Who influences your vote? It may depend on how soon the election is
2012-08-02
(Press-News.org) Neighbors' lawn signs, public opinion polls and even a conversation in the next restaurant booth can affect how people vote in an election. But it all depends on how far away the election is.
In a new research article published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, scientists Alison Ledgerwood and Shannon Callahan of the University of California, Davis conducted two different studies examining the relationship between abstract thinking and group norms people's support for different policies.
In the first study, they asked college students to complete an opinion survey about local bicycle policy. The researchers varied the wording of the survey so that participants were told that the policy would either be implemented next month (near- future) or next year (distant-future). In the second study, they asked college students to cast a vote to indicate their stance on affirmative-action policy. Again, the researchers manipulated the task such that participants were prompted to approach the issue with either an abstract mindset (thinking about why) or a more concrete mindset (thinking about how).
Ledgerwood and Callahan found that when it comes to decisions that are distant and abstract, peer group opinions carry a lot of weight.
"Research like this highlights the fact that we are social creatures," says lead researcher Alison Ledgerwood. "We clearly use other people to help us make our decisions, but what this research shows is that we rely on different people's opinions for near-future and distant-future events."
"When thinking about an election that will occur next year, rather than tomorrow, or when voting by absentee ballot rather than in person at the voting booth, individuals may be especially likely to adopt whatever opinions seem to be endorsed by a majority of their group members," Ledgerwood said.
But as an election nears, the views of individuals become more influential.
"Tuning into what the person sitting next to you happens to think about an issue is a great strategy for getting along in the current context," she said.
The research suggests that people making calls to voters months ahead of time trying to influence a vote might embrace specific tactics: "You might want to mention polling results. You might want to say: Most people in your political party think this is a good candidate or a good issue," Ledgerwood said.
However, polls announced the day or week before probably have little effect. "As we get closer to voting day, polls affect us less and less," she said. "Meanwhile, what one other person happens to think might affect us more and more. The point is, we are always influenced by what other people think, but who influences us most is going to depend on timing."
INFORMATION:
For more information about this study, please contact: Alison Ledgerwood at aledgerwood@ucdavis.edu.
The APS journal Psychological Science is the highest ranked empirical journal in psychology. For a copy of the article "The Social Side of Abstraction: Psychological Distance Enhances Conformity to Group Norms" and access to other Psychological Science research findings, please contact Anna Mikulak at 202-293-9300 or amikulak@psychologicalscience.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-08-02
EAST LANSING, Mich. — It's relatively easy to collect massive amounts of data on microbes. But the files are so large that it takes days to simply transmit them to other researchers and months to analyze once they are received.
Researchers at Michigan State University have developed a new computational technique, featured in the current issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, that relieves the logjam that these "big data" issues create.
Microbial communities living in soil or the ocean are quite complicated. Their genomic data is easy enough to ...
2012-08-02
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - If the drought forces producers to feed a larger portion of distillers dried grains with solubles, cattle can maintain gains and improve meat quality if the animals are weaned early, a Purdue University scientist has shown.
The finding, reported at the American Society of Animal Science Midwest Meetings in Des Moines, Iowa, could allow some producers to save on rising feed costs in the face of this year's drought. Distillers dried grains with solubles, or DDGS, are the leftovers from corn ethanol production. DDGS generally cost about 10 percent ...
2012-08-02
When it comes to intelligence, what factors distinguish the brains of the exceptionally smart from those of average humans?
As science has long suspected, overall brain size matters somewhat, accounting for about 6.7 percent of individual variation in intelligence. More recent research has pinpointed the brain's lateral prefrontal cortex, a region just behind the temple, as a critical hub for high-level mental processing, with activity levels there predicting another 5 percent of variation in individual intelligence.
Now, new research from Washington University in St. ...
2012-08-02
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Infants innately relieve stress by crying, turning their heads or maintaining eye contact. Adults manage emotional tension using problem-solving or by seeking support. A new study by a University of Missouri human development expert describes how adolescents' developing personalities and coping habits affect their behaviors toward others.
"We're each born with some personality tendencies; for example, we see that babies are fussy or calm," said Gustavo Carlo, the Millsap Professor of Diversity in the MU Department of Human Development and Family Studies. ...
2012-08-02
A team of researchers has developed a cheap, rechargeable and eco-friendly battery that could be used to store energy at solar power plants for a rainy day.
Led by Sri Narayan, professor of chemistry at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, the team developed an air-breathing battery that uses the chemical energy generated by the oxidation of iron plates that are exposed to the oxygen in the air – a process similar to rusting.
"Iron is cheap and air is free," Narayan said. "It's the future." Details about the battery will be published July 20 in the ...
2012-08-02
New York, NY and Oxford, UK, August 1, 2012 – The body has a built-in system known as autophagy, or 'self-eating,' that controls how cells live or die. Deregulation of autophagy is linked to the development of human diseases, including neural degeneration and cancer.
In a study published online this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists at the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research in Oxford discovered a critical molecular switch that regulates autophagy. They also studied the links between autophagy and a cellular process called senescence ...
2012-08-02
Archaeological sites that currently take years to map will be completed in minutes if tests underway in Peru of a new system being developed at Vanderbilt University go well.
The Aurora Flight Sciences unmanned aerial vehicle will be integrated into a larger system that combines the flying device that can fit into a backpack with a software system that can discern an optimal flight pattern and transform the resulting data into three-dimensional maps. The project is an interdisciplinary collaboration between Vanderbilt archaeologist Steven Wernke and engineering professor ...
2012-08-02
A pilot study in adolescents and adults has found that an investigational drug shows promise as the first potential medical treatment for children with the severest type of congenital hyperinsulinism, a rare but potentially devastating disease in which gene mutations cause insulin levels to become dangerously high.
"There is currently no effective medicine for children with the most common and most severe form of hyperinsulinism," said study leader Diva D. De Leon, M.D., a pediatric endocrinologist at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. "Our new research shows that ...
2012-08-02
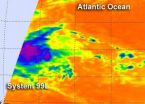
NASA's Aqua satellite spotted some very cold, high, thunderstorms around the center of a tropical low pressure area in the Atlantic Ocean today, indicating that the system is getting stronger and more organized.
The low pressure area, designated as "System 99L" was located about 850 miles east of the southern Windward Islands, near 10.7 North latitude and 46.9 West longitude. It was moving west between 15 and 20 mph.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 99L on August 1 at 0405 UTC (12:05 a.m. EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an ...
2012-08-02
Montreal, August 1, 2012 – Caffeine, which is widely consumed around the world in coffee, tea and soft drinks, may help control movement in people suffering from Parkinson's. This is the finding of a study conducted at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI MUHC) that was recently published in Neurology®, the official journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study opens the door to new treatment options for Parkinson's disease that affects approximately 100 000 Canadians.
"This is one of the first studies to show the benefits of caffeine ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Who influences your vote? It may depend on how soon the election is