theory that social relations are enhanced by a positive bias in human communication. The study by David Garcia and his colleagues from the Chair of Systems Design is published in the first issue of the new SpringerOpen journal EPJ Data Science, and is freely available to the general public as an Open Access article.
Previous studies focused on word lengths and frequency. They demonstrated ...
University of Florida physicists set new record for graphene solar cell efficiency
2012-05-28
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Doping may be a no-no for athletes, but researchers in the University of Florida's physics department say it was key in getting unprecedented power conversion efficiency from a new graphene solar cell created in their lab.
Graphene solar cells are one of industry's great hopes for cheaper, durable solar power cells in the future. But previous attempts to use graphene, a single-atom-thick honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms, in solar cells have only managed power conversion efficiencies ranging up to 2.9 percent. The UF team was able to achieve a record ...
Childhood cancer scars survivors later in life
2012-05-28
CHICAGO--- Scars left behind by childhood cancer treatments are more than skin-deep. The increased risk of disfigurement and persistent hair loss caused by childhood cancer and treatment are associated with emotional distress and reduced quality of life in adulthood, according to a new study led by a Northwestern Medicine advanced practice nurse, Karen Kinahan, and based on data from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS).
The largest study of its kind, published May 21 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, compared scarring, disfigurement and persistent hair loss ...
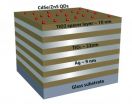
'Metamaterials,' quantum dots show promise for new technologies
2012-05-28
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers are edging toward the creation of new optical technologies using "nanostructured metamaterials" capable of ultra-efficient transmission of light, with potential applications including advanced solar cells and quantum computing.
The metamaterial - layers of silver and titanium oxide and tiny components called quantum dots - dramatically changes the properties of light. The light becomes "hyperbolic," which increases the output of light from the quantum dots.
Such materials could find applications in solar cells, light emitting diodes ...
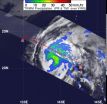
NASA's TRMM satellite sees some heavy rainfall in Typhoon Sanvu
2012-05-28
Tropical Storm Sanvu strengthened overnight as forecast and is now a Typhoon in the western North Pacific Ocean. NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite observed that most of the rainfall is falling in the eastern half of the storm.
The TRMM satellite measured the rainfall from Typhoon Sanvu on May 24, 2012.TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data shows that Sanvu's heaviest rainfall was occurring in its northeastern quadrant where some intense storms were dropping rainfall at a rate greater than 50mm/hr (~2 inches/hr). TRMM ...
NASA satellites feed forecasters information as Bud becomes a hurricane
2012-05-28
Bud has now become the first hurricane of the eastern Pacific Hurricane Season, as NASA visible and infrared satellite imagery revealed an organized structure of spiraling thunderstorms around the eye. Watches and warnings are already in effect for southwestern Mexico as Bud nears.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument onboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Hurricane Bud off the southwestern coast of Mexico on May 23 at 2035 UTC (1:35 PDT) before it reached hurricane status. The image showed the outer fringes of Bud's ...
Cyber exercise partners help you go the distance
2012-05-28
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A new study testing the benefits of a virtual exercise partner shows the presence of a moderately more capable cycling partner can significantly boost the motivation – by as much as 100 percent – to stick to an exercise program.
The research out of Michigan State University's Department of Kinesiology shows women taking part in cycling exercises exercised twice as long when working with a virtual partner, results the authors said can be used to help people meet physical activity recommendations.
The work by Brandon Irwin and colleagues is published ...
Stanford psychologists examine how race affects juvenile sentencing
2012-05-28
When it comes to holding children accountable for crimes they commit, race matters.
According to a new study by Stanford psychologists, if people imagine a juvenile offender to be black, they are more willing to hand down harsher sentences to all juveniles.
"These results highlight the fragility of protections for juveniles when race is in play," said Aneeta Rattan, lead author of the study, which appears this week in the journal PLoS ONE.
Historically, the courts have protected juveniles from the most severe sentences. It has been recognized that children are different ...
A nanoclutch for nanobots
2012-05-28
Chinese researchers have designed and tested simulations of a "nanoclutch," a speed regulation tool for nanomotors. The nanoclutch consists of two carbon nanotubes (CNTs), one inside the other, separated by a film of water. Electrowetting forces control the friction between the water and the inner and outer walls of the CNTs. When the two tubes are electrically charged, the water confined between them can transmit the torque from the inner tube to the outer tube, and the device is said to be in the engaged state. When the CNTs are uncharged, the device is in the disengaged ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] LiDAR technology reveals faults near Lake TahoeJoint GSA-USGS press release