(Press-News.org) NEW YORK, May 24, 2012 – Researchers at NYU School of Medicine have, for the first time, identified a single gene that simultaneously controls inflammation, accelerated aging and cancer.
"This was certainly an unexpected finding," said principal investigator Robert J. Schneider, PhD, the Albert Sabin Professor of Molecular Pathogenesis, associate director for translational research and co-director of the Breast Cancer Program at NYU Langone Medical Center. "It is rather uncommon for one gene to have two very different and very significant functions that tie together control of aging and inflammation. The two, if not regulated properly, can eventually lead to cancer development. It's an exciting scientific find."
The study, funded by the National Institutes of Health, appears online ahead of print today in Molecular Cell and is scheduled for the July 13 print issue.
For decades, the scientific community has known that inflammation, accelerated aging and cancer are somehow intertwined, but the connection between them has remained largely a mystery, Dr. Schneider said. What was known, due in part to past studies by Schneider and his team, was that a gene called AUF1 controls inflammation by turning off the inflammatory response to stop the onset of septic shock. But this finding, while significant, did not explain a connection to accelerated aging and cancer.
When the researchers deleted the AUF1 gene, accelerated aging occurred, so they continued to focus their research efforts on the gene. Now, more than a decade in the making, the mystery surrounding the connection between inflammation, advanced aging and cancer is finally being unraveled.
The current study reveals that AUF1, a family of four related genes, not only controls the inflammatory response, but also maintains the integrity of chromosomes by activating the enzyme telomerase to repair the ends of chromosomes, thereby simultaneously reducing inflammation, preventing rapid aging and the development of cancer, Dr. Schneider explained.
"AUF1 is a medical and scientific trinity," Dr. Schneider said. "Nature has designed a way to simultaneously turn off harmful inflammation and repair our chromosomes, thereby suppressing aging at the cellular level and in the whole animal."
With this new information, Dr. Schneider and colleagues are examining human populations for specific types of genetic alterations in the AUF1 gene that are associated with the co-development of certain immune diseases, increased rates of aging and higher cancer incidence in individuals to determine exactly how the alterations manifest and present themselves clinically.
###
About NYU School of Medicine:
NYU School of Medicine is one of the nation's preeminent academic institutions dedicated to achieving world class medical educational excellence. For 170 years, NYU School of Medicine has trained thousands of physicians and scientists who have helped to shape the course of medical history and enrich the lives of countless people. An integral part of NYU Langone Medical Center, the School of Medicine at its core is committed to improving the human condition through medical education, scientific research and direct patient care. The School also maintains academic affiliations with area hospitals, including Bellevue Hospital, one of the nation's finest municipal hospitals where its students, residents and faculty provide the clinical and emergency care to New York City's diverse population, which enhances the scope and quality of their medical education and training. Additional information about the NYU School of Medicine is available at http://school.med.nyu.edu/.
Key gene found responsible for chronic inflammation, accelerated aging and cancer
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
LiDAR technology reveals faults near Lake Tahoe
2012-05-28
CARNELIAN BAY, Calif. — Results of a new U.S. Geological Survey study conclude that faults west of Lake Tahoe, Calif., referred to as the Tahoe-Sierra frontal fault zone, pose a substantial increase in the seismic hazard assessment for the Lake Tahoe region of California and Nevada, and could potentially generate earthquakes with magnitudes ranging from 6.3 to 6.9. A close association of landslide deposits and active faults also suggests that there is an earthquake-induced landslide hazard along the steep fault-formed range front west of Lake Tahoe.
Using a new high-resolution ...
Device may inject a variety of drugs without using needles
2012-05-28
MIT researchers have engineered a device that delivers a tiny, high-pressure jet of medicine through the skin without the use of a hypodermic needle. The device can be programmed to deliver a range of doses to various depths — an improvement over similar jet-injection systems that are now commercially available.
The researchers say that among other benefits, the technology may help reduce the potential for needle-stick injuries; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that hospital-based health care workers accidentally prick themselves with needles ...
Positive words: The glue to social interaction
2012-05-28
Scientists at ETH Zurich have studied the use of language, finding that words with a positive emotional content are more frequently used in written communication. This result supports the theory that social relations are enhanced by a positive bias in human communication. The study by David Garcia and his colleagues from the Chair of Systems Design is published in the first issue of the new SpringerOpen journal EPJ Data Science, and is freely available to the general public as an Open Access article.
Previous studies focused on word lengths and frequency. They demonstrated ...
University of Florida physicists set new record for graphene solar cell efficiency
2012-05-28
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Doping may be a no-no for athletes, but researchers in the University of Florida's physics department say it was key in getting unprecedented power conversion efficiency from a new graphene solar cell created in their lab.
Graphene solar cells are one of industry's great hopes for cheaper, durable solar power cells in the future. But previous attempts to use graphene, a single-atom-thick honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms, in solar cells have only managed power conversion efficiencies ranging up to 2.9 percent. The UF team was able to achieve a record ...
Childhood cancer scars survivors later in life
2012-05-28
CHICAGO--- Scars left behind by childhood cancer treatments are more than skin-deep. The increased risk of disfigurement and persistent hair loss caused by childhood cancer and treatment are associated with emotional distress and reduced quality of life in adulthood, according to a new study led by a Northwestern Medicine advanced practice nurse, Karen Kinahan, and based on data from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS).
The largest study of its kind, published May 21 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, compared scarring, disfigurement and persistent hair loss ...
'Metamaterials,' quantum dots show promise for new technologies
2012-05-28
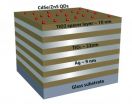
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers are edging toward the creation of new optical technologies using "nanostructured metamaterials" capable of ultra-efficient transmission of light, with potential applications including advanced solar cells and quantum computing.
The metamaterial - layers of silver and titanium oxide and tiny components called quantum dots - dramatically changes the properties of light. The light becomes "hyperbolic," which increases the output of light from the quantum dots.
Such materials could find applications in solar cells, light emitting diodes ...
NASA's TRMM satellite sees some heavy rainfall in Typhoon Sanvu
2012-05-28
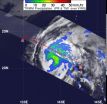
Tropical Storm Sanvu strengthened overnight as forecast and is now a Typhoon in the western North Pacific Ocean. NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite observed that most of the rainfall is falling in the eastern half of the storm.
The TRMM satellite measured the rainfall from Typhoon Sanvu on May 24, 2012.TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data shows that Sanvu's heaviest rainfall was occurring in its northeastern quadrant where some intense storms were dropping rainfall at a rate greater than 50mm/hr (~2 inches/hr). TRMM ...
NASA satellites feed forecasters information as Bud becomes a hurricane
2012-05-28
Bud has now become the first hurricane of the eastern Pacific Hurricane Season, as NASA visible and infrared satellite imagery revealed an organized structure of spiraling thunderstorms around the eye. Watches and warnings are already in effect for southwestern Mexico as Bud nears.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument onboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Hurricane Bud off the southwestern coast of Mexico on May 23 at 2035 UTC (1:35 PDT) before it reached hurricane status. The image showed the outer fringes of Bud's ...
Cyber exercise partners help you go the distance
2012-05-28
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A new study testing the benefits of a virtual exercise partner shows the presence of a moderately more capable cycling partner can significantly boost the motivation – by as much as 100 percent – to stick to an exercise program.
The research out of Michigan State University's Department of Kinesiology shows women taking part in cycling exercises exercised twice as long when working with a virtual partner, results the authors said can be used to help people meet physical activity recommendations.
The work by Brandon Irwin and colleagues is published ...
Stanford psychologists examine how race affects juvenile sentencing
2012-05-28
When it comes to holding children accountable for crimes they commit, race matters.
According to a new study by Stanford psychologists, if people imagine a juvenile offender to be black, they are more willing to hand down harsher sentences to all juveniles.
"These results highlight the fragility of protections for juveniles when race is in play," said Aneeta Rattan, lead author of the study, which appears this week in the journal PLoS ONE.
Historically, the courts have protected juveniles from the most severe sentences. It has been recognized that children are different ...