(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
MU researchers studied how college-age women view their bodies and how they feel about media messages aimed at women. Based on focus group research findings, the MU team developed an...
Click here for more information.
COLUMBIA, Mo. –When it comes to college-age individuals taking care of their bodies, appearance is more important than health, research conducted at the University of Missouri suggests. María Len-Ríos, an associate professor of strategic communication, Suzanne Burgoyne, a professor of theater, and a team of undergraduate researchers studied how college-age women view their bodies and how they feel about media messages aimed at women. Based on focus group research findings, the MU team developed an interactive play about body image to encourage frank discussions about conflicting societal messages regarding weight, values and healthful choices.
"During our focus group conversations, we learned that young people don't think about nutrition when it comes to eating," Len-Ríos said. "They think more about calorie-counting, which isn't necessarily related to a balanced diet."
The focus groups included college-age women, college-age men and mothers of college-age women, who discussed how body image is associated with engaging in restrictive diets, irregular sleep patterns and over-exercising.
"We receive so many conflicting media messages from news reports and advertising about how we should eat, how we should live and how we should look," Len-Ríos said. "Some participants said they realize images of models are digitally enhanced, but it doesn't necessarily keep them from wanting to achieve these unattainable figures—this is because they see how society rewards women for 'looking good.'"
The researchers also completed in-depth interviews with nutritional counselors who said lack of time and unhealthy food environments can keep college-age students from getting good nutrition.
"Eating well takes time, and, according to health professionals, college students are overscheduled and don't have enough time to cook something properly or might not know how to prepare something healthful," Len-Ríos said.
Based on the focus group conversations and interviews, Carlia Francis, an MU theater doctoral student and playwright, developed "Nutrition 101," a play about women's body images. During performances, characters divulge their insecurities about their own bodies, disparage other women's bodies and talk about nutrition choices. After a short, scripted performance, the actors remain in character, and audience members ask the characters questions.
"When you're developing something for interactive theater, focus groups and in-depth interviews are great at getting at stories," Len-Ríos said. "Many of the stories used in the interactive play—like valuing people because of their appearance and not their personal qualities or abilities—came from individuals' personal experiences."
Burgoyne says the play helps facilitate dialogues about nutrition, media messages and self-awareness.
"Body image is a sensitive topic, and the play helps open discussions about how individuals view themselves and how media messages influence their self-images," Burgoyne said. "An easy way to improve individuals' body images does not exist, but hopefully, the conversations that arise from the performances will help develop ways to counteract the images that the media promote."
MU student actors debuted the play last spring, and Burgoyne said performances will resume during the upcoming fall semester.
The study, "Confronting Contradictory Media Messages about Body Image and Nutrition: Implications for Public Health," was presented earlier this month at the annual Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication Conference in Chicago.
INFORMATION:
The project is part of Mizzou Advantage's food for the future initiative. Mizzou Advantage was created to increase MU's visibility, impact and stature in higher education locally, statewide, nationally and around the world. Mizzou Advantage is a program that focuses on four areas of strength: food for the future, media of the future, one health/one medicine and sustainable energy. The goals of Mizzou Advantage are to strengthen existing faculty networks, create new networks and propel Mizzou's research, instruction and other activities to the next level. Additional funding for script development and performances came from the MU Vice Chancellor for Student Affairs.
For young adults, appearance matters more than health, MU research suggests
Research inspires interactive theater, opens dialogue
2012-08-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
10 new diabetes gene links offer picture of biology underlying disease
2012-08-13
Ten more DNA regions linked to type 2 diabetes have been discovered by an international team of researchers, bringing the total to over 60.
The study provides a fuller picture of the genetics and biological processes underlying type 2 diabetes, with some clear patterns emerging.
The international team, led by researchers from the University of Oxford, the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, and the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, used a new DNA chip to probe deeper into the genetic variations that commonly occur in our DNA and which may have some connection to type ...
Yale team discovers how stress and depression can shrink the brain
2012-08-13
Major depression or chronic stress can cause the loss of brain volume, a condition that contributes to both emotional and cognitive impairment. Now a team of researchers led by Yale scientists has discovered one reason why this occurs — a single genetic switch that triggers loss of brain connections in humans and depression in animal models.
The findings, reported in the Aug. 12 issue of the journal Nature Medicine, show that the genetic switch known as a transcription factor represses the expression of several genes that are necessary for the formation of synaptic connections ...
Metabolic MAGIC
2012-08-13
Researchers have identified 38 new genetic regions that are associated with glucose and insulin levels in the blood. This brings the total number of genetic regions associated with glucose and insulin levels to 53, over half of which are associated with type 2 diabetes.
The researchers used a technology that is 100 times more powerful than previous techniques used to follow-up on genome-wide association results. This technology, Metabochip, was designed as a cost-effective way to find and map genomic regions for a range of cardiovascular and metabolic characteristics ...
World's most powerful X-ray laser beam refined to scalpel precision
2012-08-13
With a thin sliver of diamond, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have transformed the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) into an even more precise tool for exploring the nanoworld. The improvements yield laser pulses focused to higher intensity in a much narrower band of X-ray wavelengths, and may enable experiments that have never before been possible.
In a process called "self-seeding," the diamond filters the laser beam to a single X-ray color, which is then amplified. Like trading a hatchet for a scalpel, the ...
Mutations disrupt cellular recycling and cause a childhood genetic disease
2012-08-13
Genetics researchers have identified a key gene that, when mutated, causes the rare multisystem disorder Cornelia deLange syndrome (CdLS). By revealing how mutations in the HDAC8 gene disrupt the biology of proteins that control both gene expression and cell division, the research sheds light on this disease, which causes intellectual disability, limb deformations and other disabilities resulting from impairments in early development.
"As we better understand how CdLS operates at the level of cell biology, we will be better able to define strategies for devising treatments ...
Modeling reveals significant climatic impacts of megapolitan expansion
2012-08-13
TEMPE, Ariz. – According to the United Nations' 2011 Revision of World Urbanization Prospects, global urban population is expected to gain more than 2.5 billion new inhabitants through 2050. Such sharp increases in the number of urban dwellers will require considerable conversion of natural to urban landscapes, resulting in newly developing and expanding megapolitan areas. Could climate impacts arising from built environment growth pose additional concerns for urban residents also expected to deal with impacts resulting from global climate change?
In the first study to ...
Unraveling intricate interactions, 1 molecule at a time
2012-08-13
A team of researchers at Columbia Engineering, led by Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Associate Professor Latha Venkataraman and in collaboration with Mark Hybertsen from the Center for Functional Nanomaterials at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, has succeeded in performing the first quantitative characterization of van der Waals interactions at metal/organic interfaces at the single-molecule level.
In a study published online August 12 in the Advance Online Publication on Nature Materials's website , the team has shown the existence ...
Differences in the genomes of related plant pathogens
2012-08-13
This press release is available in German.
Many crop plants worldwide are attacked by a group of fungi that numbers more than 680 different species. After initial invasion, they first grow stealthily inside living plant cells, but then switch to a highly destructive life-style, feeding on dead cells. While some species switch completely to host destruction, others maintain stealthy and destructive modes simultaneously. A team of scientists led by Richard O'Connell from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research in Cologne and Lisa Vaillancourt from University ...
Smelling a skunk after a cold
2012-08-13
CHICAGO --- Has a summer cold or mold allergy stuffed up your nose and dampened your sense of smell? We take it for granted that once our nostrils clear, our sniffers will dependably rebound and alert us to a lurking neighborhood skunk or a caramel corn shop ahead.
That dependability is no accident. It turns out the brain is working overtime behind the scenes to make sure the sense of smell is just as sharp after the nose recovers.
A new Northwestern Medicine study shows that after the human nose is experimentally blocked for one week, brain activity rapidly ...
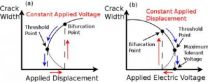
A pre-crack might propagate or stick under mechanical and electrical loading
2012-08-13
Fracture under combined mechanical and electric loading is currently a hot research area in the global fracture community, while electric sticking is a major concern in the design and fabrication of micro/nanoelectromechanical systems. Professor ZHANG Tong-Yi and his student, Mr. Tao Xie, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, found that the two problems are switchable, depending on the loading conditions, sample geometries and material properties. Based on his 20-year research experience on the fracture of dielectric ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
[Press-News.org] For young adults, appearance matters more than health, MU research suggestsResearch inspires interactive theater, opens dialogue