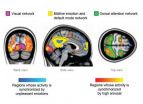
(Press-News.org) Experiencing strong emotions synchronises brain activity across individuals, research team at Aalto University and Turku PET Centre in Finland has revealed.
Human emotions are highly contagious. Seeing others' emotional expressions such as smiles triggers often the corresponding emotional response in the observer. Such synchronisation of emotional states across individuals may support social interaction: When all group members share a common emotional state, their brains and bodies process the environment in a similar fashion.
Researchers at Aalto University and Turku PET Centre have now found that feeling strong emotions makes different individuals' brain activity literally synchronous.
The results revealed that especially feeling strong unpleasant emotions synchronised brain's emotion processing networks in the frontal and midline regions. On the contrary, experiencing highly arousing events synchronised activity in the networks supporting vision, attention and sense of touch.
Sharing others' emotional states provides the observers a somatosensory and neural framework that facilitates understanding others' intentions and actions and allows to 'tune in' or 'sync' with them. Such automatic tuning facilitates social interaction and group processes, says Adjunct Professor Lauri Nummenmaa from the Aalto University.
The results have major implications for current neural models of human emotions and group behaviour. It also deepens our understanding of mental disorders involving abnormal socioemotional processing, Nummenmaa says.
Participants' brain activity was measured with functional magnetic resonance imaging while they were viewing short pleasant, neutral and unpleasant movies.
INFORMATION:
Aalto University, Finland is a new multidisciplinary science and art community in the fields of science, economics, and art and design. The University is founded on Finnish strengths, and its goal is to develop as a unique entity to become one of the world's top universities. Aalto University's cornerstones are its strengths in education and research. At the new University, there are 20,000 basic degree and graduate students as well as a staff of 5,000 of which 330 are professors.
Feeling strong emotions makes peoples' brains 'tick together'
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dramatic increase in fragility fractures expected in Latin America
2012-05-28
The International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), in cooperation with medical and patient societies from throughout Latin America, has today published a landmark report which compiles osteoporosis-related data on 14 countries and the region as a whole. The report shows that fragility fractures due to osteoporosis are predicted to more than double in some countries in the coming decades.
Osteoporosis, which literally means 'porous bones', is a disease which causes bones to become fragile and more likely to break. Older adults, and post-menopausal women in particular, are ...
In Brazil number of hip fractures expected to increase 32 percent by 2050
2012-05-28
A new Audit report on fragility fractures, issued today by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), predicts that Brazil will experience an explosion in the number of fragility fractures due to osteoporosis in the coming decades.
Osteoporosis, a disease which weakens bones and makes them more likely to fracture, is thought to affect around 33% of postmenopausal women in Brazil. Fractures due to osteoporosis mostly affect older adults, with fractures at the spine and hip causing the most suffering, disability and healthcare expenditure.
Currently, about 20% ...
Food, water safety provide new challenges for today's sensors
2012-05-28
Sensors that work flawlessly in laboratory settings may stumble when it comes to performing in real-world conditions, according to researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
These shortcomings are important as they relate to safeguarding the nation's food and water supplies, said Ali Passian, lead author of a Perspective paper published in ACS Nano. In their paper, titled "Critical Issues in Sensor Science to Aid Food and Water Safety," the researchers observe that while sensors are becoming increasingly sophisticated, little or no field ...
Exotic particles, chilled and trapped, form giant matter wave
2012-05-28
Physicists have trapped and cooled exotic particles called excitons so effectively that they condensed and cohered to form a giant matter wave.
This feat will allow scientists to better study the physical properties of excitons, which exist only fleetingly yet offer promising applications as diverse as efficient harvesting of solar energy and ultrafast computing.
"The realization of the exciton condensate in a trap opens the opportunity to study this interesting state. Traps allow control of the condensate, providing a new way to study fundamental properties of light ...
Healing the voice: New American Chemical Society video on synthetic vocal cords
2012-05-28
WASHINGTON, May 24, 2012 — An effort to develop synthetic vocal cords to heal the voices of people with scarred natural vocal tissues is the topic of the latest episode of the American Chemical Society's (ACS') Bytesize Science series. The video is available at www.BytesizeScience.com.
Filmed in the lab of 2012 ACS Priestley Medalist and David H. Koch Institute Professor Robert S. Langer, Ph.D., at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the video highlights the development of a flexible polymer material that mimics the traits of human vocal cords. The video begins ...
London researcher calls for new approach to regulating probiotics
2012-05-28
LONDON, ON – In today's Nature scientific journal Dr. Gregor Reid, Director of the Canadian R&D Centre for Probiotics at Lawson Health Research Institute and a scientist at Western University, calls for a Category Tree system to be implemented in the United States and Europe to better inform consumers about probiotics.
Globally, the market for probiotics (beneficial microorganisms) exceeds $30 billion; however, consumers have little way of knowing which products have been tested in humans and what they do for health. Furthermore, the regulatory system in the US maintains ...
Exercise does not improve lipoprotein levels in obese patients with fatty liver disease
2012-05-28
New research found that moderate exercise does not improve lipoprotein concentrations in obese patients with non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Results published in the June issue of Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, report that moderate physical activity produces only a small decrease in triglyceride and alanine transaminase (ALT) levels.
Obesity is a rampant health concern worldwide. In fact, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported in 2008 that 1.5 billion people, age 20 and older, were overweight, and of ...
NTU and I²R scientists invent revolutionary chipset for high-speed wireless data transfer
2012-05-28
Here is a new microchip that can transfer data the size of 80 MP3 song files (or 250 megabytes) wirelessly between mobile devices, in the flick of a second.
Or how about transferring a typical 2-hour, 8-gigabyte DVD movie in just half a minute compared to 8.5 hours on Bluetooth?
Such unprecedented speeds on the wireless platform are now a reality as scientists from the Nanyang Technological University (NTU) and A*STAR's Institute for Infocomm Research (I²R) have developed a revolutionary microchip that can transmit large volumes of data at ultra-high speeds of 2 Gigabits ...
Business students better equipped to evaluate peers
2012-05-28
Montreal, May 24, 2012 – Peer evaluation is a touchstone of many business school classes. But does the process of rating the work of one's classmates really shape better businesspeople? A new study from Concordia's John Molson School of Business, published in the journal of the Academy of Management Learning and Education, answers that question with a resounding yes.
Stéphane Brutus, Professor and Chair of the Department of Management, undertook the research that led to these findings after developing a standardized online peer evaluation system, or PES, in 2004. To ...
Max Planck Florida Institute study: Persistent sensory experience is good for aging brain
2012-05-28
Despite a long-held scientific belief that much of the wiring of the brain is fixed by the time of adolescence, a new study shows that changes in sensory experience can cause massive rewiring of the brain, even as one ages. In addition, the study found that this rewiring involves fibers that supply the primary input to the cerebral cortex, the part of the brain that is responsible for sensory perception, motor control and cognition. These findings promise to open new avenues of research on brain remodeling and aging.
Published in the May 24, 2012 issue of Neuron, the ...