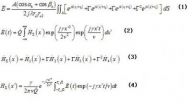(Press-News.org) The scents which permeate our health spas from aromatic essential oils may provide more benefits than just a sense of rest and well-being.
For according to a new study(1) in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, the essential oils which form the basis of aromatherapy for stress relief are also reported to have a beneficial effect on heart rate and blood pressure following short-term exposure - and may therefore reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. However, on the downside, those beneficial effects were reversed when exposure to essential oils lasted more than an hour.
The study was performed in men and women working in various spa centres in the city of Taipei in Taiwan, where the traditions of ancient Chinese civilisations are maintained in religious ceremonies and healing therapies. Aromatherapy, as practised today, is still presented as natural healing with essential oils extracted by infusion from aromatic plants.
One hundred young, healthy non-smoking spa workers taking part in the study visited the study centre on three occasions (about once a week), when each volunteer was exposed to vapours of essential oils released from an ultrasonic ioniser for two hours. During this time and on each visit three repeated measurements – resting heart rate, systolic blood pressure (SBP), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) – were taken from each spa worker in the study room, a small space measuring 4 metres in height by 3.5 m in length and 3.2 m in width. Before each participant entered the study room, 100% pure bergamot essential oil was vaporised for 1 hour.
Essential oils are volatile organic compounds (VOCs) composed of hundreds of aromatic chemicals, and VOC levels in the room were also measured throughout the study period.
Results showed (after adjusting for age, sex, BMI, day of the week, and visit order) that the room's VOC level was significantly associated with reduced blood pressure and heart rate for between 15 and 60 minutes after the start of exposure. These associations were statistically significant. For example, after 45 minutes exposure 15-minute SBP had reduced by a mean of 2.10 mmHg and heart rate by 2.21 beats per minute.
However, after exposure for more than 1 hour - from 75 to 120 minutes after the start of exposure - VOC levels became associated with an increased 15-minute mean blood pressure and heart rate. After 120 minutes, for example, mean SBP had risen from baseline by 2.19 mmHg, and heart rate by 1.70 beats per minutes. Thus, say the authors, "prolonged exposure for longer than 1 hour to essential oils may be harmful to cardiovascular health in young, healthy subjects".
As background to the study the authors note that aromatherapy has long been used for stress relief and associated with some healing properties. Even exposure to the essential oil vapours from fragrant candles has been found to reduce test-taking anxiety among nursing school students in the USA.
However, says investigator Dr Kai-Jen Chuang from Taipei Medical University in Taiwan, it is still unknown if exposure to essential oil increases the risk of cardiovascular events through a partial effect on blood pressure and heart rate.
"Our results suggest that exposure to essential oil for 1 hour would be effective in reducing heart rate and blood pressure," said Dr Chuang. "However, the most interesting finding of our study is that exposure to essential oil for over an hour was associated with elevated blood pressure and heart rate."
Dr Chuang explained that, although the effect of essential oils on stress reduction has been well documented, epidemiological studies have reported an association between VOCs and cardiopulmonary effects - asthma among hairdressers, for example. Studies by Chuang's own group in Taiwan have already shown that exposure to VOCs for over an hour in hair salons can lead to increased serum levels of C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation) and 8-OHdG (a marker of oxidative stress). Overexposure to essential oils, he suggested, may in such ways be harmful to cardiovascular health in young, healthy subjects.
He also noted the opinion of the American Heart Association on air pollution in the development of cardiovascular disease. This acknowledges the direct effects of air pollution on the lung and cardiovascular system through neural and central mechanisms to cause a systemic inflammatory response. "These potential biological processes may also be applied to the adverse effects of VOC exposure on cardiovascular health, although at this time there is no proof available for this hypothesis," said Dr Chuang.
###
Notes for editors
(1) Chuang K-J, Chen H-W, Liu I-J, et al. The effect of essential oil on heart rate and blood pressure among solus por aqua workers. Eur J Prevent Cardiol 2012; DOI: 10.1177/2047487312469474
* The European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation is a journal of the European Society of Cardiology.
* More information on this press release and a PDF of the paper is available from the ESC's Press Office: press@escardio.org. END
Short-term exposure to essential oils lowers blood pressure and heart rate
...but only when exposure is less than one hour
2012-11-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prenatal exposure to testosterone leads to verbal aggressive behavior
2012-11-29
Washington, DC (November 27, 2012) –A new study in the Journal of Communication links verbal aggression to prenatal testosterone exposure. The lead researcher, at University at Buffalo – The State University of New York, used the 2D:4D measure to predict verbal aggression. This study is the first to use this method to examine prenatal testosterone exposure as a determinant of a communication trait.
Allison Z. Shaw, University at Buffalo – The State University of New York, Michael R. Kotowski, University of Tennessee, and Franklin J. Boster and Timothy R. Levine, Michigan ...
Enzyme inhibition protects against Huntington's disease damage in 2 animal models
2012-11-29
Treatment with a novel agent that inhibits the activity of SIRT2, an enzyme that regulates many important cellular functions, reduced neurological damage, slowed the loss of motor function and extended survival in two animal models of Huntington's disease. The study led by Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers will appear in the Dec. 27 issue of Cell Reports and is receiving advance online release.
"I believe that the drug efficacy demonstrated in two distinct genetic HD mouse models is quite unique and highly encouraging," says Aleksey Kazantsev, PhD, of ...
Biology behind brain development disorder
2012-11-29
Researchers have defined the gene responsible for a rare developmental disorder in children. The team showed that rare variation in a gene involved in brain development causes the disorder. This is the first time that this gene, UBE3B, has been linked to a disease.
By using a combination of research in mice and sequencing the DNA of four patients with the disorder, the team showed that disruption of this gene causes symptoms including brain abnormalities and reduced growth, highlighting the power of mouse models for understanding the biology behind rare diseases.
"Ubiquitination, ...
When good service means bad behavior
2012-11-29
Economists and professionals praise the merits of competition, as it leads to lower prices and improvements in quality. But in the automobile smog-testing industry, competition can lead to corruption and even public health problems, according to research by USC Marshall School of Business Assistant Professor of Management Victor Bennett.
Bennett, along with colleagues Lamar Pierce of Washington University's Olin School of Business, Jason Snyder at the UCLA Anderson School of Management and Michael W. Toffel of Harvard Business School, found that the structure of the smog-testing ...
Study reinforces safety of whooping cough vaccine for older adults
2012-11-29
PASADENA, Calif., Nov. 29, 2012 – Immunizing older adults with the tetanus-diphtheria-acellular-pertussis vaccine (Tdap) to prevent pertussis (more commonly referred to as whooping cough) was found to be as safe as immunizing them with the tetanus and diphtheria (Td) vaccine, according to a study by Kaiser Permanente published in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Researchers examined the electronic health records of nearly 120,000 people ages 65 and older at seven U.S. health systems between Jan. 1, 2006 and Dec. 31, 2010. The study looked at a number of medical ...
A new anti-windup design paradigm for control systems with actuator saturation was developed
2012-11-29
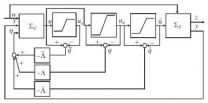
Actuator saturation is ubiquitous in engineering systems. Anti-windup approach to dealing with actuator saturation has been receiving considerable attention from both the industry and the academic community during the past decades. Professor Zongli Lin and his student Xiongjun Wu developed a new anti-windup design paradigm that is capable of achieving significantly improved performances of the resulting closed-loop system. Their work, entitled "Design of multiple anti-windup loops for multiple activations," was published in SCIENCE CHINA Information Sciences, 55(9), 2012. ...
Method for accurate extraction of a target profile developed at Beijing Institute of Technology
2012-11-29
The detection and recognition of an object with small RCS, such as a stealth target, is the most difficult problem to solve for the modern radar system. Professor Hu Cheng and his group at Radar Research Lab, Beijing Institute of Technology set out to tackle this problem. After seven years of innovative research, they have developed a series of methods to detect, track and recognize some targets with small RCS. In particular, they proposed a novel imaging method based on the principle of shadow inverse synthetic aperture radar (SISAR) to extract the target profile accurately ...
Technology use in the classroom helps autistic children communicate
2012-11-29
The use of technology in the classroom is nothing new, but Topcliffe Primary School in Birmingham is breaking new ground by using technology to help pupils with autism communicate more effectively.
The school, which teaches around 30 children with various levels of autism, was one of four schools across UK, which participated in the ECHOES research project, jointly funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) and the Engineering and Physical Science Research Council (EPSRC) from universities across the UK to explore how technology can make a difference in ...
Scientific advice to ensure the sustainability of shark populations in Ocean waters
2012-11-29
Together with the Basque R+D centre's researchers, the group of advisers is made up of researchers from the Spanish Institute of Oceanography (IEO), the French Institute for Exploration of the Sea (IFREMER), the French Institute for Research for Development (IRD),and the Portuguese Institute for Fisheries and Sea Research (IPIMAR).This work comes within the 'European Community's Action Plan on Sharks' which has funding from the European Commission's Directorate-General for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries, and is set to take 15 months.
Shark are caught with fishing gear ...
Next-generation treatments for Fragile X syndrome
2012-11-29
Philadelphia, PA, November 29, 2012 – A potential new therapeutic strategy for treating Fragile X syndrome is detailed in a new report appearing in the current issue of Biological Psychiatry, from researchers led by Dr. Lucia Ciranna at University of Catania in Italy.
Fragile X syndrome (FXS), the most common heritable form of autism and intellectual disability, is one of the most exciting areas in brain research at the moment.
A decade ago, Dr. Mark Bear and his colleagues discovered that an animal model for FXS was associated with a distinctive alteration in brain ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
[Press-News.org] Short-term exposure to essential oils lowers blood pressure and heart rate...but only when exposure is less than one hour