(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have found that recovery from an emerging, minimally invasive surgical technique called Laparo-Endoscopic Single-Site Surgery (LESS) was less painful for kidney cancer patients than traditional laparoscopic surgery. Study results were published in the September online edition of Urology.
"In the largest prospective study of kidney cancer patients to date, the UC San Diego study showed less use of narcotic pain medication and lower pain scores upon hospital discharge," said Ithaar Derweesh, MD, senior author and urologic oncologist at UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center. "For patients and surgeons, this research shows that reducing the number of incisions to one confers benefits beyond fewer scars."
Led by Derweesh, the study compared single-site laparoscopy, also known as LESS, and traditional multiport laparoscopy in a total of 74 patients needing either complete or partial removal of the kidney for malignancy. LESS was performed with one small incision in the umbilicus through which all tools were inserted to reach the tumor. The patients undergoing traditional laparoscopy underwent four to six incisions.
After surgery, surgeons used the visual analog pain (VAP) test to establish a patient's comfort level. The test is composed of simple line drawings of the human face. One end of the scale shows a smile and "no hurt," the opposite end expresses tears and "hurts worst."
"We found that patients rated the LESS surgery as 40 percent less painful than traditional laparoscopic surgery, while requiring approximately 50 percent less narcotic pain medication," said Derweesh. "This is an excellent sign that the LESS technique may further improve the quality of life of appropriate patients undergoing major cancer surgery."
The incidence of renal cell carcinoma is increasing worldwide. In the United States, kidney cancer is the most lethal of the commonly diagnosed urologic malignancies, diagnosed in more than 64,000 Americans every year. According to the American Cancer Society, kidney cancer is increasing at a rate of two to three percent each year in the U.S.
INFORMATION:
Additional contributors to this paper include Wassim M. Bazzi, Sean P. Stroup, Ryan P. Kopp, Seth A. Cohen, and Kyoko Sakamoto from the UC San Diego School of Medicine.
Single-site laparoscopic surgery reduces pain of tumor removal
2012-09-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cyborg surgeon: Hand and technology combine in new surgical tool that enables superhuman precision
2012-09-27
VIDEO:
This video shows how the SMART surgical tool is able to “hold still” by responding to unexpected movement from a surgical target (in this case, a chicken embryo). In the...
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON, Sept. 27, 2012—Even the most skilled and steady surgeons experience minute, almost imperceptible hand tremors when performing delicate tasks. Normally, these tiny motions are inconsequential, but for doctors specializing in fine-scale surgery, such as ...
Learning to overcome fear is difficult for teens
2012-09-27
NEW YORK (Sept. 27, 2012) -- A new study by Weill Cornell Medical College researchers shows that adolescents' reactions to threat remain high even when the danger is no longer present. According to researchers, once a teenager's brain is triggered by a threat, the ability to suppress an emotional response to the threat is diminished which may explain the peak in anxiety and stress-related disorders during this developmental period.
The study, published Sept. 17 in the early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), is the first to decode ...
Experts call on Congress to create first US Weather Commission
2012-09-27
WASHINGTON, D.C. — With the U.S. economy vulnerable to weather events costing billions of dollars, an expert panel today asked Congress to create the first U.S. Weather Commission. The commission would provide guidance to policymakers on leveraging weather expertise across government and the private sector to better protect lives and businesses.
"The nation must focus its weather resources on the areas of greatest need in order to keep our economy competitive and provide maximum protection of lives and property," says Thomas Bogdan, president of the University Corporation ...
Big quake was part of crustal plate breakup
2012-09-27
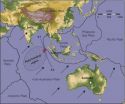
SALT LAKE CITY Sept. 26, 2012 – Seismologists have known for years that the Indo-Australian plate of Earth's crust is slowly breaking apart, but they saw it in action last April when at least four faults broke in a magnitude-8.7 earthquake that may be the largest of its type ever recorded.
The great Indian Ocean quake of April 11, 2012 previously was reported as 8.6 magnitude, and the new estimate means the quake was 40 percent larger than had been believed, scientists from the University of Utah and University of California, Santa Cruz, report in the Sept. 27 issue of ...
Study reveals complex rupture process in surprising 2012 Sumatra quake
2012-09-27
SANTA CRUZ, CA--The massive earthquake that struck under the Indian Ocean southwest of Sumatra on April 11, 2012, came as a surprise to seismologists and left them scrambling to figure out exactly what had happened. Analysis of the seismic waves generated during the event has now revealed a complicated faulting process unlike anything seen before.
"Nobody was anticipating an earthquake of this size and type, and the complexity of the faulting surprised everybody I've spoken to about this," said Thorne Lay, professor of Earth and planetary sciences at the University of ...
Men on the mind: Study finds male DNA in women's brains
2012-09-27
SEATTLE – Male DNA is commonly found in the brains of women, most likely derived from prior pregnancy with a male fetus, according to first-of-its-kind research conducted at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. While the medical implications of male DNA and male cells in the brain are unknown, studies of other kinds of microchimerism – the harboring of genetic material and cells that were exchanged between fetus and mother during pregnancy – have linked the phenomenon to autoimmune diseases and cancer, sometimes for better and other times for worse.
The study findings ...
Pregnancy generates maternal immune-suppressive cells that protect the fetus
2012-09-27
A new study published online in the journal Nature suggests it might be possible to develop vaccines to prevent premature birth and other pregnancy complications. If so, such vaccines would be the first intended to stimulate the subset of regulatory CD4 T cells that suppress the immune response.
Current vaccines are specifically designed to stimulate T cell subsets that activate the immune response.
The study, led by a researcher at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, shows the immune system of a pregnant mother stimulates cells that selectively prevent ...
Researchers define 2 categories of multiple sclerosis patients
2012-09-27
BOSTON, MA—There are approximately 400,000 people in the United States with multiple sclerosis. Worldwide, the number jumps to more than 2.1 million people. Rather than a one-size-fits-all approach to treating the millions with multiple sclerosis, what if doctors could categorize patients to create more personalized treatments? A new study by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) may one day make this idea a reality in the fight against the debilitating autoimmune disease.
A research team led by Philip De Jager, MD, PhD, BWH Department of Neurology, senior ...
Touch-sensitive tentacles catapult prey into carnivorous plant traps
2012-09-27
Swift predators are common in the animal world but are rare in the plant kingdom. New research shows that Drosera glanduligera, a small sundew from southern Australia, deploys one of the fastest and most spectacular trapping mechanisms known among carnivorous plants.
The study, published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE, is a collaboration between the Plant Biomechanics Group at the University of Freiburg and private sundew cultivators from Weil am Rhein, and provides the first experimental demonstration of fast-moving snap tentacles in sundew plants propelling ...
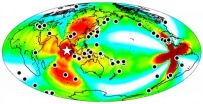
Large 2012 earthquake triggered temblors worldwide for nearly a week
2012-09-27
This year's largest earthquake, a magnitude 8.6 temblor on April 11 centered in the East Indian Ocean off Sumatra, did little damage, but it triggered quakes around the world for at least a week, according to a new analysis by seismologists from the University of California, Berkeley, and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS).
The April 11 quake was unusually large – the tenth largest in the last 100 years and, similar to a few other recent large quakes, triggered small quakes during the three hours it took for seismic waves to travel through Earth's crust.
The new study ...