Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, October 2012
2012-10-05
(Press-News.org) ELECTRICITY-- Spotlight on outages . . .
When a storm knocks out power, among the first questions to be answered are how many people are affected and when electricity will be restored. Oak Ridge National Laboratory's Energy Awareness and Resiliency Standardized Services application, or EARSS, uses publicly available data and can help by showing grid status in real time. The goal is to enhance situational awareness for the emergency response community, according to EARSS co-developer Steve Fernandez of ORNL's Computational Sciences and Engineering Division. "Working from up-to-date information, responders on the ground can preposition emergency generators and supplies where they are needed most," said Fernandez, who also wrote an algorithm that predicts regionally when power will be restored. [Contact: Ron Walli, (865) 576-0226; wallira@ornl.gov]
AUTOMOTIVE -- Calculate your trip . . .
Fueleconomy.gov's new "My Trip Calculator" is an interactive trip calculator and mapping tool that helps travelers plan a route, pick a car and estimate fuel cost for the trip. My Trip Calculator prompts users to enter a start and destination address, set the city driving percentage and select up to three cars for comparison. Based on the traveler's input, My Trip Calculator displays the EPA fuel economy estimate ("MPG"), the national average fuel cost ("Fuel Price"), the amount of fuel used ("Fuel Used (gal)") and the cost of fuel used ("Fuel Cost") for each car. The website, a collaboration between the Environmental Protection Agency and the Department of Energy, updates the national average fuel cost each week. Because it's based on a mapping tool, My Trip Calculator provides estimated miles and driving time for your trip, turn-by-turn driving directions and a trip map. [Contact: Bill Cabage, (865) 574-4399; cabagewh@ornl.gov]
INSTRUMENTATION -- Focus on perfection . . .
Through a cooperative research and development agreement, Hinds Instruments and Oak Ridge National Laboratory are refining a microscope that can play a role in the success of next-generation nuclear reactors. The 2-MGEM microscope, which won an R&D 100 Award in 2008, delivers unsurpassed performance for characterization and quality control of the coated particle fuel, TRISCO. This fuel, which consists of small kernels of nuclear material sealed with multiple layers of carbon and silicon carbide, will be used in Generation IV very high temperature reactors. The goal is to further refine the microscope to expand the user interface, increase processing speed, replace obsolete third-party components and introduce remote field service capability. With the 2-MGEM microscope, developed by ORNL's Jay Jellison and John Hunn, researchers hope to optimize the microstructure of the carbon layers of the coated particle fuel. [Contact: Ron Walli, (865) 576-0226; wallira@ornl.gov]
LIGHTING -- Next-generation source . . .
A team from the University of California at Santa Barbara has used NOMAD, the new Nanoscale-Ordered Materials Diffractometer at the Spallation Neutron Source at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, to study the potential of a green-yellow emitting oxyfluoride solid solution phosphor for high-quality solid-state lighting. Solid-state white lighting offers many advantages over traditional lighting, including longer life, reduced energy consumption and an environmentally friendly design without the need for mercury. Researchers used a combination of density functional theory, synchrotron X-ray and neutron powder diffraction and total scattering, and electron paramagnetic resonance to discover that chemical substitutions play a crucial role in tuning the optical properties of the newly developed phosphor. [Contact: Agatha Bardoel, (865) 574-0644; bardoelaa@ornl.gov]
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-10-05
RICHMOND, Va. (Oct. 4, 2012) – A new study reveals that a significant amount of carbon released into the atmosphere from lakes and rivers in Southern Québec, Canada, is very old – approximately 1,000 to 3,000 years old – challenging the current models of long-term carbon storage in lakes and rivers.
Previous studies have suggested that there is a tight coupling between the terrestrial and aquatic environment such that aquatic bacteria rapidly consume modern carbon. The new findings of the respiration of old carbon in aquatic systems suggests there may be significant lags ...
2012-10-05
New Haven, Conn.—Dramatic shifts in the planet's climate and geography over millions of years changed the course of evolutionary history for conifer trees, according to a Yale paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Yale researchers examined the fossil record and genetic makeup of 489 out of more than 600 living conifer species and discovered that while most conifers belong to ancient lineages, most Northern Hemisphere species, including the majority of pines and spruces, appeared within the past 5 million years.
They argue that the migration ...
2012-10-05
Controlling "mixing" between acceptor and donor layers, or domains, in polymer-based solar cells could increase their efficiency, according to a team of researchers that included physicists from North Carolina State University. Their findings shed light on the inner workings of these solar cells, and could lead to further improvements in efficiency.
Polymer-based solar cells consist of two domains, known as the acceptor and the donor layers. Excitons, the energy particles created by solar cells, must be able to travel quickly to the interface of the donor and acceptor ...
2012-10-05
CORVALLIS, Ore. – More than 40 percent of older breast cancer survivors are insufficiently active after leaving a supervised program. But new research shows that those women who developed behavioral skills such as self-confidence and motivation during their program were far more likely to continue exercising on their own.
Regular exercise may reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence and breast cancer-related mortality, experts say, making it crucial to effectively target breast cancer survivors who do not engage in regular physical activity for interventions.
Researchers ...
2012-10-05
At first blush, many people would probably love to get rid of insects, such as pesky mosquitoes, ants and roaches. But a new study indicates that getting rid of insects could trigger some unwelcome ecological consequences, such as the rapid loss of desired traits in plants, including their good taste and high yields.
Specifically, the study--described in the Oct. 5, 2012 issue of Science and funded by the National Science Foundation showed that evening primroses grown in insecticide-treated plots quickly lost, through evolution, defensive traits that helped protect them ...
2012-10-05
Suicide is the third-leading cause of death for teens, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Now, a University of Missouri public health expert has identified factors that will help parents, medical professionals and educators recognize teens at risk for self injury and suicide.
"For many young people, suicide represents an escape from unbearable situations—problems that seem impossible to solve or negative emotions that feel overwhelming," said Lindsay Taliaferro, an assistant professor of health sciences at MU. "Adults can help these teens dissect ...
2012-10-05
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. – Sandia National Laboratories published the second annual 2012 Wind Plant Reliability Benchmark on Monday, and the results should help the nation's growing wind industry benchmark its performance, understand vulnerabilities and enhance productivity.
Until now, wind farm owners and operators had no way to compare their output with the output of similar operations. To benchmark the reliability of the U.S. wind turbine fleet and identify major causes of failures and downtime, the DOE commissioned Sandia in 2010 to build the Continuous Reliability Enhancement ...
2012-10-05
To believe that technologies once dreamed of in science fiction novels, television shows, and comic strips may one day be a reality, or that real-world technologies might make the fantastic devices of fiction obsolete, you'd need to be either an optimist…or a futurist in the Department of Homeland Security (DHS)'s Science and Technology Directorate (S&T).
To keep dreams grounded, S&T maintains a team of futurists in Arlington, Va., at the Homeland Security Studies & Analysis Institute (HSSAI). There, in the Resilience and Emergency Preparedness / Response Branch, analysts ...
2012-10-05
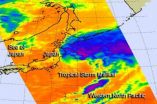
Tropical Storm Maliksi is putting the final touches on Japan, that is, the edge of the storm was seen brushing the country's northern coast as it pulled away on NASA satellite imagery.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Maliksi on Oct. 4 at 0329 UTC (11:29 p.m. EDT, Oct. 3, EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the storm brushing the Tohoku and Hokkaido prefectures of northern Japan.
On Oct. 4, 2012 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued their final advisory on Maliksi. At ...
2012-10-05
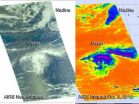
NASA's Aqua satellite provided two different infrared views of the two tropical storms swirling in the Atlantic Ocean. Oscar is battling wind shear that appears destined to tear it apart, while Nadine is merging with a cold front.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over both Tropical Storm Nadine and Tropical Depression 15 (TD15) on Oct. 3 at 1553 UTC (11:53 a.m. EDT), before TD15 became Tropical Storm Oscar. While overhead, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard Aqua captured two different images of both storms. One image was near infrared and almost visible ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, October 2012