(Press-News.org) TORONTO, Sept. 17, 2012—Whether your neighbourhood is conducive to walking could determine your risk for developing diabetes, according to a new study by researchers at St. Michael's Hospital and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences.
Researchers found this risk was particularly high for new immigrants living in low-income neighbourhoods. A new immigrant living in a less walkable neighbourhood – fewer destinations within a 10-minute walk, lower residential density, poorly connected streets – was about 50 per cent more likely to develop diabetes when compared to long-term residents living in the most walkable areas, regardless of neighbourhood income.
"Although diabetes can be prevented through physical activity, healthy eating and weight loss, we found the environment in which one lives is also an important indicator for determining risk," said Dr. Gillian Booth, an endocrinologist and researcher at St. Michael's and lead author of the study published online in the journal Diabetes Care today.
For new immigrants, environment is an especially important factor as past research has shown an accelerated risk of obesity-related conditions including diabetes within the first 10 years of arrival to Canada, said Dr. Booth, who is also an adjunct scientist at ICES.
While diabetes is on the rise in Canada, the same trends are occurring globally, even in less industrialized countries. This is due in part to the move from rural to urban living in developing countries – often associated with increased exposure to unhealthy foods, fewer opportunities for physical activity and a heightened risk of becoming obese and developing diabetes.
The study looked at data from the entire population of Toronto aged 30-64 – more than 1 million people – and identified those who didn't have diabetes. It then followed them for five years to see if their risk of developing diabetes increased based on where they live.
To determine which neighbourhoods were more conducive to walking, researchers developed an index looking at factors such as population density, street connectivity and the availability of walkable destinations such as retail stores and service within a 10-minute walk.
Dr. Booth said neighbourhoods that were the least walkable were often newly developed areas – characterized by urban sprawl – in part because of the reliance on cars caused by suburban design.
"Previous studies have looked at how walkable neighbourhoods affect health behaviour, but this is the first to look at the risk of developing a disease," said Dr. Booth.
Dr. Booth said the results emphasize the importance of neighbourhood design in influencing the health of urban populations.
INFORMATION:
About St. Michael's Hospital
St. Michael's Hospital provides compassionate care to all who enter its doors. The hospital also provides outstanding medical education to future health care professionals in more than 23 academic disciplines. Critical care and trauma, heart disease, neurosurgery, diabetes, cancer care, and care of the homeless are among the Hospital's recognized areas of expertise. Through the Keenan Research Centre and the Li Ka Shing International Healthcare Education Center, which make up the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, research and education at St. Michael's Hospital are recognized and make an impact around the world. Founded in 1892, the hospital is fully affiliated with the University of Toronto.
For more information, or to speak to Dr. Booth, please contact:
Kate Taylor
Communications Adviser
St. Michael's Hospital
Phone: 416-864-6060 x. 6537
TaylorKa@smh.ca
Inspired Care. Inspiring Science
www.stmichaelshospital.com
END
The NFL season is off and running and with it comes the proverbial hamstring injury, the torn tendon, the groin strain – injuries that players have come to expect as part of this high-energy contact sport. Far less top of mind is the rare but catastrophic cervical spine injury, but that's exactly the injury that Mercyhurst University researchers are working with Sports Medicine Concepts and the National Football League (NFL) to mitigate.
One tragic example came Sept. 8 when Tulane University safety Devon Walker fractured his spine in a head-on collision with a teammate ...
A new study that identifies ways to reduce the factors that lead to an asthma attack gives hope to asthma sufferers. A UCSF researcher and his colleagues believe they have found a way to help asthma sufferers by impeding the two most significant biological responses that lead to an asthma attack.
Asthma, a respiratory disorder that causes shortness of breath, coughing and chest discomfort, results from changes in the airways that lead to the lungs. It affects 18.7 million adults and 7.0 million children in the US, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. — The discovery of a new gene could lead to better bug-resistant plants.
Research led by Michigan State University and appearing on the cover of this week's Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, demonstrates that domestic tomatoes could re-learn a thing or two from their wild cousins.
Long-term cultivation has led to tomato crops losing beneficial traits common to wild tomatoes. Anthony Schilmiller, MSU research assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology, was able to identify a gene that is involved in one of these beneficial ...
When Kayla Dehnert tells friends and family in Northern California about life as a St. Jude Children's Research Hospital patient, she pulls out a string of beads taller than she is.
"This is a learning-to-take medicine bead," Kayla explains, fingering the bumps of a bluish-lavender bead and working her way down the long strand. "This yellow bead is the change-the-bandage bead, and the tiger bead is the losing-your-hair bead."
Kayla, 8, of Novato, Calif., is one of hundreds of St. Jude patients who have participated in the hospital's Legacy Bead program since its launch ...
DURHAM, N.C.— By studying how birds master songs used in courtship, scientists at Duke University have found that regions of the brain involved in planning and controlling complex vocal sequences may also be necessary for memorizing sounds that serve as models for vocal imitation.
In a paper appearing in the September 2012 issue of the journal Nature Neuroscience, researchers at Duke and Harvard universities observed the imitative vocal learning habits of male zebra finches to pinpoint which circuits in the birds' brains are necessary for learning their songs.
Knowing ...
NASA's Hurricane Severe Storms Sentinel (HS3) Mission is in full-swing and one of the unmanned Global Hawk aircraft investigate Tropical Storm Nadine on Sept. 14 and 15, while NASA satellites continued to obtain imagery of the storm as seen from space.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a true-color image of Hurricane Nadine in the Atlantic Ocean on Sept. 16 at 1345 UTC (9:45 a.m. EDT) while NASA's Global Hawk was flying around the storm. Nadine strengthened to a hurricane on Friday, Sept. 14 at 11 p.m. EDT, and weakened ...
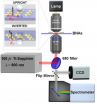
Using ultra-low input power densities, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated for the first time how low-power "optical nanotweezers" can be used to trap, manipulate, and probe nanoparticles, including fragile biological samples.
"We already know that plasmonic nanoantennas enhance local fields by up to several orders of magnitude, and thus, previously showed that we can use these structures with a regular CW laser source to make very good optical tweezers," explains, Kimani Toussaint, Jr., assistant professor of mechanical science ...
Typhoon Sanba made landfall in southern South Korea on Monday, Sept. 17 and was moving northeast bringing heavy rainfall, and gusty winds along its path. Sanba downed trees, and caused power outages, canceled flights and canceled ferries. NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Sanba on Sept. 17 after it made landfall and observed the large extent of its cloud cover from South Korea to eastern Siberia.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Sanba on Sept. 17 at 0430 UTC (12:30 a.m. EDT/1:30 p.m. local time Seoul, South Korea) and the Moderate Resolution ...
NEW YORK (Sept. 17, 2012) -- The power of taxane-based chemotherapy drugs are misunderstood and potentially underestimated, according to researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College in the September 15 issue of the journal Cancer Research.
Most physicians and investigators believe that taxane chemotherapy (paclitaxel, docetaxel and cabazitaxel) just does one thing -- stop a cancer cell from dividing -- but the team of Weill Cornell scientists have revealed it acts much more powerfully and broadly, especially against prostate cancer.
"Taxanes are one of the best class ...
While Tropical Storm Kristy faded into a remnant low pressure area, Lane strengthened into a hurricane. NASA's Terra satellite caught a look at both storms when it passed overhead on Sept. 16 and showed a much tighter circulation within Hurricane Lane than in weakening Tropical Storm Kristy.
When NASA's Terra satellite passed over the Eastern Pacific on Sept. 16 at 18:45 UTC (2:45 p.m. EDT) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument aboard the satellite captured Tropical Storm Kristy (at the time a tropical storm) and Hurricane Lane, located to Kristy's ...