(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
UCLA stem cell researchers have found for the first time a surprising and unexpected plasticity in the embryonic endothelium, the place where blood stem cells are made in early development....
Click here for more information.
UCLA stem cell researchers have found for the first time a surprising and unexpected plasticity in the embryonic endothelium, the place where blood stem cells are made in early development.
Scientists found that the lack of one transcription factor, a type of gene that controls cell fate by regulating other genes, allows the precursors that normally generate blood stem and progenitor cells in blood forming tissues to become something very unexpected - beating cardiomyocytes, or heart muscle cells.
The finding is important because it suggests that the endothelium can serve as a source of heart muscle cells. The finding may provide new understanding of how to make cardiac stem cells for use in regenerative medicine, said study senior author Dr. Hanna Mikkola, an associate professor of molecular, cell and developmental biology in Life Sciences and a researcher with the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA.
"It was absolutely unbelievable. These findings went beyond anything that we could have imagined," Mikkola said. "The microenvironment in the embryonic vasculature that normally gives rise to blood cells can generate cardiac cells when only one factor, Scl, is removed, essentially converting a hematopoietic organ into a cardiogenic organ."
The two-year study is published Aug. 3, 2012 in the peer-reviewed journal Cell.
The findings were so surprising, in fact, that Mikkola and her team did not want to believe the results until all subsequent assays proved the finding to be true, said Amelie Montel-Hagen, study co-first author and a post-doctoral fellow.
"To make sure we had not switched the samples between blood forming tissues and the heart we ran the experiments again and repeatedly got the same results," Montel-Hagen said. "It turns out Scl acts as a conductor in the orchestra, telling the other genes in the endothelium who should be playing and who shouldn't be playing."
The team used microarray technology to determine which genes were "playing" in embryonic endothelium to generate blood stem and progenitor cells and found that in the absence of Scl, the genes required for making cardiomyocytes were activated instead, said study co-first author Ben Van Handel, a post-doctoral fellow.
The lone difference was that Scl was missing in the process that resulted in the fate switch between blood and heart.
"Scl has a known role as a master regulator of blood development and when we removed it from the equation, no blood cells were made," Van Handel said. "That the removal of Scl resulted in fully functional cardiomyocytes in blood forming tissues was unprecedented."
The team used the yolk sac – the first tissue where blood cells are made - from embryos that lacked Scl and within four hours of plating on the culture dish, the tissue had generated beating cardiomyocytes. The team also found similar cardiomyocyte potential in Scl-deficient embryos in the endocardium that lines the heart chambers. They also looked for genetic signatures that would suggest that these endothelial precursors could potentially also make other closely related tissues such as skeletal muscle, bone or kidney, but found no evidence of such plasticity. The default fate of the endothelium was to make cardiomyocytes in the absence of Scl, Mikkola said.
The findings may also have implications in cell reprogramming, which generally calls for adding factors to induce cell fate change, a process that can be problematic. It might be safer to suppress a factor like Scl to nudge cells into a cardiomyocyte fate, Mikkola said.
"This study opens new ways to think about what could be a potential source of cardiac stem cells," she said. "We now have a better understanding of how cardiac progenitor cells can be made and regulated, and this may one day lead us to a way to treat heart attacks by creating new heart muscle cells to replace those that were damaged."
Going forward, Mikkola and her team plan to investigate the developmental and regenerative potential of the endothelium-derived cardiac progenitor cells, and define the mechanisms by which Scl can at the same time activate one fate while suppressing another.
"These results call for future studies to examine the prospect of harnessing the latent cardiogenic potential in the vasculature for use in regenerative medicine, and to investigate whether similar development plasticity exists in other major cell fate decisions in the developing embryo," the study states.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by a California Institute of Regenerative Medicine New Faculty Award, a National Institutes of Health's National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (RO1 HL097766-01), an Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA Innovation Award, a National Institutes of Health Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Awards (GM07185 and T32 HL69766), the European Molecular Biology Organization, the Human Frontier Science Program, the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research, European Social Fund (Mobilitas), and the Center of Excellence in Molecular Hematology from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
The stem cell center was launched in 2005 with a UCLA commitment of $20 million over five years. A $20 million gift from the Eli and Edythe Broad Foundation in 2007 resulted in the renaming of the center. With more than 200 members, the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research is committed to a multi-disciplinary, integrated collaboration of scientific, academic and medical disciplines for the purpose of understanding adult and human embryonic stem cells. The center supports innovation, excellence and the highest ethical standards focused on stem cell research with the intent of facilitating basic scientific inquiry directed towards future clinical applications to treat disease. The center is a collaboration of the David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA's Jonsson Cancer Center, the Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science and the UCLA College of Letters and Science. To learn more about the center, visit our web site at http://www.stemcell.ucla.edu.
Embryonic blood vessels that make blood stem cells can also make beating heart muscles
2012-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stanford expert brings climate change science to heated Capitol Hill
2012-08-02
Now's the time to prepare for the heat waves, heavy rains and droughts that climate change will bring, says Stanford's Chris Field, a noted climate researcher.
Speaking Wednesday at a contentious U.S. Senate hearing on climate change, Stanford's Chris Field, an expert on climate change, offered a stark yet hopeful analogy.
Just as speeding increases the chance of having a car accident, climate change intensifies the risk of heat waves, droughts and heavy precipitation, said Field, a senior fellow at the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment. He testified before ...
Study finds healthy seafood comes from sustainable fish
2012-08-02
TEMPE, Ariz. – When ordering seafood, the options are many and so are some of the things you might consider in what you order. Is your fish healthy? Is it safe? Is it endangered? While there are many services and rankings offered to help you decide – there's even an iPhone app – a group of researchers have found a simple rule of thumb applies.
"If the fish is sustainable, then it is likely to be healthy to eat too," said Leah Gerber, an associate professor and senior sustainability scientist at Arizona State University.
Gerber and colleagues ran an analysis of existing ...
Usain Bolt could break his own record with the help of altitude and the wind
2012-08-02
Imagine the following situation. The 100 metres finals in the London Olympic Games. The Jamaican Usain Bolt wins. Up to this point everything sounds normal except for the fact that he would break his own record again with a time of 9.48 seconds. According to the New Zealand researchers, this would be his record if there were a 2 metre per second tailwind (maximum allowable wind) and the race took place at an altitude of 999 metres. This record will of course have to wait because London lies just 24 metres above sea level. Scientists are sure though that environment conditions ...
Health care organizations quest for reduced costs and improved quality
2012-08-02
Rochester, MN, August 2, 2012 – Many health care systems across the US have declined to participate in the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services' (CMMS) Accountable Care Organization (ACO) program, developed under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), to improve efficiency and quality of health care delivery. In a groundbreaking collection of commentaries in the current issue of Mayo Clinic Proceedings, representatives of six leading health care organizations write about the challenges of reducing health care costs while improving health care quality. ...
Detecting thyroid disease by computer
2012-08-02
Researchers in India have developed an improved expert system for the diagnosis of thyroid disease. They describe details of their approach to screening medical data in a forthcoming issue of the International Journal of Computational Science and Engineering.
Thyroid disease in which either too much thyroid hormone is produced (hyperthyroidism) or too little is made (hypothyroidism) are common health problems across the globe. An overactive thyroid can lead to increased perspiration, a raise pulse, tremors, anxiety, nervousness, and irritability, insomnia, thinning of ...
Psychology of possibilities can enhance health, happiness, research says
2012-08-02
ORLANDO, Fla. -- First-time mothers who pay attention to their emotional and physical changes during their pregnancy may feel better and have healthier newborns than new mothers who don't, according to research to be presented at American Psychological Association's 120th Annual Convention.
"These findings continue more than 40 years of research that has made clear that whether you are mindless or mindful makes a big difference in every aspect of your health and well-being -- from competence to longevity," Ellen Langer, professor of psychology at Harvard University and ...
Note to waitresses: Wearing red can be profitable
2012-08-02
Los Angeles, CA (02 August, 2012) In many restaurants throughout the world, wait staff's income depends largely on the tips received from customers. According to a new study, male restaurant customers give higher tips to waitresses wearing red. This study was published in a recent issue of Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research (published by SAGE, on behalf of the International Council on Hotel, Restaurant, and Institutional Education).
In their study of 272 restaurant customers, researchers Nicolas Guéguen and Céline Jacob found not only that male patrons gave ...
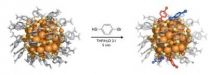
New structural information on functionalization of gold nanoparticles
2012-08-02
Nanometre-scale gold particles are currently intensively investigated for possible applications as catalysts, sensors, biolabels, drug delivery devices, biological contrast agents and as components in photonics and molecular electronics. The particles are prepared in a solution from gold salts and their reactive gold cores can be stabilized with various organic ligands. Particularly stable particles can be synthesized by using organothiol ligands that have a strong chemical interaction to gold, producing precise compositions in the size range of 1 to 3 nanometres. Modification ...
Mechanisms for a beneficial effect of moderate alcohol consumption on osteoporosis in women
2012-08-02
Women after menopause tend to develop weaker bones from what is known as osteoporosis, which may lead to fractures (especially hip fractures) from falling. The weakness of the bones results from an imbalance between the normal resorption (a type of dissolving of old bone) and the laying down of new bone, an ongoing process for both men and women referred to as "bone turnover." For poorly understood reasons, after menopause the resorption of old bone in women continues but new bone is laid down less well, leading to a decrease in bone density. A variety of substances ...
Infants exposed to specific molds have higher asthma risk
2012-08-02
CINCINNATI—In the United States, one in 10 children suffers from asthma but the potential environmental factors contributing to the disease are not well known. Cincinnati-based researchers now report new evidence that exposure to three types of mold during infancy may have a direct link to asthma development during childhood.
These forms of mold—Aspergillus ochraceus, Aspergillus unguis and Penicillium variabile—are typically found growing in water-damaged homes, putting a spotlight on the importance of mold remediation for public health.
Lead author Tiina Reponen, ...