(Press-News.org) Physicists have trapped and cooled exotic particles called excitons so effectively that they condensed and cohered to form a giant matter wave.
This feat will allow scientists to better study the physical properties of excitons, which exist only fleetingly yet offer promising applications as diverse as efficient harvesting of solar energy and ultrafast computing.
"The realization of the exciton condensate in a trap opens the opportunity to study this interesting state. Traps allow control of the condensate, providing a new way to study fundamental properties of light and matter," said Leonid Butov, professor of physics at the University of California, San Diego. A paper reporting his team's success was recently published in the scientific journal Nano Letters.
Excitons are composite particles made up of an electron and a "hole" left by a missing electron in a semiconductor. Created by light, these coupled pairs exist in nature. The formation and dynamics of excitons play a critical role in photosynthesis, for example.
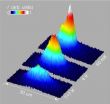
Like other matter, excitons have a dual nature of both particle and wave, in a quantum mechanical view. The waves are usually unsynchronized, but when particles are cooled enough to condense, their waves synchronize and combine to form a giant matter wave, a state that others have observed for atoms.
Scientists can easily create excitons by shining light on a semiconductor, but in order for the excitons to condense they must be chilled before they recombine.
The key to the team's success was to separate the electrons far enough from their holes so that excitons could last long enough for the scientists to cool them into a condensate. They accomplished this by creating structures called "coupled quantum wells" that separate electrons from holes in different layers of alloys made of gallium, arsenic and aluminum.
Then they set an electrostatic trap made by a diamond-shaped electrode and chilled their special semiconducting material in an optical dilution refrigerator to as cold as 50 milli-Kelvin, just a fraction of a degree above absolute zero.
A laser focused on the surface of the material created excitons, which began to accumulate at the bottom of the trap as they cooled. Below 1 Kelvin, the entire cloud of excitons cohered to form a single matter wave, a signature of a state called a Bose-Einstein condensate.
Other scientists have seen whole atoms do this when confined in a trap and cooled, but this is the first time that scientists have seen subatomic particles form coherent matter waves in a trap.
Varying the size and depth of the trap will alter the coherent exciton state, providing this team, and others, the opportunity to study the properties of light and mater in a new way.
INFORMATION:
This most recent discovery stems from an ongoing collaboration between Leonid Butov's research group in UC San Diego's Division of Physical Sciences, including Alexander High, Jason Leonard and Mikas Remeika, and Micah Hanson and Arthur Gossard in UC Santa Barbara's Materials Department. The Army Research Office and the National Science Foundation funded the experiments, and the Department of Energy supported the development of spectroscopy in the optical dilution refrigerator, the technique used to observe the exciton condensate in a trap.
Exotic particles, chilled and trapped, form giant matter wave
Excitons form Bose-Einstein condensate
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Healing the voice: New American Chemical Society video on synthetic vocal cords
2012-05-28
WASHINGTON, May 24, 2012 — An effort to develop synthetic vocal cords to heal the voices of people with scarred natural vocal tissues is the topic of the latest episode of the American Chemical Society's (ACS') Bytesize Science series. The video is available at www.BytesizeScience.com.
Filmed in the lab of 2012 ACS Priestley Medalist and David H. Koch Institute Professor Robert S. Langer, Ph.D., at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the video highlights the development of a flexible polymer material that mimics the traits of human vocal cords. The video begins ...
London researcher calls for new approach to regulating probiotics
2012-05-28
LONDON, ON – In today's Nature scientific journal Dr. Gregor Reid, Director of the Canadian R&D Centre for Probiotics at Lawson Health Research Institute and a scientist at Western University, calls for a Category Tree system to be implemented in the United States and Europe to better inform consumers about probiotics.
Globally, the market for probiotics (beneficial microorganisms) exceeds $30 billion; however, consumers have little way of knowing which products have been tested in humans and what they do for health. Furthermore, the regulatory system in the US maintains ...
Exercise does not improve lipoprotein levels in obese patients with fatty liver disease
2012-05-28
New research found that moderate exercise does not improve lipoprotein concentrations in obese patients with non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Results published in the June issue of Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, report that moderate physical activity produces only a small decrease in triglyceride and alanine transaminase (ALT) levels.
Obesity is a rampant health concern worldwide. In fact, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported in 2008 that 1.5 billion people, age 20 and older, were overweight, and of ...
NTU and I²R scientists invent revolutionary chipset for high-speed wireless data transfer
2012-05-28
Here is a new microchip that can transfer data the size of 80 MP3 song files (or 250 megabytes) wirelessly between mobile devices, in the flick of a second.
Or how about transferring a typical 2-hour, 8-gigabyte DVD movie in just half a minute compared to 8.5 hours on Bluetooth?
Such unprecedented speeds on the wireless platform are now a reality as scientists from the Nanyang Technological University (NTU) and A*STAR's Institute for Infocomm Research (I²R) have developed a revolutionary microchip that can transmit large volumes of data at ultra-high speeds of 2 Gigabits ...
Business students better equipped to evaluate peers
2012-05-28
Montreal, May 24, 2012 – Peer evaluation is a touchstone of many business school classes. But does the process of rating the work of one's classmates really shape better businesspeople? A new study from Concordia's John Molson School of Business, published in the journal of the Academy of Management Learning and Education, answers that question with a resounding yes.
Stéphane Brutus, Professor and Chair of the Department of Management, undertook the research that led to these findings after developing a standardized online peer evaluation system, or PES, in 2004. To ...
Max Planck Florida Institute study: Persistent sensory experience is good for aging brain
2012-05-28
Despite a long-held scientific belief that much of the wiring of the brain is fixed by the time of adolescence, a new study shows that changes in sensory experience can cause massive rewiring of the brain, even as one ages. In addition, the study found that this rewiring involves fibers that supply the primary input to the cerebral cortex, the part of the brain that is responsible for sensory perception, motor control and cognition. These findings promise to open new avenues of research on brain remodeling and aging.
Published in the May 24, 2012 issue of Neuron, the ...
Relationship between social status and wound-healing in wild baboons
2012-05-28
Turns out it's not bad being top dog, or in this case, top baboon.
Results of a study by University of Notre Dame biologist Beth Archie and colleagues from Princeton University and Duke University finds that male baboons that have a high rank within their society recover more quickly from injuries, and are less likely to become ill than other males.
The finding is somewhat surprising, given that top-ranked males also experience high stress, which should suppress immune responses.
Archie, Jeanne Altmann of Princeton and Susan Alberts of Duke examined health records ...
Newly modified nanoparticle opens window on future gene editing technologies
2012-05-28
AMES, Iowa – The scientific and technological literature is abuzz with nanotechnology and its manufacturing and medical applications. But it is in an area with a less glitzy aura—plant sciences—where nanotechnology advancements are contributing dramatically to agriculture.
Researchers at Iowa State University have now demonstrated the ability to deliver proteins and DNA into plant cells, simultaneously. This is important because it now opens up opportunities for more sophisticated and targeted plant genome editing—techniques that require the precise delivery of both ...
Key gene found responsible for chronic inflammation, accelerated aging and cancer
2012-05-28
NEW YORK, May 24, 2012 – Researchers at NYU School of Medicine have, for the first time, identified a single gene that simultaneously controls inflammation, accelerated aging and cancer.
"This was certainly an unexpected finding," said principal investigator Robert J. Schneider, PhD, the Albert Sabin Professor of Molecular Pathogenesis, associate director for translational research and co-director of the Breast Cancer Program at NYU Langone Medical Center. "It is rather uncommon for one gene to have two very different and very significant functions that tie together ...
LiDAR technology reveals faults near Lake Tahoe
2012-05-28
CARNELIAN BAY, Calif. — Results of a new U.S. Geological Survey study conclude that faults west of Lake Tahoe, Calif., referred to as the Tahoe-Sierra frontal fault zone, pose a substantial increase in the seismic hazard assessment for the Lake Tahoe region of California and Nevada, and could potentially generate earthquakes with magnitudes ranging from 6.3 to 6.9. A close association of landslide deposits and active faults also suggests that there is an earthquake-induced landslide hazard along the steep fault-formed range front west of Lake Tahoe.
Using a new high-resolution ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] Exotic particles, chilled and trapped, form giant matter waveExcitons form Bose-Einstein condensate