(Press-News.org) MANHATTAN, KAN. -- For two Kansas State University professors, receiving one of software engineering's most prestigious awards was more than 10 years in the making.
A seven-member research team that included K-State's John Hatcliff, professor of computer and information science, and Robby, associate professor of computing and information science, set out in 1998 to illustrate how different technologies could test for problems that arise when computer programs multitask. The team published "Bandera: Extracting Finite-State Models from Java Source code" in 2000.
The publication recently received the Most Influential Paper Award from the International Conference on Software Engineering, the world's largest academic software engineering conference. The award honors the publication that has the biggest influence on the theory and practice of software engineering in the 10 years since it was published.
"Our main contribution was to illustrate how model checking, a technique based on discrete mathematics and formal logic, could be applied to software systems to reason about systems that were multitasking in nature," Hatcliff said. "Because it provides systematic reasoning about a computer system, model checking can uncover bugs that were hard to detect using existing techniques, such as conventional testing and manual source code inspections."
Other members of Hatcliff and Robby's research team included: James Corbett, a faculty member at the University of Hawaii at the time of writing and now a Google employee; Matthew Dwyer, a K-State faculty member at the time and now a faculty member at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln; Shawn Laubach, a K-State graduate student at the time; Corina Pasareanu, a K-State doctoral student at the time who now works at NASA; and Hongjun Zheng, a K-State postdoctoral student at the time of writing.
Academic citations show the continuing influence of the team's work. The publication is the most-cited paper published in the 30-year conference history, and the second most-cited of more than 10,000 papers published by the Association of Computing Machinery's SIGSOFT, the leading professional software engineering association. The Google Scholar citation index says the paper currently has more than 800 citations.
"What was interesting about this project was that it brought together a number of different technologies, and that was really one of the things that made this paper stand out," Robby said.
The project idea developed in the 1990s with the proliferation of the embedded system. As computer software was able to multitask, it became more difficult to test and predict errors. The researchers wanted to develop a way to foresee a program's behavior, so they applied a technique called model checking, which had been used by hardware engineers to explore how computer chips could execute tasks.
"To get model checking to work for software, we had to develop a lot of sophisticated techniques that automatically discover important properties of a system's source code," Hatcliff said. "The goal of these techniques was to boil all the complex features of software down to a relatively clean mathematical model that we can analyze with model checking technology."
Since the researchers published their work, organizations such as Microsoft and NASA have built off of it, and other groups are working to better design concurrent programming and to build software in different ways. When NASA's Java Path Finder model checking project received NASA's prestigious Turning Goals Into Reality award in 2003, the K-State researchers were listed as members of the project because of the influential contributions and collaboration from their 2000 publication. Pasareanu now leads the Java Path Finder project at NASA.
INFORMATION:
Although the researchers are no longer working on the same project, many of them continue working on related technologies. They have received a total of more than $12 million from various funding agencies -- including the Army Research Office, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, Lockheed Martin Corp., Boeing Co., Intel Corp., IBM Corp., Fujitsu Limited and Rockwell Collins Inc. -- to continue research based on the original publication. Hatcliff and Robby have both been funded by Faculty Early Career Development Program, or CAREER, awards from the National Science Foundation for their derivative research.
K-State researchers honored for influential contributions to software engineering field
2010-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Technique to reattach teeth using stem cells developed at UIC
2010-09-30
A new approach to anchor teeth back in the jaw using stem cells has been developed and successfully tested in the laboratory for the first time by researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
The new strategy represents a potential major advance in the battle against gum disease, a serious infection that eventually leads to tooth loss. About 80 percent of U.S. adults suffer from gum disease, according to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research.
Researchers in UIC's Brodie Laboratory for Craniofacial Genetics used stem cells obtained from ...
After traumatic event, early intervention reduces odds of PTSD in children by 73 percent
2010-09-30
PHILADELPHIA – After experiencing a potentially traumatic event – a car accident, a physical or sexual assault, a sports injury, witnessing violence – as many as 1 in 5 children will develop Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD).
A new approach that helps improve communication between child and caregiver, such as recognizing and managing traumatic stress symptoms and teaching coping skills, was able to prevent chronic and sub-clinical PTSD in 73 percent of children. The intervention, called the Child and Family Traumatic Stress Intervention (CFTSI) also reduced PTSD symptoms ...
IU researchers: Chemotherapy alters brain tissue in breast cancer patients
2010-09-30
INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers at the Indiana University Melvin and Bren Simon Cancer Center have published the first report using imaging to show that changes in brain tissue can occur in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
The cognitive effects of chemotherapy, often referred to as "chemobrain," have been known for years. However, the IU research is the first to use brain imaging to study women with breast cancer before and after treatment, showing that chemotherapy can affect gray matter. The researchers reported their findings in the October 2010 edition ...
Alcohol consumers are becoming the norm, UT Southwestern analysis finds
2010-09-30
DALLAS – Sept. 29, 2010 – More people are drinking than 20 years ago, according to a UT Southwestern Medical Center analysis of national alcohol consumption patterns. Gathered from more than 85,000 respondents, the data suggests that a variety of factors, including social, economic and ethnic influences and pressures, are involved in the increase.
"The reasons for the uptick vary and may involve complex sociodemographic changes in the population, but the findings are clear: More people are consuming alcohol now than in the early 1990s," said Dr. Raul Caetano, dean of ...
Milky Way sidelined in galactic tug-of-war
2010-09-30
The Magellanic Stream is an arc of hydrogen gas spanning more than 100 degrees of the sky as it trails behind the Milky Way's neighbor galaxies, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. Our home galaxy, the Milky Way, has long been thought to be the dominant gravitational force in forming the Stream by pulling gas from the Clouds. A new computer simulation by Gurtina Besla (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) and her colleagues now shows, however, that the Magellanic Stream resulted from a past close encounter between these dwarf galaxies rather than effects of the ...
Hepatitis C virus faces new weapon from Florida State scientists
2010-09-30
In recent human trials for a promising new class of drug designed to target the hepatitis C virus (HCV) without shutting down the immune system, some of the HCV strains being treated exhibited signs of drug resistance.
In response, an interdisciplinary team of Florida State University biologists, chemists and biomedical researchers devised a novel genetic screening method that can identify the drug-resistant HCV strains and the molecular-level mechanisms that make them that way –– helping drug developers to tailor specific therapies to circumvent them.
The potentially ...
Surgery offers long-term survival for early stage prostate cancer patients
2010-09-30
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- In the largest, most modern, single-institution study of its kind, Mayo Clinic urologists mined a long-term data registry for survival rates of patients who underwent radical prostatectomy (http://www.mayoclinic.org/radical-prostatectomy/) for localized prostate cancer. The findings are being presented at the North Central Section of the American Urological Association's 84th Annual Meeting in Chicago.
A radical prostatectomy is an operation to remove the prostate gland and some of the tissue around it. In this study, Mayo Clinic researchers discovered ...
Correction: Abatacept found ineffective in treatment of non-life threatening lupus
2010-09-30
Results from a 12-month multi-center clinical trial did not show therapeutic benefit of abatacept over placebo in patients with non-life threatening systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Abatacept failed to prevent new disease flares in SLE patients tapered from corticosteroids in an analysis where mild, moderate and severe disease flares were evaluated together. Full details of the phase IIb clinical trial are published in the October issue of Arthritis & Rheumatism, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The ACR estimates that 161,000 to 322,000 adults ...
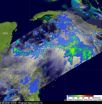
NASA uses 3 satellites to see strengthening Tropical Storm Nicole
2010-09-30
NASA is providing data from three satellites to give forecasters valuable information on newly strengthened Tropical Storm Nicole. Nicole was Tropical Depression 16 until 11 a.m. EDT, Sept. 29 and NASA data helped confirm her new designation. Satellite data from NASA showed frigid thunderstorm cloud top temperatures, heavy rainfall, and extensive cloud cover as Nicole strengthened.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument uses infrared technology to take a tropical cyclone's temperature. AIRS sits on NASA's Aqua satellite and captured an image of those cloud ...
Penn biologists say species accumulate on Earth at slower rates than in the past
2010-09-30
PHILADELPHIA –- Computational biologists at the University of Pennsylvania say that species are still accumulating on Earth but at a slower rate than in the past.
In the study, published in the journal PLoS Biology, Penn researchers developed a novel computational approach to infer the dynamics of species diversification using the family trees of present-day species. Using nine patterns of diversification as alternative models, they examined 289 phylogenies, or evolutionary trees, representing amphibians, arthropods, birds, mammals, mollusks and flowering plants.
The ...