(Press-News.org) So many acts in our daily lives – refusing that second slice of cake, walking past the store with the latest gadgets, working on your tax forms when you'd rather watch TV – seem to boil down to one essential ingredient: self-control. Self-control is what enables us to maintain healthy habits, save for a rainy day, and get important things done.
But what is self-control, really? And how does it work?
In a new article in the September 2012 issue of Perspectives on Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, researchers Michael Inzlicht of the University of Toronto and Brandon Schmeichel of Texas A&M University argue that the prevailing model of self-control may not be as precise as researchers once thought. Rather than being a limited resource, self-control may actually be more like a motivation- and attention-driven process.
Research on self-control has surged in the last decade and much of it has centered on the resource model of self-control. According to this model, originally proposed by Roy Baumeister and colleagues, self-control is a limited resource – if we exercise a lot of self-control by refusing a second slice of cake, we may not have enough self-control later in the day to resist the urge to shop or watch TV.
Over 100 papers have produced findings that support this model. Research has found, for example, that people who are required to manage their emotions show impaired performance on later tasks, such as solving a difficult puzzle, squeezing a handgrip exerciser, and keeping items in working memory.
But Inzlicht and Schmeichel point out that a newer crop of studies are yielding results that don't fit with this idea of self-control as a depletable resource. Recent studies have shown that incentives, individual perceptions of task difficulty, personal beliefs about willpower, feedback on task performance, and changes in mood all seem to influence our ability to exercise self-control. These results suggest that self-control may not rely on a limited resource after all.
To accommodate these new findings and get at the mechanisms that underlie self-control, Inzlicht and Schmeichel propose an alternative model that describes self-control as a process involving motivation and attention.
"Engaging in self-control by definition, is hard work; it involves deliberation, attention, and vigilance," the authors write. If we resist that second slice of cake, we may experience a shift in motivation so that we feel justified in indulging ourselves later on. It's not necessarily the case that we can't control ourselves because we're "out" of self-control but rather that we choose not to control ourselves any longer.
At the same time, our attention shifts so that we're less likely to notice cues that signal the need for self-control (cake = empty calories) and we pay more attention to cues that signal some kind of reward (cake = delicious treat).
In laying out the basic components of this process model, Inzlicht and Schmeichel want to motivate researchers to ask critical questions about how self-control really works. "The idea that self-control is a resource is one possibility, but there are alternative possibilities that can accommodate more of the accumulated data," Inzlicht says.
Identifying the mechanisms that underlie self-control can help us to understand behaviors related to a wide range of important problems, including obesity, impulsive spending, gambling, and drug abuse. Inzlicht and Schmeichel hope that researchers will ultimately be able to use this knowledge to design effective methods for improving self-control.
###For more information about this study, please contact: Michael Inzlicht at michael.inzlicht@utoronto.ca.
Perspectives on Psychological Science is ranked among the top 10 general psychology journals for impact by the Institute for Scientific Information. It publishes an eclectic mix of thought-provoking articles on the latest important advances in psychology. For a copy of the article "What Is Ego Depletion? Toward a Mechanistic Revision of the Resource Model of Self-Control" and access to other Perspectives on Psychological Science research findings, please contact Anna Mikulak at 202-293-9300 or amikulak@psychologicalscience.org.
Self-control may not be a limited resource after all
2012-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How is grief unique to young adults with cancer?
2012-09-12
New Rochelle, NY, September 12, 2012—The life disruption and losses experienced by young adults battling advanced cancer can result in a unique burden of grief that is too often overlooked, as described in an article in Journal of Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology (JAYAO), (http://www.liebertpub.com/JAYAO) a multidisciplinary peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. (http://www.liebertpub.com) JAYAO is the Official Journal of the Society for Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology. The article is available free online at the JAYAO (http://www.liebertpub.com/JAYAO) ...
New clinical guidelines for managing hypothyroid disease presented in Thyroid Journal
2012-09-12
New Rochelle, NY, September 12, 2012—New evidence-based guidelines have been released for the diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism, a complex disease caused by an underactive thyroid gland that cannot produce enough thyroid hormone. These updated clinical recommendations are published in Thyroid (http://www.liebertpub.com/thy), a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers (http://www.liebertpub.com). The new guidelines (http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/pdfplus/10.1089/thy.2012.0205), developed jointly by the American Thyroid Association (ATA) (http://www.thyroid.org) ...
With food insecurity rising in US, SNAP benefits should be left alone
2012-09-12
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a time of record-high food insecurity rates in the U.S., cutting the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (the former Food Stamp Program) is the wrong approach to fighting hunger, says a University of Illinois economist who studies the efficacy of food assistance programs on public health.
Whether it's some Republicans who have proposed modifying funding, or some Democrats who have proposed restricting what kind of food beneficiaries are allowed to buy, restructuring SNAP would likely only lead to more food insecurity, says Craig Gundersen, a ...
Body heat, fermentation drive new drug-delivery 'micropump'
2012-09-12
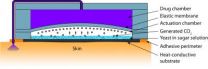
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have created a new type of miniature pump activated by body heat that could be used in drug-delivery patches powered by fermentation.
The micropump contains bakers yeast and sugar in a small chamber. When water is added and the patch is placed on the skin, the body heat and the added water causes the yeast and sugar to ferment, generating a small amount of carbon dioxide gas. The gas pushes against a membrane and has been shown to continually pump for several hours, said Babak Ziaie, a Purdue University professor of electrical and computer ...
Hearing impaired ears hear differently in noisy environments
2012-09-12
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - The world continues to be a noisy place, and Purdue University researchers have found that all that background chatter causes the ears of those with hearing impairments to work differently.
"When immersed in the noise, the neurons of the inner ear must work harder because they are spread too thin," said Kenneth S. Henry, a postdoctoral researcher in Purdue's Department of Speech, Language and Hearing Sciences. "It's comparable to turning on a dozen television screens and asking someone to focus on one program. The result can be fuzzy because these ...
Planets can form in the galactic center
2012-09-12
At first glance, the center of the Milky Way seems like a very inhospitable place to try to form a planet. Stars crowd each other as they whiz through space like cars on a rush-hour freeway. Supernova explosions blast out shock waves and bathe the region in intense radiation. Powerful gravitational forces from a supermassive black hole twist and warp the fabric of space itself.
Yet new research by astronomers at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics shows that planets still can form in this cosmic maelstrom. For proof, they point to the recent discovery of a ...
Improved nanoparticles deliver drugs into brain
2012-09-12
The brain is a notoriously difficult organ to treat, but Johns Hopkins researchers report they are one step closer to having a drug-delivery system flexible enough to overcome some key challenges posed by brain cancer and perhaps other maladies affecting that organ.
In a report published online on August 29 in Science Translational Medicine, the Johns Hopkins team says its bioengineers have designed nanoparticles that can safely and predictably infiltrate deep into the brain when tested in rodent and human tissue.
"We are pleased to have found a way to prevent drug-embedded ...
Newly discovered letters and translated German ode expand Texas link to infamous Bone Wars
2012-09-12
In the late 1800s, a flurry of fossil speculation across the American West escalated into a high-profile national feud called the Bone Wars.
Drawn into the spectacle were two scientists from the Lone Star State: geologist Robert T. Hill, now acclaimed as the Father of Texas Geology, and naturalist Jacob Boll, who made many of the state's earliest fossil discoveries.
Hill and Boll had supporting roles in the Bone Wars through their work for one of the feud's antagonists, Edward Drinker Cope. A new study by vertebrate paleontologist Louis L. Jacobs at Southern Methodist ...
Scripps Research scientists devise powerful new method for finding therapeutic antibodies
2012-09-12
LA JOLLA, CA, September 11, 2012 – Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute have found a new technique that should greatly speed the discovery of medically and scientifically useful antibodies, immune system proteins that detect and destroy invaders such as bacteria and viruses. New methods to discover antibodies are important because antibodies make up the fastest growing sector of human therapeutics; it is estimated that by 2014 the top-three selling drugs worldwide will be antibodies.
The new technique, described in an article this week published online ahead of ...
Ageism presents dilemmas for policymakers worldwide
2012-09-12
The negative consequences of age discrimination in many countries are more widespread than discrimination due to race or gender, yet differential treatment based on a person's age is often seen as more acceptable and even desirable, according to the newest edition of the Public Policy & Aging Report (PP&AR). This publication, which features cross-national perspectives, was jointly produced by The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) and AGE UK.
The PP&AR explores how discriminatory behaviors manifest themselves, steps that are being taken to address those behaviors, ...