(Press-News.org) Bethesda, MD—President Obama's national plan to fight Alzheimer's disease just got a lift thanks to a team of international researchers whose recent discovery may lead to enhanced imaging of and improved drug delivery to the brain. A research report appearing in The FASEB Journal, describes an entirely new class of antibody discovered in camelids (camels, dromedaries, llamas, and alpacas) that is able to cross the blood-brain barrier, diffuse into brain tissue, and reach specific targets. Having such antibodies, which are naturally available, may be part of a "game changer" in the outcomes for people with brain diseases that are poorly diagnosed and treated, at best, using today's tools.
"This basic biological investigation opens new pathways toward innovative therapeutic solutions for intractable diseases such as Alzheimer's disease or brain tumors," said Pierre Lafaye, Ph.D., a researcher involved in the work from the Institut Pasteur, PF: Production de Protéines Recombinantes et d'Anticorps –Proteopole in Paris, France. "The importance of this study is the hope that this novel approach may be a useful tool in crossing the blood brain barrier for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes," added Babbette Weksler, MD, Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, another author of the study and editorial board member of The FASEB Journal.
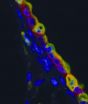
Lafaye and colleagues studied alpacas, a member of the camelid family, and discovered an antibody naturally able to cross the blood brain barrier without chemical modification. Then, additional research showed that after these antibodies entered the brain successfully, they diffused into the brain tissue to reach a target, which in this study was astrocytes. This study shows, for the first time, an antibody penetrated into the brain in vivo, under normal physiological conditions. In addition to the obvious clinical applications of this finding, it opens the doors to new research involving the body's systems for recognizing self v. "nonself."
"Camels may be most famous for helping people travel to the outermost reaches of the desert, but soon they could be also known for helping us reach the innermost parts of our brains," said Gerald Weissmann, M.D., Editor-in-Chief of The FASEB Journal. "It appears that these prized animals are far more capable of helping get to hard-to-reach places than we ever could have imagined."
###
Receive monthly highlights from The FASEB Journal by e-mail. Sign up at http://www.faseb.org/fjupdate.aspx. The FASEB Journal is published by the Federation of the American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB) and is the most cited biology journal worldwide according to the Institute for Scientific Information. In 2010, the journal was recognized by the Special Libraries Association as one of the top 100 most influential biomedical journals of the past century. FASEB is composed of 26 societies with more than 100,000 members, making it the largest coalition of biomedical research associations in the United States. Celebrating 100 Years of Advancing the Life Sciences in 2012, FASEB is rededicating its efforts to advance health and well-being by promoting progress and education in biological and biomedical sciences through service to our member societies and collaborative advocacy.
Tengfei Li, Jean-Pierre Bourgeois, Susanna Celli, Fabienne Glacial, Anne-Marie Le Sourd, Salah Mecheri, Babette Weksler, Ignacio Romero, Pierre-Olivier Couraud, François Rougeon, and Pierre Lafaye. Cell-penetrating anti-GFAP VHH and corresponding fluorescent fusion protein VHH-GFP spontaneously cross the blood-brain barrier and specifically recognize astrocytes: application to brain imaging. FASEB J October 2012, 26:3969-3979; doi:10.1096/fj.11-201384 ; http://www.fasebj.org/content/26/10/3969.abstract
Camels give President Obama's Alzheimer's plan a lift
New research in The FASEB Journal suggests that serum from animals such as camels, llamas, and alpacas could enhance brain imaging and help drugs pass through the blood-brain barrier
2012-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Therapeutic time window important factor for cord blood cell transplantation after stoke
2012-10-01
Putnam Valley, NY. (Oct. 1, 2012) – A research team from Germany has found that optimal benefit and functional improvement for ischemic stroke results when human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells (hUCB MNCs) are transplanted into rat stroke models within 72 hours of the stroke.
Their study is published in the current issue of Cell Transplantation (21:6), now freely available on-line at: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/.
"Ischemic stroke is one of the most frequent causes of death and the most common reason for permanent disabilities in adults in ...
MRI images transplanted islet cells with help of positively charged nanoparticles
2012-10-01
Tampa, Fla. (Oct. 1, 2012) – In a study to investigate the detection by MRI of six kinds of positively-charged magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles designed to help monitor transplanted islet cells, a team of Japanese researchers found that the charged nanoparticles they developed transduced into cells and could be visualized by MRI while three kinds of commercially available nanoparticles used for controls could not.
The study is published in a recent special issue of Cell Medicine [3(1)], now freely available on-line at: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/cm.
"Our ...
Low birth weight may increase risk for cardiovascular disease, kidney disease and diabetes
2012-10-01
Bethesda, MD— Being underweight at birth may have consequences above and beyond the known short-term effects says a research report published in the October 2012 issue of The FASEB Journal. The report shows that rats with a low birth weight have an increased long-term risk for developing cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and diabetes. What's more, older females are at higher risk of developing high blood pressure before and during pregnancy, which in turn, may restrict growth in the womb, putting offspring at risk for being born at a low birth weight.
"Ensuring ...
Biological markers increase clinical trial success rate of new breast cancer drugs
2012-10-01
Using biological markers--genetic characteristics that are associated with some patients with breast cancer--can increase the success rate of clinical trials for breast cancer drugs by almost 50 per cent, says new research from the University of Toronto Mississauga.
"It's been increasingly difficult for pharmaceutical companies to bring new drugs to market," says Jayson Parker, a faculty member in the Department of Biology and medical biotechnology analyst at the University of Toronto. "On average, about 80 per cent of drugs fail at some point in the clinical trial process."
There ...
Genetically engineered immune system fights melanoma
2012-10-01
MAYWOOD, Il. - Loyola University Medical Center has launched the first clinical trial in the Midwest of an experimental melanoma treatment that genetically engineers a patient's immune system to fight the deadly cancer.
A batch of the immune system's killer T cells will be removed from the patient and genetically modified in a Loyola lab. Two genes will be inserted into the T cells so that they will recognize tumor cells as abnormal.
The patient will undergo high-dose chemotherapy to kill most of his or her remaining T cells. This will make room for the genetically modified ...
AGU journal highlights -- 1 October 2012
2012-10-01
The following highlights summarize research papers that have been recently
published in Geophysical Research Letters (GRL), Journal of Geophysical
Research - Solid Earth (JGR-B), Journal of Geophysical Research - Oceans
(JGR-C), and Water Resources Research (WRR).
In this release:
1. The pros and cons of trading water: A case study in Australia
2. Linking typhoon tracks with rainfall patterns and flood timing
3. Novel observations of currents and drag generated by a tsunami
4. More water stored along major rivers during El Nino years
5. Model suggests Earth ...
New insights on control of pituitary hormone outside of brain has implications for breast cancer
2012-10-01
PHILADELPHIA - The hormone prolactin is produced by the pituitary gland in the brain and then travels via the bloodstream to cells throughout the body, where it exerts multiple reproductive and metabolic effects, most notably on the breast where it is the master regulator of lactation. In recent years researchers have found that prolactin is also produced by some tissues outside the brain, however little is known about the functions of extra-pituitary prolactin or how its production is regulated in these tissues.
Now, the laboratory of Lewis A. Chodosh, MD, PhD, chair ...
Fish getting smaller as the oceans warm: UBC research
2012-10-01
Changes in ocean and climate systems could lead to smaller fish, according to a new study led by fisheries scientists at the University of British Columbia.
The study, published today in the journal Nature Climate Change, provides the first-ever global projection of the potential reduction in the maximum size of fish in a warmer and less-oxygenated ocean.
The researchers used computer modeling to study more than 600 species of fish from oceans around the world and found that the maximum body weight they can reach could decline by 14-20 per cent between years 2000 and ...
Researchers discover key mechanism for controlling the body's inflammatory response
2012-10-01
Researchers at Queen Mary, University of London have discovered how a key molecule controls the body's inflammatory responses. The molecule, known as p110delta, fine-tunes inflammation to avoid excessive reactions that can damage the organism. The findings, published in Nature Immunology today (30 September), could be exploited in vaccine development and new cancer therapies.
A healthy immune system reacts to danger signals – from microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses, or from the body's own rogue cells, such as cancer cells. This tightly controlled reaction starts ...
Researchers discover gene that causes deafness
2012-10-01
CINCINNATI—Researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have found a new genetic mutation responsible for deafness and hearing loss associated with Usher syndrome type 1.
These findings, published in the Sept. 30 advance online edition of the journal Nature Genetics, could help researchers develop new therapeutic targets for those at risk for this syndrome.
Partners in the study included the National Institute on Deafness and other Communication Disorders (NIDCD), Baylor College of Medicine and the University of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Camels give President Obama's Alzheimer's plan a liftNew research in The FASEB Journal suggests that serum from animals such as camels, llamas, and alpacas could enhance brain imaging and help drugs pass through the blood-brain barrier