(Press-News.org) Despite a long-held scientific belief that much of the wiring of the brain is fixed by the time of adolescence, a new study shows that changes in sensory experience can cause massive rewiring of the brain, even as one ages. In addition, the study found that this rewiring involves fibers that supply the primary input to the cerebral cortex, the part of the brain that is responsible for sensory perception, motor control and cognition. These findings promise to open new avenues of research on brain remodeling and aging.
Published in the May 24, 2012 issue of Neuron, the study was conducted by researchers at the Max Planck Florida Institute (MPFI) and at Columbia University in New York.
"This study overturns decades-old beliefs that most of the brain is hard-wired before a critical period that ends when one is a young adult," said MPFI neuroscientist Marcel Oberlaender, PhD, first author on the paper. "By changing the nature of sensory experience, we were able to demonstrate that the brain can rewire, even at an advanced age. This may suggest that if one stops learning and experiencing new things as one ages, a substantial amount of connections within the brain may be lost."
The researchers conducted their study by examining the brains of older rats, focusing on an area of the brain known as the thalamus, which processes and delivers information obtained from sensory organs to the cerebral cortex. Connections between the thalamus and the cortex have been thought to stop changing by early adulthood, but this was not found to be the case in the rodents studied.
Being nocturnal animals, rats mainly rely on their whiskers as active sensory organs to explore and navigate their environment. For this reason, the whisker system is an ideal model for studying whether the brain can be remodeled by changing sensory experience. By simply trimming the whiskers, and preventing the rats from receiving this important and frequent form of sensory input, the scientists sought to determine whether extensive rewiring of the connections between the thalamus and cortex would occur.
On examination, they found that the animals with trimmed whiskers had altered axons, nerve fibers along which information is conveyed from one neuron (nerve cell) to many others; those whose whiskers were not trimmed had no axonal changes. Their findings were particularly striking as the rats were considered relatively old – meaning that this rewiring can still take place at an age not previously thought possible. Also notable was that the rewiring happened rapidly – in as little as a few days.
"We've shown that the structure of the rodent brain is in constant flux, and that this rewiring is shaped by sensory experience and interaction with the environment," said Dr. Oberlaender. "These changes seem to be life-long and may pertain to other sensory systems and species, including people. Our findings open the possibility of new avenues of research on development of the aging brain using quantitative anatomical studies combined with noninvasive imaging technologies suitable for humans, such as functional MRI (fMRI)."
The study was possible due to recent advances in high-resolution imaging and reconstruction techniques, developed in part by Dr. Oberlaender at MPFI. These novel methods enable researchers to automatically and reliably trace the fine and complex branching patterns of individual axons, with typical diameters less than a thousandth of a millimeter, throughout the entire brain.
###Dr. Oberlaender is part of the Max Planck Florida Institute's Digital Neuroanatomy group, led by Nobel laureate Dr. Bert Sakmann. The group focuses on the functional anatomy of circuits in the cerebral cortex that form the basis of simple behaviors (e.g. decision making). One of the group's most significant efforts is a program dedicated to obtaining a three-dimensional map of the rodent brain. This work will provide insight into the functional architecture of entire cortical areas, and will lay the foundation for a mechanistic understanding of sensory perception and behavior.
This study was carried out in collaboration with the group of Dr. Randy M. Bruno in the Neuroscience Department of Columbia University, New York.
About the Max Planck Florida Institute
The first institute established by Germany's prestigious Max Planck Society outside of Europe, the Max Planck Florida Institute is also the first research institute of its kind in North America. MPFI seeks to provide new insight into understanding the functional organization of the nervous system, its capacity to produce perception, thought, language, memory, emotion, and action. Neural circuits, the complex synaptic networks of the brain, hold the key to understanding who we are, why we behave the way we do, and how the debilitating effects of neurological and psychiatric disorders can be ameliorated. MPFI meets this challenge by forging links between different levels of analysis—genetic, molecular, cellular, circuit, and behavioral—and developing new technologies that make cutting edge scientific discoveries possible. For more information, visit www.maxplanckflorida.org.
Max Planck Florida Institute study: Persistent sensory experience is good for aging brain
Brain can rewire throughout life
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Relationship between social status and wound-healing in wild baboons
2012-05-28
Turns out it's not bad being top dog, or in this case, top baboon.
Results of a study by University of Notre Dame biologist Beth Archie and colleagues from Princeton University and Duke University finds that male baboons that have a high rank within their society recover more quickly from injuries, and are less likely to become ill than other males.
The finding is somewhat surprising, given that top-ranked males also experience high stress, which should suppress immune responses.
Archie, Jeanne Altmann of Princeton and Susan Alberts of Duke examined health records ...
Newly modified nanoparticle opens window on future gene editing technologies
2012-05-28
AMES, Iowa – The scientific and technological literature is abuzz with nanotechnology and its manufacturing and medical applications. But it is in an area with a less glitzy aura—plant sciences—where nanotechnology advancements are contributing dramatically to agriculture.
Researchers at Iowa State University have now demonstrated the ability to deliver proteins and DNA into plant cells, simultaneously. This is important because it now opens up opportunities for more sophisticated and targeted plant genome editing—techniques that require the precise delivery of both ...
Key gene found responsible for chronic inflammation, accelerated aging and cancer
2012-05-28
NEW YORK, May 24, 2012 – Researchers at NYU School of Medicine have, for the first time, identified a single gene that simultaneously controls inflammation, accelerated aging and cancer.
"This was certainly an unexpected finding," said principal investigator Robert J. Schneider, PhD, the Albert Sabin Professor of Molecular Pathogenesis, associate director for translational research and co-director of the Breast Cancer Program at NYU Langone Medical Center. "It is rather uncommon for one gene to have two very different and very significant functions that tie together ...
LiDAR technology reveals faults near Lake Tahoe
2012-05-28
CARNELIAN BAY, Calif. — Results of a new U.S. Geological Survey study conclude that faults west of Lake Tahoe, Calif., referred to as the Tahoe-Sierra frontal fault zone, pose a substantial increase in the seismic hazard assessment for the Lake Tahoe region of California and Nevada, and could potentially generate earthquakes with magnitudes ranging from 6.3 to 6.9. A close association of landslide deposits and active faults also suggests that there is an earthquake-induced landslide hazard along the steep fault-formed range front west of Lake Tahoe.
Using a new high-resolution ...
Device may inject a variety of drugs without using needles
2012-05-28
MIT researchers have engineered a device that delivers a tiny, high-pressure jet of medicine through the skin without the use of a hypodermic needle. The device can be programmed to deliver a range of doses to various depths — an improvement over similar jet-injection systems that are now commercially available.
The researchers say that among other benefits, the technology may help reduce the potential for needle-stick injuries; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that hospital-based health care workers accidentally prick themselves with needles ...
Positive words: The glue to social interaction
2012-05-28
Scientists at ETH Zurich have studied the use of language, finding that words with a positive emotional content are more frequently used in written communication. This result supports the theory that social relations are enhanced by a positive bias in human communication. The study by David Garcia and his colleagues from the Chair of Systems Design is published in the first issue of the new SpringerOpen journal EPJ Data Science, and is freely available to the general public as an Open Access article.
Previous studies focused on word lengths and frequency. They demonstrated ...
University of Florida physicists set new record for graphene solar cell efficiency
2012-05-28
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Doping may be a no-no for athletes, but researchers in the University of Florida's physics department say it was key in getting unprecedented power conversion efficiency from a new graphene solar cell created in their lab.
Graphene solar cells are one of industry's great hopes for cheaper, durable solar power cells in the future. But previous attempts to use graphene, a single-atom-thick honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms, in solar cells have only managed power conversion efficiencies ranging up to 2.9 percent. The UF team was able to achieve a record ...
Childhood cancer scars survivors later in life
2012-05-28
CHICAGO--- Scars left behind by childhood cancer treatments are more than skin-deep. The increased risk of disfigurement and persistent hair loss caused by childhood cancer and treatment are associated with emotional distress and reduced quality of life in adulthood, according to a new study led by a Northwestern Medicine advanced practice nurse, Karen Kinahan, and based on data from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS).
The largest study of its kind, published May 21 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, compared scarring, disfigurement and persistent hair loss ...
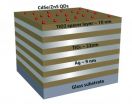
'Metamaterials,' quantum dots show promise for new technologies
2012-05-28
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers are edging toward the creation of new optical technologies using "nanostructured metamaterials" capable of ultra-efficient transmission of light, with potential applications including advanced solar cells and quantum computing.
The metamaterial - layers of silver and titanium oxide and tiny components called quantum dots - dramatically changes the properties of light. The light becomes "hyperbolic," which increases the output of light from the quantum dots.
Such materials could find applications in solar cells, light emitting diodes ...
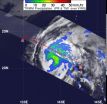
NASA's TRMM satellite sees some heavy rainfall in Typhoon Sanvu
2012-05-28
Tropical Storm Sanvu strengthened overnight as forecast and is now a Typhoon in the western North Pacific Ocean. NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite observed that most of the rainfall is falling in the eastern half of the storm.
The TRMM satellite measured the rainfall from Typhoon Sanvu on May 24, 2012.TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data shows that Sanvu's heaviest rainfall was occurring in its northeastern quadrant where some intense storms were dropping rainfall at a rate greater than 50mm/hr (~2 inches/hr). TRMM ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
[Press-News.org] Max Planck Florida Institute study: Persistent sensory experience is good for aging brainBrain can rewire throughout life