(Press-News.org) AMES, Iowa - Some fisheries in the United States are poised to undergo major changes in the regulations used to protect fish stocks, and Iowa State University researchers have estimated that the new system will be an economic boon to the fishing industry.
Quinn Weninger and Rajesh Singh, both associate professors in economics, estimated harvesting costs under the old system and compared that to the newly proposed fishing regulations that lift many restrictions that cause inefficiency while still limiting amounts to be harvested.
Their analysis focused on the Pacific Groundfish fishery, which manages fishing in waters off the Northwest coast of the United States, and found the Groundfish fleet could save between $18 million and $22 million annually under the new regulatory system.
Pacific Groundfish fishery is one of several fisheries around the country that monitors fish harvest by location and types of fish. Similar economic conclusions would apply to other areas and other fish types, according to Weninger.
"What we've tried to do is come up with the cost savings that would be involved when we change from the old to the new system," he said.
The new system controls catch amounts through a system of tradable fishing permits and allocates a certain amount of fish to be harvested by each fisherman each year, said Weninger. The amount of each fisherman's total harvest is determined by the total number of permits he holds.
Fisheries managers, who are National Marine Fisheries Service employees, monitor fish stocks and calculate the total harvest that will allow fish numbers to remain at sustainable levels while letting fishermen survive economically.
Under the new system, for example, if a fisherman owns 1 percent of the permits, that fisherman can harvest 1 percent of the total amount of fish, which is chosen annually by the manager.
The new regulations begin by allocating permits to active fishermen based on that fisherman's past annual haul of fish. A key feature is that the permits can be bought and sold, allowing more flexibility for fishermen.
Under the old system, fishermen faced a host of regulations designed to ensure the fleet did not overfish the resource.
These regulations included imposing gear restrictions, seasonal closures, area closures, limits on the number of boats, bimonthly catch limits and other regulations that make harvesting fish less and less efficient and more costly.
"Prior to the new system, an entire years' halibut was harvested in two, six-hour openings," said Weninger. "We're talking about thousands of boats going out there and filling their boats to the point of sinking on the way home with all of these fish."
While the new system has gained popularity in recent years, little was known about how much money would be saved industry-wide.
Weninger and Singh answered that question.
The $18 million to $22 million savings for the Pacific Groundfish fishery will result mainly from reducing the size of the fishing fleet from around 117 vessels, to around 40 to 60 that will be required to catch the government-set limit. That is a reduction of more than 50 percent.
"Basically the revenues stay the same [under the new system], but you're able to harvest those fish at a fraction of the cost," Weninger said.
The old systems had too many redundant boats providing the same service, he added.
The findings are published in the journal Marine Resource Economics.
Weninger said the cost savings could eventually lower prices at the supermarket.
Another benefit for consumers is the availability of fresh fish. In the past, since all the halibut had to be harvested in just a few hours, consumers had to settle for frozen fish for much of the year. Now, with the expanded time window to catch fish, there will be fresh halibut available for more of the year, he said.
Another benefit is safety. Since fishermen won't be required to fish during a time preset by the government regulations regardless of weather conditions, they can fish when conditions are favorable and fishing is safer.
INFORMATION:
New fisheries system will save about $20 million, Iowa State University researchers find
2010-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Animations show extent of marcellus shale development
2010-10-06
The pace and extent of Marcellus Shale development across Pennsylvania can be "seen" in animated maps produced by the Penn State Marcellus Center for Outreach and Research.
Based on data from the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection, the animations (http://www.marcellus.psu.edu/resources/maps.php) show both the number of drilling permits issued for the Marcellus Shale target and the number of wells drilled by year from 2007 through August 2010. Although permits were issued prior to 2007, information on those permits did not include latitude and longitude.
"These ...
A thirst for excitement is hidden in your genes
2010-10-06
Sensation seeking—the urge to do exciting things—has been linked to dopamine, a chemical that carries messages in your brain. For a new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, scientists analyzed genes in the dopamine system and found a group of mutations that help predict whether someone is inclined toward sensation seeking.
Sensation seeking has been linked to a range of behavior disorders, such as drug addiction. It isn't all bad, though. "Not everyone who's high on sensation seeking becomes a drug addict. They ...
UNH researcher helps identify key reproductive hormone in oldest vertebrate
2010-10-06
DURHAM, N.H. -- Looking at a hagfish – an eyeless, snot-covered, worm-like scavenger of the deep –the last thing that comes to mind is sex. Yet the reproductive functioning of these ancient vertebrates is such an enduring enigma that a gold medal was once offered to anyone who could elucidate it.
Although the prize expired, unclaimed, long ago, University of New Hampshire professor of biochemistry Stacia Sower and colleagues at two Japanese universities have identified the first reproductive hormone of the hagfish – a gonadatropin -- representing a significant step toward ...
Early lung cancer detection
2010-10-06
Researchers from Northwestern University and NorthShore University HealthSystem (NorthShore) have developed a method to detect early signs of lung cancer by examining cheek cells in humans using pioneering biophotonics technology.
"By examining the lining of the cheek with this optical technology, we have the potential to prescreen patients at high risk for lung cancer, such as those who smoke, and identify the individuals who would likely benefit from more invasive and expensive tests versus those who don't need additional tests," said Hemant K. Roy, M.D., director ...
Air pollution alters immune function, worsens asthma symptoms
2010-10-06
Berkeley – Exposure to dirty air is linked to decreased function of a gene that appears to increase the severity of asthma in children, according to a joint study by researchers at Stanford University and the University of California, Berkeley.
While air pollution is known to be a source of immediate inflammation, this new study provides one of the first pieces of direct evidence that explains how some ambient air pollutants could have long-term effects.
The findings, published in the October 2010 issue of the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, come from ...
Doppler radars help increase monsoon rainfall prediction accuracy
2010-10-06
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Doppler weather radar will significantly improve forecasting models used to track monsoon systems influencing the monsoon in and around India, according to a research collaboration including Purdue University, the National Center for Atmospheric Research and the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi.
Dev Niyogi, a Purdue associate professor of agronomy and earth and atmospheric sciences, said modeling of a monsoon depression track can have a margin of error of about 200 kilometers for landfall, which can be significant for storms that produce as ...
GOES-13 sees another potential tropical depression in Caribbean Sea
2010-10-06
The GOES-13 satellite passed over a low pressure area designated as "System 97L" earlier today and captured a visible image of the low in the eastern Caribbean Sea. System 97L appears in a good place for development into a tropical depression in the next day or two.
The National Hurricane Center currently gives the low pressure area known as System 97L an "80 percent chance of developing into a tropical depression in the next 48 hours." The low pressure area is located just north of the Virgin Islands near 19.0 North latitude and 65.3 West longitude. The visible image ...
NASA AIRS Satellite instrument sees Tropical Depression 14W form
2010-10-06
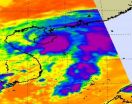
The northwestern Pacific Ocean is just as active as the Atlantic Ocean this hurricane season. The fourteenth tropical depression formed near Hainan Island, China this morning and its birth was captured by a NASA infrared satellite instrument. The NASA image showed the depression's strong thunderstorms near its center and east of its center.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Depression 14W (TD14W) today, October 5 at 06:05 UTC (2:05 a.m. EDT). Infrared imagery from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard the Aqua satellite revealed a concentrated ...
New fossil suggests dinosaurs not so fierce after all
2010-10-06
A new species of dinosaur discovered in Arizona suggests dinosaurs did not spread throughout the world by overpowering other species, but by taking advantage of a natural catastrophe that wiped out their competitors.
The new dinosaur, named Sarahsaurus, was studied by an international team of scientists, including Robert R. Reisz, professor and chair of biology at the University of Toronto Mississauga, Tim Rowe, professor of paleontology at the University of Texas at Austin's Jackson School of Geosciences and Hans-Dieter Sues, curator of vertebrate paleontology at the ...
MAVEN mission to investigate how sun steals Martian atmosphere
2010-10-06
The Red Planet bleeds. Not blood, but its atmosphere, slowly trickling away to space. The culprit is our sun, which is using its own breath, the solar wind, and its radiation to rob Mars of its air. The crime may have condemned the planet's surface, once apparently promising for life, to a cold and sterile existence.
Features on Mars resembling dry riverbeds, and the discovery of minerals that form in the presence of water, indicate that Mars once had a thicker atmosphere and was warm enough for liquid water to flow on the surface. However, somehow that thick atmosphere ...