(Press-News.org) When it comes to intelligence, what factors distinguish the brains of the exceptionally smart from those of average humans?
As science has long suspected, overall brain size matters somewhat, accounting for about 6.7 percent of individual variation in intelligence. More recent research has pinpointed the brain's lateral prefrontal cortex, a region just behind the temple, as a critical hub for high-level mental processing, with activity levels there predicting another 5 percent of variation in individual intelligence.
Now, new research from Washington University in St. Louis suggests that another 10 percent of individual differences in intelligence can be explained by the strength of neural pathways connecting the left lateral prefrontal cortex to the rest of the brain.
Published in the Journal of Neuroscience, the findings establish "global brain connectivity" as a new approach for understanding human intelligence.
"Our research shows that connectivity with a particular part of the prefrontal cortex can predict how intelligent someone is," suggests lead author Michael W. Cole, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in cognitive neuroscience at Washington University.
The study is the first to provide compelling evidence that neural connections between the lateral prefrontal cortex and the rest of the brain make a unique and powerful contribution to the cognitive processing underlying human intelligence, says Cole, whose research focuses on discovering the cognitive and neural mechanisms that make human behavior uniquely flexible and intelligent.
"This study suggests that part of what it means to be intelligent is having a lateral prefrontal cortex that does its job well; and part of what that means is that it can effectively communicate with the rest of the brain," says study co-author Todd Braver, PhD, professor of psychology in Arts & Sciences and of neuroscience and radiology in the School of Medicine. Braver is a co-director of the Cognitive Control and Psychopathology Lab at Washington University, in which the research was conducted.
One possible explanation of the findings, the research team suggests, is that the lateral prefrontal region is a "flexible hub" that uses its extensive brain-wide connectivity to monitor and influence other brain regions in a goal-directed manner.
"There is evidence that the lateral prefrontal cortex is the brain region that 'remembers' (maintains) the goals and instructions that help you keep doing what is needed when you're working on a task," Cole says. "So it makes sense that having this region communicating effectively with other regions (the 'perceivers' and 'doers' of the brain) would help you to accomplish tasks intelligently."
While other regions of the brain make their own special contribution to cognitive processing, it is the lateral prefrontal cortex that helps coordinate these processes and maintain focus on the task at hand, in much the same way that the conductor of a symphony monitors and tweaks the real-time performance of an orchestra.
"We're suggesting that the lateral prefrontal cortex functions like a feedback control system that is used often in engineering, that it helps implement cognitive control (which supports fluid intelligence), and that it doesn't do this alone," Cole says.
The findings are based on an analysis of functional magnetic resonance brain images captured as study participants rested passively and also when they were engaged in a series of mentally challenging tasks associated with fluid intelligence, such as indicating whether a currently displayed image was the same as one displayed three images ago.
Previous findings relating lateral prefrontal cortex activity to challenging task performance were supported. Connectivity was then assessed while participants rested, and their performance on additional tests of fluid intelligence and cognitive control collected outside the brain scanner was associated with the estimated connectivity.
Results indicate that levels of global brain connectivity with a part of the left lateral prefrontal cortex serve as a strong predictor of both fluid intelligence and cognitive control abilities.
Although much remains to be learned about how these neural connections contribute to fluid intelligence, new models of brain function suggested by this research could have important implications for the future understanding — and perhaps augmentation — of human intelligence.
The findings also may offer new avenues for understanding how breakdowns in global brain connectivity contribute to the profound cognitive control deficits seen in schizophrenia and other mental illnesses, Cole suggests.
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors include Tal Yarkoni, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Psychology and Neuroscience at the University of Colorado at Boulder; Grega Repovs, PhD, professor of psychology at the University of Ljubljana, Slovenia; and Alan Anticevic, an associate research scientist in psychiatry at Yale University School of Medicine.
Funding from the National Institute of Mental Health supported the study (National Institutes of Health grants MH66088, NR012081, MH66078, MH66078-06A1W1, and 1K99MH096801).
Brain imaging can predict how intelligent you are, study finds
'Global Brain Connectivity' explains 10 percent of variance in individual intelligence
2012-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adolescents' personalities and coping habits affect social behaviors, MU researcher says
2012-08-02
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Infants innately relieve stress by crying, turning their heads or maintaining eye contact. Adults manage emotional tension using problem-solving or by seeking support. A new study by a University of Missouri human development expert describes how adolescents' developing personalities and coping habits affect their behaviors toward others.
"We're each born with some personality tendencies; for example, we see that babies are fussy or calm," said Gustavo Carlo, the Millsap Professor of Diversity in the MU Department of Human Development and Family Studies. ...
Breaking the barriers for low-cost energy storage
2012-08-02
A team of researchers has developed a cheap, rechargeable and eco-friendly battery that could be used to store energy at solar power plants for a rainy day.
Led by Sri Narayan, professor of chemistry at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, the team developed an air-breathing battery that uses the chemical energy generated by the oxidation of iron plates that are exposed to the oxygen in the air – a process similar to rusting.
"Iron is cheap and air is free," Narayan said. "It's the future." Details about the battery will be published July 20 in the ...
Molecular switch identified that controls key cellular process
2012-08-02
New York, NY and Oxford, UK, August 1, 2012 – The body has a built-in system known as autophagy, or 'self-eating,' that controls how cells live or die. Deregulation of autophagy is linked to the development of human diseases, including neural degeneration and cancer.
In a study published online this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists at the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research in Oxford discovered a critical molecular switch that regulates autophagy. They also studied the links between autophagy and a cellular process called senescence ...
Test flight over Peru ruins could revolutionize archaeological mapping
2012-08-02
Archaeological sites that currently take years to map will be completed in minutes if tests underway in Peru of a new system being developed at Vanderbilt University go well.
The Aurora Flight Sciences unmanned aerial vehicle will be integrated into a larger system that combines the flying device that can fit into a backpack with a software system that can discern an optimal flight pattern and transform the resulting data into three-dimensional maps. The project is an interdisciplinary collaboration between Vanderbilt archaeologist Steven Wernke and engineering professor ...
In pilot study, a peptide controls blood sugar in people with congenital hyperinsulinism
2012-08-02
A pilot study in adolescents and adults has found that an investigational drug shows promise as the first potential medical treatment for children with the severest type of congenital hyperinsulinism, a rare but potentially devastating disease in which gene mutations cause insulin levels to become dangerously high.
"There is currently no effective medicine for children with the most common and most severe form of hyperinsulinism," said study leader Diva D. De Leon, M.D., a pediatric endocrinologist at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. "Our new research shows that ...
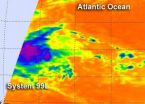
NASA satellite sees strength in developing Atlantic tropical low
2012-08-02
NASA's Aqua satellite spotted some very cold, high, thunderstorms around the center of a tropical low pressure area in the Atlantic Ocean today, indicating that the system is getting stronger and more organized.
The low pressure area, designated as "System 99L" was located about 850 miles east of the southern Windward Islands, near 10.7 North latitude and 46.9 West longitude. It was moving west between 15 and 20 mph.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 99L on August 1 at 0405 UTC (12:05 a.m. EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an ...
Caffeine may ease Parkinson's symptoms
2012-08-02
Montreal, August 1, 2012 – Caffeine, which is widely consumed around the world in coffee, tea and soft drinks, may help control movement in people suffering from Parkinson's. This is the finding of a study conducted at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI MUHC) that was recently published in Neurology®, the official journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study opens the door to new treatment options for Parkinson's disease that affects approximately 100 000 Canadians.
"This is one of the first studies to show the benefits of caffeine ...
Researchers discover female spiders produce mating plugs to prevent unwanted sex from males
2012-08-02
Scientists at the Smithsonian and their colleagues have discovered a new mechanism of animal mating plug production. In the giant wood spider Nephila pilipes, a highly sexually dimorphic and polygamous species, many small males compete with one other for access to a few huge females. During copulation these males are known to sever their own genitals in an attempt to plug the female, thereby gaining paternity advantage by preventing other males from mating with her.
Until recently however, nothing has been known about the origin and function of additional and very solid ...
NASA sees twin typhoons headed for double China landfall
2012-08-02
NASA's Terra satellite captured two tropical cyclones on visible imagery today, August 1 as they head for landfall. Typhoon Saola is approaching Taiwan and Typhoon Damrey approaching southern Japan, are both headed for landfall in China. Saola is forecast to landfall south of Shanghai on August 3, while Damrey is forecast to make landfall north of Shanghai on August 2.
NASA satellites have been tracking the twin tropical troublemakers, providing forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center with visible, infrared and microwave imagery. The Moderate Resolution Imaging ...
Wrecks and effects
2012-08-02
A study by a University of Iowa economist finds that many car race fans do, indeed, watch NASCAR races because they want to see car wrecks, but more of them have been tuning in to see who actually wins the race since the circuit adopted its Chase for the Cup championship series in 2004.
John Solow, a professor of economics in the Tippie College of Business, and co-author Peter Von Allmen of Skidmore College, looked at 135 NASCAR races between 2001 and 2009. They used a formula that measured the impact on each race's television ratings by incorporating a dozen statistics, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] Brain imaging can predict how intelligent you are, study finds'Global Brain Connectivity' explains 10 percent of variance in individual intelligence