(Press-News.org) A new study by researchers at UT Dallas' Center for Vital Longevity, Duke University, and the University of Michigan has found that the strength of communication between the left and right hemispheres of the brain predicts performance on basic arithmetic problems. The findings shed light on the neural basis of human math abilities and suggest a possible route to aiding those who suffer from dyscalculia-- an inability to understand and manipulate numbers.
It has been known for some time that the parietal cortex, the top/middle region of the brain, plays a central role in so-called numerical cognition--our ability to process numerical information. Previous brain imaging studies have shown that the right parietal region is primarily involved in basic quantity processing (like gauging relative amounts of fruit in baskets), while the left parietal region is involved in more precise numerical operations like addition and subtraction. What has not been known is whether the two hemispheres can work together to improve math performance. The new study demonstrates that they can. The findings were recently published online in Cerebral Cortex.
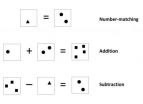
In the study, conducted in Dallas and led by Dr. Joonkoo Park, now a postdoctoral fellow at Duke University, researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging, or fMRI, to measure the brain activity of 27 healthy young adults while they performed simple numerical and arithmetic tasks. In one task, participants were asked to judge whether two groups of shapes contained the same or different numbers of items. In two other tasks, participants were asked to solve simple addition and subtraction problems.
Consistent with previous studies, the researchers found that the basic number-matching task activated the right parietal cortex, while the addition and subtraction tasks produced additional activity in the left parietal cortex. But they also found something new: During the arithmetic tasks, communication between the left and right hemispheres increased significantly compared with the number-matching task. Moreover, people who exhibited the strongest connection between hemispheres were the fastest at solving the subtraction problems.
"Our results suggest that subtraction performance is optimal when there is high coherence in the neural activity in these two brain regions. Two brain areas working together rather than either region alone appears to be key" said co-author Dr. Denise C. Park, co-director of the UT Dallas Center for Vital Longevity and Distinguished University Chair in the School of Behavioral and Brain Sciences. Park (no relation to the lead author) helped direct the study along with Dr. Thad Polk, professor of psychology at the University of Michigan.
Lead author Dr. Joonkoo Park points out that the findings suggest that disrupted or inefficient neural communication between the hemispheres may contribute to the impaired math abilities seen in dyscalculia, the numerical equivalent of dyslexia. "If such a causal link exists," he said, "one very interesting avenue of research would be to develop training tasks to enhance parietal connectivity and to test whether they improve numerical competence."
Such a training program might help develop math ability in children and could also help older adults whose arithmetic skills begin to falter as a normal part of age-related cognitive decline.
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by a grant to Dr. Denise C. Park from the National Institute on Aging.
Math ability requires crosstalk in the brain
2012-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New 'traffic light' test could save lives with earlier diagnosis of liver disease
2012-08-29
A new 'traffic light' test devised by Dr Nick Sheron and colleagues at University of Southampton and Southampton General Hospital could be used in primary care to diagnose liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in high risk populations more easily than at present.
Liver disease develops silently without symptoms, and many people have no idea they have liver failure until it is too late – one-third of people admitted to hospital with end-stage liver disease die within the first few months. A simple test available in primary care could diagnose disease much earlier, enabling those ...
Internet addiction -- Causes at the molecular level
2012-08-29
"It was shown that Internet addiction is not a figment of our imagination," says the lead author, Privatdozent Dr. Christian Montag from the Department for Differential and Biological Psychology at the University of Bonn. "Researchers and therapists are increasingly closing in on it." Over the past years, the Bonn researchers have interviewed a total of 843 people about their Internet habits. An analysis of the questionnaires shows that 132 men and women in this group exhibit problematic behavior in how they handle the online medium; all their thoughts revolve around the ...
Twitter data crunching: The new crystal ball
2012-08-29
Fabio Ciulla from Northeastern University, Boston, USA, and his colleagues demonstrated that the elimination of contestants in TV talent shows based on public voting, such as American Idol, can be anticipated. They unveiled the predictive power of microblogging Twitter signals--used as a proxy for the general preference of an audience--in a study recently published in EPJ Data Science¹.
The authors considered the voting system of these shows as a basic test to assess the predictive power of Twitter signals. They relied on the overlap between Twitter users and show audience ...
Earphones 'potentially as dangerous as noise from jet engines,' according to new study
2012-08-29
Turning the volume up too high on your headphones can damage the coating of nerve cells, leading to temporary deafness; scientists from the University of Leicester have shown for the first time.
Earphones or headphones on personal music players can reach noise levels similar to those of jet engines, the researchers said.
Noises louder than 110 decibels are known to cause hearing problems such as temporary deafness and tinnitus (ringing in the ears), but the University of Leicester study is the first time the underlying cell damage has been observed.
The study has ...
New research eclipses existing theories on moon formation
2012-08-29
Oxford, August 29, 2012 - The Moon is believed to have formed from a collision, 4.5 billion years ago, between Earth and an impactor the size of Mars, known as "Theia." Over the past decades scientists have simulated this process and reproduced many of the properties of the Earth-Moon system; however, these simulations have also given rise to a problem known as the Lunar Paradox: the Moon appears to be made up of material that would not be expected if the current collision theory is correct. A recent study published in Icarus proposes a new perspective on the theory in ...
Don't cut lifesaving ICDs during financial crisis, ESC warns
2012-08-29
Implantable devices for treating cardiac arrhythmias, which include ICDs, are already underused in parts of Eastern and Central Europe and there is a risk that the financial crisis could exacerbate the problem. The European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a registered branch of the ESC, is tackling this issue through ICD for Life. The initiative aims to raise awareness about the importance of ICDs and sudden cardiac death in countries in Central and Eastern Europe.
ICD implantation rates in Europe vary widely, ranging from 1 ICD implantation per million inhabitants in ...
Gold standards of success defined for AF ablation
2012-08-29
The 2012 expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation was developed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society (ECAS) and published in their respective journals: Heart Rhythm, EP Europace (1) and the Journal of Interventional Cardiovascular Electrophysiology (JICE).
Since the previous consensus document was published in 2007 catheter and surgical ablation of AF have become standard treatments ...
A CNIO team creates a unique mouse model for the study of aplastic anaemia
2012-08-29
Aplastic anaemia is characterised by a reduction in the number of the bone marrow cells that go on to form the different cell types present in blood (essentially red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets). In most cases, the causes of the disorder are hard to determine, but some patients have been found to have genetic alterations leading to a shortening of their telomeres (the end regions of chromosomes that protect and stabilise DNA).
A team at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) led by María Blasco has successfully created a transgenic mouse model ...
Oversized fat droplets: Too much of a good thing
2012-08-29
KANSAS CITY, MO—As the national waistline expands, so do pools of intra-cellular fat known as lipid droplets. Although most of us wish our lipid droplets would vanish, they represent a cellular paradox: on the one hand droplets play beneficial roles by corralling fat into non-toxic organelles. On the other, oversized lipid droplets are associated with obesity and its associated health hazards.
Until recently researchers understood little about factors that regulate lipid droplet size. Now, a study from the Stowers Institute of Medical Research published in an upcoming ...
Climate change could increase levels of avian influenza in wild birds
2012-08-29
ANN ARBOR, Mich.—Rising sea levels, melting glaciers, more intense rainstorms and more frequent heat waves are among the planetary woes that may come to mind when climate change is mentioned. Now, two University of Michigan researchers say an increased risk of avian influenza transmission in wild birds can be added to the list.
Population ecologists Pejman Rohani and Victoria Brown used a mathematical model to explore the consequences of altered interactions between an important species of migratory shorebird and horseshoe crabs at Delaware Bay as a result of climate ...