(Press-News.org) The negative consequences of age discrimination in many countries are more widespread than discrimination due to race or gender, yet differential treatment based on a person's age is often seen as more acceptable and even desirable, according to the newest edition of the Public Policy & Aging Report (PP&AR). This publication, which features cross-national perspectives, was jointly produced by The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) and AGE UK.
The PP&AR explores how discriminatory behaviors manifest themselves, steps that are being taken to address those behaviors, and the challenges associated with asserting elders' individual rights while acknowledging vulnerabilities that are inevitably — although variably — associated with advanced chronological age.
Five separate articles illuminate the issues and options that face policymakers as they seek to eliminate negative discriminatory behaviors. Yet, the authors wrestle as well with how to identify and preserve age-biased provisions and practices that bring legitimate and needed benefits to older people. In particular, they ask if age discrimination is ever acceptable and whom might such discrimination advantage.
"We find that age-based discrimination raises a series of unique dilemmas for policymaking and service delivery," said GSA Executive Director James Appleby, RPh, MPH. "We're proud to partner with AGE UK to bring together the top minds from United States and the United Kingdom to address them."
Authors Dominic Abrahms, PhD, and Hannah J. Swift pint out that among the 28 countries assessed in the 2008-2009 European Social Survey, 24 percent of respondents reported that they had experienced prejudice because of their gender and 16 percent because of their race or ethnicity. However, 34 percent reported having experienced age prejudice in the last year, 37 percent said they had felt a lack of respect because of their age, and 28 percent said they had been treated badly because of their age. Overall, 46 percent of respondents said they had experienced at least one of these forms of age prejudice in the last year.
Tay K. McNamara, PhD, and John Williamson, PhD, provide data from the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, which show that the percentage of the charges filed with the commission attributable to age has increased steadily over the past 15 years. In 2011, for example, almost one in four claims was related to age discrimination. Yet these authors go on to identify examples of possible acceptable treatment of people of different ages, including mandatory retirement in certain occupations (e.g., firefighting and law enforcement), senior citizen discounts, age-restricted communities, more frequent testing of older drivers, and lower positioning of older people on organ transplant waiting lists.
The new PP&AR, "Cross-National Perspectives on Age Discrimination," is available for purchase at www.geron.org/bookstore. Reporters may request electronic review copies.
"This valuable research highlights that age discrimination is widespread on both sides of the Atlantic," said James Goodwin, PhD, the head of research at Age UK. "It explores some of the contradictions evident in both the UK and the USA — for example why older people continue to be portrayed as a burden to society, ignoring their economic contribution. We need to look beyond someone's age at their individual strengths and strive for a society where older people are active, in better health, and accepted as individuals who are important to a community and capable of contributing to the economics of the country as consumers and as producers."
###
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) is the nation's oldest and largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to research, education, and practice in the field of aging. The principal mission of the Society — and its 5,400+ members — is to advance the study of aging and disseminate information among scientists, decision makers, and the general public. GSA's structure also includes a policy institute, the National Academy on an Aging Society, and an educational branch, the Association for Gerontology in Higher Education.
END
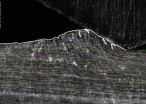
"We see phenomena normally associated with fluids, not solids," said Srinivasan Chandrasekar, a professor of industrial engineering at Purdue University, working with postdoctoral research associates Narayan Sundaram and Yang Guo.
Numerous mechanical parts, from bearings to engine pistons, undergo such sliding.
"It has been known that little pieces of metal peel off from sliding surfaces," Chandrasekar said. "The conventional view is that this requires many cycles of rubbing, but what we are saying is that when you have surface folding you don't need too many cycles for ...
NASA's Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel (HS3) airborne mission sent an unmanned Global Hawk aircraft this morning to study newborn Tropical Depression 14 in the central Atlantic Ocean that seems primed for further development. The Global Hawk left NASA's Wallops Flight Facility on Wallops Island, Va., this morning for a planned 26-hour flight to investigate the depression.
NASA's latest hurricane science field campaign began on Sept. 7 when the Global Hawk flew over Hurricane Leslie in the Atlantic Ocean. HS3 marks the first time NASA is flying Global Hawks from the ...
Western scrub jays summon others to screech over the body of a dead jay, according to new research from the University of California, Davis. The birds' cacophonous "funerals" can last for up to half an hour.
Anecdotal reports have suggested that other animals, including elephants, chimpanzees and birds in the crow family, react to dead of their species, said Teresa Iglesias, the UC Davis graduate student who carried out the work. But few experimental studies have explored this behavior.
The new research by Iglesias and her colleagues appears in the Aug. 27 issue of ...
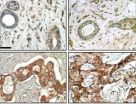
A gene that may possibly belong to an entire new family of oncogenes has been linked by researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) to the resistance of breast cancer to a well-regarded and widely used cancer therapy.
One of the world's leading breast cancer researchers, Mina Bissell, Distinguished Scientist with Berkeley Lab's Life Sciences Division, led a study in which a protein known as FAM83A was linked to resistance to the cancer drugs known as EGFR-TKIs (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase ...
Freezing positions and cutting workforces
Trimming pension and health care costs and passing them to employees
Lowering service delivery levels, but not imposing many new fees
Using technology to reduce costs where possible
Receiving added pressure but little help from States and the Federal Government
This important new research sheds light on the challenges faced by city and county governments that must provide most basic services. Unlike federal or state governments, these local governments have limited ability to generate revenue and are often mandated to pay for ...
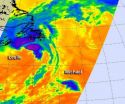
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the Atlantic on Sept. 11 it caught Tropical Storm Leslie's clouds over Newfoundland and peanut-shaped Tropical Storm Michael to its southwest. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured infrared data on Tropical Storms Leslie and Michael when it passed overhead on Sept. 11.
Michael Appears Peanut-Shaped on Satellite Imagery
Tropical Storm Michael forecast to become a remnant low later today, Sept. 11, but as of 11 a.m. EDT Michael still had maximum sustained winds near 45 mph (75 kmh). It was located about 1,090 ...
A couple of years ago, Hesham Rakha misjudged a yellow traffic light and entered an intersection just as the light turned red. A police officer handed him a ticket.
"There are circumstances, as you approach a yellow light, where the decision is easy. If you are close to the intersection, you keep going. If you are far away, you stop. If you are almost at the intersection, you have to keep going because if you try to stop, you could cause a rear-end crash with the vehicle behind you and would be in the middle of the intersection anyway," said Rakha, professor of civil ...
Researchers from Sainte-Justine University Hospital Center and University of Montreal have identified several novel genes that make some children more efficient than others in the way their immune system responds to malaria infection. This world-first in integrative efforts to track down genes predisposing to specific immune responses to malaria and ultimately to identify the most suitable targets for vaccines or treatments was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by lead author Dr. Youssef Idaghdour and senior author Pr. Philip Awadalla, whose ...
The ageing process has its roots deep within the cells and molecules that make up our bodies. Experts have previously identified the molecular pathway that react to cell damage and stems the cell's ability to divide, known as cell senescence.
However, in cells that do not have this ability to divide, such as neurons in the brain and elsewhere, little was understood of the ageing process. Now a team of scientists at Newcastle University, led by Professor Thomas von Zglinicki have shown that these cells follow the same pathway.
This challenges previous assumptions ...
Philadelphia, PA, September 12, 2012 – Post-stroke depression is a major issue affecting approximately 33% of stroke survivors. A new study published in the current issue of Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation reports that the level to which survivors are uncertain about the outcome of their illness is strongly linked to depression. The relationship is more pronounced for men than for women.
"Male stroke survivors in the US who subscribe to traditional health-related beliefs may be accustomed to, and value highly, being in control of their health," says ...