(Press-News.org) Computer scientists from the University of Bonn have developed a new robot whose source code and design plan is publicly accessible. It is intended to facilitate the entry into research on humanoids, in particular, the TeenSize Class of the RoboCup. The scientists recently introduced the new robot at the IROS Conference (International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems) in Portugal.
With its white head and black body, "NimbRo-OP" looks almost human. After all, at a height of 95 centimeters, it is almost the size of a small child. Among soccer robots, it counts as a "grown-up." Thanks to light-weight materials, its weight of 6.6 kilograms is, however, clearly less than that of a child. It has a total of 20 drive elements that convert computer commands into mechanical motions. This is also why "NimbRo-OP" is very agile - it has no problems kicking a soccer ball, and it can also get up from a prone position like a human, for soccer players also sometimes fall down.
The robot's source code and design are open source
"We have made very effort to keep the design simple to allow other working groups to also use this robot as a basis for their work, modify and repair it," says Prof. Dr. Sven Behnke, lead of the Autonomous Intelli¬gent Systems working group from the University of Bonn. Source code and design plan of "NimbRo-OP" are open source. This is intended to facilitate entry into research on humanoids, in particular, the TeenSize Class of the RoboCup.
The Bonn researchers used different humanoid robots as the inspiration for their project. "There are also other very interesting robots; but they are clearly smaller than ours," says Prof. Behnke. "But its size is essential for being able to do certain things, such as in robo-soccer." In addition, "NimbRo-OP" has a special wide-angle camera to get a view of the soccer field, and high processing capacity for swift response.
"NimbRo-OP" to participate in RoboCup
This robot, which was recently presented at the IROS Conference (International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems) in Portugal, is a prototype. "NimbRo-OP is not suitable for consumers," says Prof. Behnke. "Our target group consists of scientists who want to program robots based on this hard- and software." The scientists from the Uni¬versity of Bonn also want to enter their robot in the RoboCup.
This is a first step in the development project. "With this platform, we would like to achieve compatibility with other robots," says the computer scientist. Over the next three years, the development project will be continued together with igus GmbH Köln, an application partner, within a knowledge transfer project entitled "A humanoid TeenSize open-platform soccer robot." Prof. Behnke explains, "The goal of the project is accelerating progress in the humanoid robot area by intensifying the sharing with other groups of researchers."
Robots' soccer skills still inferior to those of humans
Chess computers have already proven that they can best human capabilities. "But humans are still clearly better at soccer than robots," the computer scientist from the University of Bonn reports. The requirements for soccer robots are high; they have to perceive environ¬mental conditions via cameras and inclination sensors, detect the goal posts, opponents and obstacles, and make and implement decisions in¬volving their team members. "There is still much to do to solve all the problems out on the pitch," adds Prof. Behnke.
Robo-soccer as a testing grounds for future everyday applications
The scientists are using the RoboCup to experiment with complex challenges for bipedal robots that can potentially be used in many practically relevant environments beyond soccer. "For example, they are capable of using tools, climbing stairs, and passing bottlenecks that are too narrow for wheeled or tracked robots," explains Prof. Behnke. In addition, they can also use human facial expressions, gestures and body language for communicating.
He adds, "Our goal is to stop re-inventing the wheel over and over; by using an open platform together with other researchers, we want to find solutions while saving on effort and expenses." The working group around Prof. Behnke is the most successful humanoid team worldwide at the RoboCup, and with wins in eleven individual competitions, quite likely even the most successful RoboCup team overall.
Information on "NimbRo-OP" can be found online at: http://www.ais.uni-bonn.de/nimbro/OP
### END
Off to the Future with a new Soccer Robot
Computer scientists from the University of Bonn have developed a prototype to inspire many research groups
2012-10-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New tool aims to ensure software security policies reflect user needs
2012-10-31
Researchers from North Carolina State University and IBM Research have developed a new natural language processing tool that businesses or other customers can use to ensure that software developers have a clear idea of the security policies to be incorporated into new software products.
Specifically, the research focuses on access control policies (ACPs), which are the security requirements that software developers need to bear in mind when developing new software. For example, an ACP for a university grading program needs to allow professors to give grades to students, ...
American consumers overvalue US-produced apparel, MU study finds
2012-10-31
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- In today's globalized economy, a large percentage of apparel products are multinational products as raw materials are produced, transported and assembled in different countries. However, consumers have little information about where and to what extent their apparel is produced domestically or overseas. Now, University of Missouri researchers have found that American consumers place a much higher value on apparel produced entirely in the US with US raw materials as opposed to products produced partially or entirely overseas. The value is so high, in fact, ...
Study suggests new way to prevent recurrent ear infections
2012-10-31
Eliminating bacteria's DNA and boosting antimicrobial proteins that already exist may help prevent middle ear infections from reoccurring. These are the findings from a Nationwide Children's Hospital study that examined how an immune defense protein common in the middle ear interacts with a structure meant to protect a colony of bacteria.
The bacterium nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHI) causes a wide range of diseases of both the lower and upper airways, including middle ear infection. NTHI, like most other bacteria, can form a biofilm, a robust community of ...
Finding triggers of birth defects in an embryo heart
2012-10-31
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have found a way to create three-dimensional maps of the stress that circulating blood places on the developing heart in an animal model – a key to understanding triggers of heart defects.
The team has begun testing the technology to uncover how alcohol, drugs and other factors set off events that result in defects found in newborn humans.
Passing blood cells drag on the endothelial cells that line the growing heart, a phenomenon called shear stress, which has been linked to changes in gene expression that results in defects, ...
Low-resistance connections facilitate multi-walled carbon nanotubes for interconnects
2012-10-31
Using a new method for precisely controlling the deposition of carbon, researchers have demonstrated a technique for connecting multi-walled carbon nanotubes to the metallic pads of integrated circuits without the high interface resistance produced by traditional fabrication techniques.
Based on electron beam-induced deposition (EBID), the work is believed to be the first to connect multiple shells of a multi-walled carbon nanotube to metal terminals on a semiconducting substrate, which is relevant to integrated circuit fabrication. Using this three-dimensional fabrication ...
Bullying has long-term health consequences
2012-10-31
HUNTSVILLE, TX (10/30/12) -- Childhood bullying can lead to long term health consequences, including general and mental health issues, behavioral problems, eating disorders, smoking, alcohol use, and homelessness, a study by the Crime Victims' Institute at Sam Houston State University found.
"What is apparent from these results is that bullying victimization that occurs early in life may have significant and substantial consequences for those victims later in life," said Leana Bouffard, Director of the Crime Victims' Institute. "Thus, the adverse health consequences of ...
Metabolic syndrome makes a difference in hormone therapy risk
2012-10-31
CLEVELAND, Ohio (October 29, 2012)—A new analysis of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) trials show that women who had metabolic syndrome before they started hormone therapy had a greatly increased risk of heart attack or dying of heart disease. Women who didn't have metabolic syndrome beforehand showed no increased risk. The study was published this month online in Menopause, the journal of the North American Menopause Society.
"Our findings emphasize the importance of assessing cardiovascular disease risk status when hormone therapy is considered for relief of menopausal ...
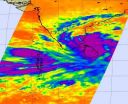
ASA infrared eye sees tropical cyclone Nilam soak Sri Lanka
2012-10-31
Tropical Storm 02B was renamed Tropical Cyclone Nilam when NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the storm soaking Sri Lanka on its crawl to a landfall in southern India.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Tropical Cyclone Nilam on Oct. 29 at 2029 4:29 p.m. EDT. At the time of the AIRS image, the strongest storms with coldest cloud top temperatures were covering Sri Lanka and stretched into the open waters of the Northern Indian Ocean. Cloud top temperatures in those areas were ...
NASA satellites capture Hurricane Sandy's massive size
2012-10-31
NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image Sandy's massive circulation. Sandy covers 1.8 million square miles, from the Mid-Atlantic to the Ohio Valley, into Canada and New England.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image Sandy's massive circulation on October 29 at 18:20 UTC (2:20 p.m. EDT). Sandy covered 1.8 million square miles, from the Mid-Atlantic to the Ohio Valley, into Canada and New England. Sandy made landfall hours after the MODIS image was taken.
Sandy was still a hurricane ...
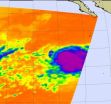
NASA sees Tropical Storm Rosa being born and powering up quickly
2012-10-31
The seventeenth tropical depression of the eastern Pacific Ocean hurricane season formed early on October 30 and quickly strengthened into Tropical Storm Rosa. Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed strong convection in the storm's center, hinting at that intensification.
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Depression 17E at 5:41 a.m. EDT (0951 UTC) on Tuesday, October 30, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument took an infrared picture of the storm. The AIRS data showed a large, circular area of very strong convection (rising air that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
A universal 'instruction manual' helps immune cells protect our organs
Fifteen-year results from SWOG S0016 trial suggest follicular lymphoma is curable
The breasts of a breastfeeding mother may protect a newborn from the cold – researchers offer a new perspective on breast evolution
More organ donations now come from people who die after their heart stops beating
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
[Press-News.org] Off to the Future with a new Soccer RobotComputer scientists from the University of Bonn have developed a prototype to inspire many research groups