(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. — There's nothing like a new pair of eyeglasses to bring fine details into sharp relief. For scientists who study the large molecules of life from proteins to DNA, the equivalent of new lenses have come in the form of an advanced method for analyzing data from X-ray crystallography experiments.
The findings, just published in the journal Science, could lead to new understanding of the molecules that drive processes in biology, medical diagnostics, nanotechnology and other fields.
Like dentists who use X-rays to find tooth decay, scientists use X-rays to reveal the shape and structure of DNA, proteins, minerals and other molecules.
As X-rays pass through atoms they reflect distinctive patterns, which reveal what atoms are present and how atoms are bonded to each other. However, some data are typically discarded because of concerns over quality. In particular, data derived from edge regions of the pattern — although very important for understanding the details of structure — are often overwhelmed by the random errors associated with a weak signal in the midst of a lot of background noise.
Oregon State University biophysicist Andy Karplus and his colleague Kay Diederichs at the University of Konstanz in Germany have now proven that useful information can be gleaned from data that have about five times the noise level that was previously considered acceptable.
"The criteria that have been used in the past are way too conservative," said Karplus. "These data that people have been throwing out are actually good."
The bottom line for crystallographers is the accuracy of their molecular models. The better the model, the better it will predict the pattern created by X-rays passing through a molecule, and the better it will be to develop new drugs and nanotechnologies that operate at the molecular scale.
The new method may be the most important conceptual advance in the past 20 years in how these data are used in modeling, the scientists said. It shows how data from "noisy" parts of the measurement can still provide information, and allows scientists to see directly where the model is limited by noise in the data and where the model is a better estimate of molecular structure than experimental data.
"The question is, 'Where do we cut it off?'" said Karplus. By adding data at incremental steps and showing how the model improved, Karplus and Diederichs showed that scientists had been cutting off their analyses too soon and discarding data that could sharpen their view of molecular structure.
"The big impact on the field will be that every structure determined from here on out will be a little more accurate because people won't throw away data that are okay," Karplus said. "If you have a crummy image of the protein, it will get a little sharper. If you have a good image of the protein, it will also get a little sharper."
While the method will be an important step for X-ray crystallographers, the scientists said that other physical sciences may also find ways to benefit from this type of data quality analysis. They noted that one branch of science has been using this type of statistical analysis for many years. The field of psychometrics — the analysis of data from psychological tests — has used a similar technique called the "Spearman-Brown prophecy formula" to determine the minimum length of such tests.
"Now that we know that very noisy data are useful, this will presumably enable still further improvements as it stimulates new software development to do a better job of handling such weak data," said Karplus.
### END
Discarded data may hold the key to a sharper view of molecules
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
No new neurons in the human olfactory bulb
2012-05-28
Research from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden shows that the human olfactory bulb – a structure in the brain that processes sensory input from the nose – differs from that of other mammals in that no new neurons are formed in this area after birth. The discovery, which is published in the scientific journal Neuron, is based on the age-determination of the cells using the carbon-14 method, and might explain why the human sense of smell is normally much worse than that of other animals.
"I've never been so astonished by a scientific discovery," says lead investigator Jonas ...
Gene discovery points towards new type of male contraceptive
2012-05-28
A new type of male contraceptive could be created thanks to the discovery of a key gene essential for sperm development.
The finding could lead to alternatives to conventional male contraceptives that rely on disrupting the production of hormones, such as testosterone and can cause side-effects such as irritability, mood swings and acne.
Research, led by the University of Edinburgh, has shown how a gene – Katnal1 – is critical to enable sperm to mature in the testes.
If scientists can regulate the Katnal1 gene in the testes, they could prevent sperm from maturing ...
Drug allergy discovery
2012-05-28
A research team led by the University of Melbourne and Monash University, Australia, has discovered why people can develop life-threatening allergies after receiving treatment for conditions such as epilepsy and AIDS.
The finding could lead to the development of a diagnostic test to determine drug hypersensitivity.
The study published today in the journal Nature, revealed how some drugs inadvertently target the immune system to alter how the body's immune system perceives it's own tissues, making them look foreign.
The immune system then attacks the foreign nature ...
Beetle-infested pine trees contribute to air pollution and haze in forests
2012-05-28
The hordes of bark beetles that have bored their way through more than six billion trees in the western United States and British Columbia since the 1990s do more than kill stately pine, spruce and other trees.
Results of a new study show that these pests can make trees release up to 20 times more of the organic substances that foster haze and air pollution in forested areas.
A paper reporting the findings appears today in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, published by the American Chemical Society.
Scientists Kara Huff Hartz of Southern Illinois University ...
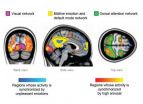
Feeling strong emotions makes peoples' brains 'tick together'
2012-05-28
Experiencing strong emotions synchronises brain activity across individuals, research team at Aalto University and Turku PET Centre in Finland has revealed.
Human emotions are highly contagious. Seeing others' emotional expressions such as smiles triggers often the corresponding emotional response in the observer. Such synchronisation of emotional states across individuals may support social interaction: When all group members share a common emotional state, their brains and bodies process the environment in a similar fashion.
Researchers at Aalto University and ...
Dramatic increase in fragility fractures expected in Latin America
2012-05-28
The International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), in cooperation with medical and patient societies from throughout Latin America, has today published a landmark report which compiles osteoporosis-related data on 14 countries and the region as a whole. The report shows that fragility fractures due to osteoporosis are predicted to more than double in some countries in the coming decades.
Osteoporosis, which literally means 'porous bones', is a disease which causes bones to become fragile and more likely to break. Older adults, and post-menopausal women in particular, are ...
In Brazil number of hip fractures expected to increase 32 percent by 2050
2012-05-28
A new Audit report on fragility fractures, issued today by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), predicts that Brazil will experience an explosion in the number of fragility fractures due to osteoporosis in the coming decades.
Osteoporosis, a disease which weakens bones and makes them more likely to fracture, is thought to affect around 33% of postmenopausal women in Brazil. Fractures due to osteoporosis mostly affect older adults, with fractures at the spine and hip causing the most suffering, disability and healthcare expenditure.
Currently, about 20% ...
Food, water safety provide new challenges for today's sensors
2012-05-28
Sensors that work flawlessly in laboratory settings may stumble when it comes to performing in real-world conditions, according to researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
These shortcomings are important as they relate to safeguarding the nation's food and water supplies, said Ali Passian, lead author of a Perspective paper published in ACS Nano. In their paper, titled "Critical Issues in Sensor Science to Aid Food and Water Safety," the researchers observe that while sensors are becoming increasingly sophisticated, little or no field ...
Exotic particles, chilled and trapped, form giant matter wave
2012-05-28
Physicists have trapped and cooled exotic particles called excitons so effectively that they condensed and cohered to form a giant matter wave.
This feat will allow scientists to better study the physical properties of excitons, which exist only fleetingly yet offer promising applications as diverse as efficient harvesting of solar energy and ultrafast computing.
"The realization of the exciton condensate in a trap opens the opportunity to study this interesting state. Traps allow control of the condensate, providing a new way to study fundamental properties of light ...
Healing the voice: New American Chemical Society video on synthetic vocal cords
2012-05-28
WASHINGTON, May 24, 2012 — An effort to develop synthetic vocal cords to heal the voices of people with scarred natural vocal tissues is the topic of the latest episode of the American Chemical Society's (ACS') Bytesize Science series. The video is available at www.BytesizeScience.com.
Filmed in the lab of 2012 ACS Priestley Medalist and David H. Koch Institute Professor Robert S. Langer, Ph.D., at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the video highlights the development of a flexible polymer material that mimics the traits of human vocal cords. The video begins ...