(Press-News.org) In a major breakthrough, an international team of scientists has proven that addiction to morphine and heroin can be blocked, while at the same time increasing pain relief.
The team from the University of Adelaide and University of Colorado has discovered the key mechanism in the body's immune system that amplifies addiction to opioid drugs.
Laboratory studies have shown that the drug (+)-naloxone (pronounced: PLUS nal-OX-own) will selectively block the immune-addiction response.
The results – which could eventually lead to new co-formulated drugs that assist patients with severe pain, as well as helping heroin users to kick the habit – will be published tomorrow in the Journal of Neuroscience.
"Our studies have shown conclusively that we can block addiction via the immune system of the brain, without targeting the brain's wiring," says the lead author of the study, Dr Mark Hutchinson, ARC Research Fellow in the University of Adelaide's School of Medical Sciences.
"Both the central nervous system and the immune system play important roles in creating addiction, but our studies have shown we only need to block the immune response in the brain to prevent cravings for opioid drugs."
The team has focused its research efforts on the immune receptor known as Toll-Like receptor 4 (TLR4).
"Opioid drugs such as morphine and heroin bind to TLR4 in a similar way to the normal immune response to bacteria. The problem is that TLR4 then acts as an amplifier for addiction," Dr Hutchinson says.
"The drug (+)-naloxone automatically shuts down the addiction. It shuts down the need to take opioids, it cuts out behaviours associated with addiction, and the neurochemistry in the brain changes – dopamine, which is the chemical important for providing that sense of 'reward' from the drug, is no longer produced."
Senior author Professor Linda Watkins, from the Center for Neuroscience at the University of Colorado Boulder, says: "This work fundamentally changes what we understand about opioids, reward and addiction. We've suspected for some years that TLR4 may be the key to blocking opioid addiction, but now we have the proof.
"The drug that we've used to block addiction, (+)-naloxone, is a non-opioid mirror image drug that was created by Dr Kenner Rice in the 1970s. We believe this will prove extremely useful as a co-formulated drug with morphine, so that patients who require relief for severe pain will not become addicted but still receive pain relief . This has the potential to lead to major advances in patient and palliative care," Professor Watkins says.
The researchers say clinical trials may be possible within the next 18 months.
INFORMATION:
This study has been funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) in the United States and the Australian Research Council (ARC).
Media Contacts:
Dr Mark Hutchinson
ARC Research Fellow
Discipline of Physiology
School of Medical Sciences
The University of Adelaide
Phone: +61 8 8313 0322
Cell phone: +61 466 304 980
mark.hutchinson@adelaide.edu.au
Professor Linda Watkins
Distinguished Professor
Center for Neuroscience
Department of Psychology
University of Colorado Boulder
Phone: +1 303 492 7034
linda.watkins@colorado.edu
Scientists can now block heroin, morphine addiction
Clinical trials possible within 18 months
2012-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study proves that 1 extinction leads to another
2012-08-15
When a carnivore becomes extinct, other predatory species could soon follow, according to new research. Scientists have previously put forward this theory, but a University of Exeter team has now carried out the first experiment to prove it.
Published today (15 August 2012) in the Royal Society journal Biology Letters, the study shows how the demise of one carnivore species can indirectly cause another to become extinct. The University of Exeter team believes any extinction can create a ripple effect across a food web, with far-reaching consequences for many other animals. ...
Plants exhibit a wide range of mechanical properties, engineers find
2012-08-15
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- From an engineer's perspective, plants such as palm trees, bamboo, maples and even potatoes are examples of precise engineering on a microscopic scale. Like wooden beams reinforcing a house, cell walls make up the structural supports of all plants. Depending on how the cell walls are arranged, and what they are made of, a plant can be as flimsy as a reed, or as sturdy as an oak.
An MIT researcher has compiled data on the microstructures of a number of different plants, from apples and potatoes to willow and spruce trees, and has found that plants exhibit ...
How do they do it? Predictions are in for Arctic sea ice low point
2012-08-15
It's become a sport of sorts, predicting the low point of Arctic sea ice each year. Expert scientists with decades of experience do it but so do enthusiasts, whose guesses are gamely included in a monthly predictions roundup collected by Sea Ice Outlook, an effort supported by the U.S. government.
When averaged, the predictions have come in remarkably close to the mark in the past two years. But the low and high predictions are off by hundreds of thousands of square kilometers.
Researchers are working hard to improve their ability to more accurately predict how much ...
Girls with ADHD more prone to self-injury, suicide as they enter adulthood
2012-08-15
Girls with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) – and their families – often look forward to the likely decline in visible symptoms such as fidgety or disruptive behavior as they mature into young women.
However, new findings from UC Berkeley caution that, as they enter adulthood, girls with histories of ADHD are more prone to internalize their struggles and feelings of failure – a development that can manifest itself in self-injury and even attempted suicide.
"Like boys with ADHD, girls continue to have problems with academic achievement and relationships, ...
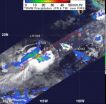
NASA sees more rain for the Philippines from Tropical Storm Kai-Tak
2012-08-15
An intensifying Tropical storm called Kai-Tak (locally known as Helen) is causing more rain in the Philippines as it passes over northern Luzon. The Philippines have had a very wet month with the capital of Manila experiencing massive flooding earlier this month. NASA's TRMM satellite identified where the heavy rain was falling.
Kai-tak has caused another day of warnings in the Philippines. On August 14, Public storm warning signal #1 is in effect for these provinces in Luzon: La Union, Nueva Ecija, Pangasinan, Rest of Aurora, and Tarlac.
In addition, Public storm warning ...
NASA's TRMM Satellite sees a small area of heavy rain left in Tropical Storm Hector
2012-08-15
Tropical Storm Hector is battling wind shear over the open waters of the Eastern Pacific Ocean, and NASA satellite data shows that has been affecting its organization and rainfall rates.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM is managed by both NASA and the Japanese Space Agency. From its orbit in space, TRMM's instruments can estimate rainfall from tropical cyclones.
The TRMM satellite captured rainfall rates from Tropical Storm Hector on August 14, 2012 1:28 a.m. EDT. TRMM data showed that Hector had a small area of moderate to heavy rainfall ...
NASA seeing sprites
2012-08-15
VIDEO:
Filmed at 10,000 frames per second by Japan's NHK television, movies like this of electromagnetic bursts called "sprites " will help scientists better understand how weather high in the atmosphere relates...
Click here for more information.
High above the clouds during thunderstorms, some 50 miles above Earth a different kind of lightning dances. Bursts of red and blue light, known as "sprites," flash for a scant one thousandth of a second. They are often ...
Meditation reduces loneliness
2012-08-15
Many elderly people spend their last years alone. Spouses pass and children scatter. But being lonely is much more than a silent house and a lack of companionship. Over time, loneliness not only takes a toll on the psyche but can have a serious physical impact as well.
Feeling lonely has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, Alzheimer's disease, depression and even premature death. Developing effective treatments to reduce loneliness in older adults is essential, but previous treatment efforts have had limited success.
What to do? Researchers at UCLA ...
Need an expert? Try the crowd
2012-08-15
In 1714, the British government held a contest. They offered a large cash prize to anyone who could solve the vexing "longitude problem" — how to determine a ship's east/west position on the open ocean — since none of their naval experts had been able to do so.
Lots of people gave it a try. One of them, a self-educated carpenter named John Harrison, invented the marine chronometer — a rugged and highly precise clock — that did the trick. For the first time, sailors could accurately determine their location at sea.
A centuries-old problem was solved. And, arguably, crowdsourcing ...
An artificial retina with the capacity to restore normal vision
2012-08-15
Two researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College have deciphered a mouse's retina's neural code and coupled this information to a novel prosthetic device to restore sight to blind mice. The researchers say they have also cracked the code for a monkey retina — which is essentially identical to that of a human —and hope to quickly design and test a device that blind humans can use.
The breakthrough, reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), signals a remarkable advance in longstanding efforts to restore vision. Current prosthetics provide blind ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Scientists can now block heroin, morphine addictionClinical trials possible within 18 months