Study shows breath analysis could help diagnose pulmonary nodules
In pilot study, authors recommend using larger cohort to validate results
2012-09-15
(Press-News.org) DENVER – A pilot study, published in the October 2012 issue of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer's (IASLC) Journal of Thoracic Oncology, showed that breath testing could be used to discriminate between benign and malignant pulmonary nodules. The study looked at 74 patients who were under investigation for pulmonary nodules and attended a referral clinic in Colorado between March 2009 and May 2010.
Researchers from Israel and Colorado collected exhaled breath from each patient, analyzing the exhaled volatile organic compounds using gas chromatography with mass spectrometry and information from chemical nanoarrays, which have been developed by Prof. Hossam Haick and his colleagues in the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology. The patients also underwent a bronchoscopy, wedge resection and/or lobectomy, whichever was required for final diagnosis. Nodules that either regressed or remained stable over a 24-month period were considered benign.
The two techniques accurately identified that 53 pulmonary nodules were malignant and 19 were benign. Furthermore, the nanoarrays method discriminated between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma and between early versus advanced disease.
This kind of testing could help solve some of the problems computed tomography screening has created. While low-dose CT screening has reduced the mortality rate by 20 percent, many people have to undergo invasive procedures only to find out their pulmonary nodules are not cancerous. The false positive rate is 96 percent. This testing could serve as a secondary screener for patients who were found to have pulmonary nodules after CT screening.
Authors say, "the reported breath test in this study could have significant impact on reducing unnecessary inves¬tigation and reducing the risk of procedure-related morbid¬ity and costs. In addition, it could facilitate faster therapeutic intervention, replacing time-consuming clinical follow-up that would eventually lead to the same intervention."
### The leading authors of this work include Dr. Nir Peled, Meggie Hakim and IASLC member Dr. Hossam Haick. Co-authors include AISCL members Dr. Paul Bunn, Dr. York Miller, Dr. Fred Hirsch, Dr. Timothy Kennedy and Dr. John Mitchell.
About the IASLC:
The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) is the only global organization dedicated to the study of lung cancer. Founded in 1974, the association's membership includes more than 3,500 lung cancer specialists in 80 countries. To learn more about IASLC please visit www.iaslc.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-09-15
Family members who care for terminally ill patients at home can be helped by nurses throughout the course of the illness and particularly after the patient's death, according to Penn State nursing researchers.
The death of a loved one can be particularly hard for those who were involved in the day-to-day care of the person. This transition can be eased by existing support from nurses and other medical professionals.
"What we know is that the caregiver's primary contact with the health care system is during brief office visits [for the patient]," said Janice L. Penrod, ...
2012-09-15
Children of immigrants are outperforming children whose family trees have deeper roots in the United States, learning more in school and then making smoother transitions into adulthood, according to sociologists at The Johns Hopkins University.
Researchers Lingxin Hao and Han S. Woo tracked nearly 11,000 children from as young as age 13 into their early 30s, coming from families with diverse backgrounds. When comparing children with similar socioeconomic status and school conditions, Hao and Woo found that the best students, and later the most successful young adults, ...
2012-09-15
Habituation refers to the ability of an organism to stop responding to repeated stimulation.
A new study has examined the impact of maternal drinking on fetal habituation or learning abilities while still residing in the mother's womb.
Results showed that those fetuses exposed to heavy binge drinking required significantly more trials to habituate, and also exhibited a greater variability in test performance.
While it has become clear that drinking during pregnancy can damage the fetal central nervous system, these outcomes can also be influenced by factors such ...
2012-09-15
Contact: Peter Malik, M.D.
peter.malik@i-med.ac.at
43.512.504.81629 (Austria)
Medical University Innsbruck
Add'l contact: Sergei Mechtcheriakov, M.D.
s.mechtcheriakov@i-med.ac.at
43.512.504.23636 (Austria)
Medical University Innsbruck
Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research
Abstinence from alcohol plus physical exercise can help reclaim bone loss due to alcoholism
Abstinence from alcohol plus physical exercise can help reclaim bone loss due to alcoholism
Alcoholism is known to cause osteoporosis, or reduced bone mineral density (BMD).
New ...
2012-09-15
Contact: Kenneth S. Kendler, M.D.
kendler@vcu.edu
804.828.8590
Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine
Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research
Symptoms of alcohol abuse, not dependence, may better reflect family risk for alcohol use disorders
Symptoms of alcohol abuse, not dependence, may better reflect family risk for alcohol use disorders
Individuals with alcohol use disorders (AUDs) vary widely in their age of onset of use, patterns of drinking, and symptom profiles. AUDs are often 'divided' into two categories: alcohol abuse (AA) and ...
2012-09-15
(Edmonton) The thud of a bird hitting a window is something many Canadian home owners experience. Up until now, little research has been done to document the significant these collisions for Canada's bird populations. A University of Alberta biology class project supervised by researcher Erin Bayne suggests that many birds meet their end in run-ins with Canadian homes.
The U of A students estimate a staggering 22 million birds a year die from colliding with windows of homes across the country.
The research was done in Edmonton and surrounding area using evidence gathered ...
2012-09-15
EUGENE, Ore. -- Despite the disruptions they cause, large wildfires are a mixed economic bag for nearby communities, according to findings from a research project by the University of Oregon's Ecosystem Workforce Program and its collaborators.
Wildfires disrupt the lives of workers, employers and families, and lead to longer-term instability in local labor markets, the project funded by Joint Fire Science Program found. But on the flip side of the coin, countywide employment and wages increase in some sectors during the wildfires, often mitigating the short-term employment ...
2012-09-15
Work stress, job satisfaction and health problems due to high stress have more to do with genes than you might think, according to research by Timothy Judge, professor of management at the University of Notre Dame's Mendoza College of Business.
The lead author of "Genetic influences on core self-evaluations, job satisfaction, work stress, and employee health: A behavioral genetics mediated model," published in Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, Judge studied nearly 600 twins – some identical, some fraternal – who were raised together and reared apart. ...
2012-09-15
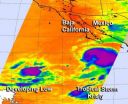
The Eastern Pacific Ocean has become "tropically" alive on NASA satellite data today, Sept. 14. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of weakening Tropical Storm Kristy and another low pressure area that is developing and has the potential to become a new tropical depression.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the eastern Pacific Ocean on Sept. 14 at 5:23 a.m. ED, and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of Kristy and a new developing low pressure area. The infrared data indicated the strongest thunderstorms and heaviest rainfall ...
2012-09-15
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Biomedical scientists collaborating on translational research at two Buffalo institutions are reporting the discovery of a novel, and heretofore unrecognized, set of genes essential for the growth of potentially lethal, drug-resistant bacteria. The study not only reveals multiple, new drug targets for this human infection, it also suggests that the typical methods of studying bacteria in rich laboratory media may not be the best way to identify much-needed antimicrobial drug targets.
The paper (http://mbio.asm.org/content/3/4/e00113-12) focuses on a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study shows breath analysis could help diagnose pulmonary nodules
In pilot study, authors recommend using larger cohort to validate results