(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
Humans perceive numerous categories of objects and actions, but where are these categories represented spatially in the brain? Researchers reporting in the Dec. 20 issue of the Cell Press journal...
Click here for more information.
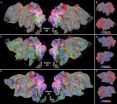
Humans perceive numerous categories of objects and actions, but where are these categories represented spatially in the brain? Researchers reporting in the December 20 issue of the Cell Press journal Neuron present their study that undertook the remarkable task of determining how the brain maps over a thousand object and action categories when subjects watched natural movie clips. The results demonstrate that the brain efficiently represents the diversity of categories in a compact space. Instead of having a distinct brain area devoted to each category, as previous work had identified, for some but not all types of stimuli, the researchers uncovered that brain activity is organized by the relationship between categories.
"Humans can recognize thousands of categories. Given the limited size of the human brain, it seems unreasonable to expect that every category is represented in a distinct brain area," says first author Alex Huth, a graduate student working in Dr. Jack Gallant's laboratory at the University of California, Berkeley.
The authors proposed that perhaps a more efficient way for the brain to represent object and action categories would be to organize them into a continuous space that reflects the similarity between categories.
To test this hypothesis, they used blood oxygen level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD fMRI) to measure human brain activity evoked by natural movies in five people. They then mapped out how 1,705 distinct object and action categories are represented across the surface of the cortex of the brain. Their results show that categories are organized as smooth gradients that cover much of the surface of the visual as well as nonvisual cortex, such that similar categories are located next to each other, and notably, this organization was shared across the individuals imaged.
"Discovering the feature space that the brain uses to represent information helps us to recover functional maps across the cortical surface. The brain probably uses similar mechanisms to map other kinds of information across the cortical surface, so our approach should be widely applicable to other areas of cognitive neuroscience," says Dr. Gallant.
INFORMATION:
Huth et al.: "A continuous semantic space describes the representation of thousands of object and action categories across the human brain."
Study reveals how the brain categorizes thousands of objects and actions
2012-12-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Western University-led research debunks the IQ myth
2012-12-19
After conducting the largest online intelligence study on record, a Western University-led research team has concluded that the notion of measuring one's intelligence quotient or IQ by a singular, standardized test is highly misleading.
The findings from the landmark study, which included more than 100,000 participants, were published today in the journal Neuron. The article, "Fractionating human intelligence," was written by Adrian M. Owen and Adam Hampshire from Western's Brain and Mind Institute (London, Canada) and Roger Highfield, Director of External Affairs, Science ...
Brake on nerve cell activity after seizures discovered
2012-12-19
SAN ANTONIO (Dec. 19, 2012) — Given that epilepsy impacts more than 2 million Americans, there is a pressing need for new therapies to prevent this disabling neurological disorder. New findings from the neuroscience laboratory of Mark S. Shapiro, Ph.D., at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, published Dec. 20 in the high-impact scientific journal, Neuron, may provide hope.
"A large fraction of epilepsy sufferers cannot take drugs for their disorder or the existing drugs do not manage it," said Dr. Shapiro, professor of physiology in the School ...
UofL scientist uncovers how airway cells regenerate after chlorine gas injury
2012-12-19
LOUISVILLE, Ky. - Scarring of the airways can lead to long-term breathing problems for some people exposed to high levels of chlorine gas from events such as an industrial accident, chemical spill following a train derailment or terroristic chemical warfare. Household mishaps from mixing bleach with acidic cleaning products also can cause release of chlorine gas; if this occurs in a poorly ventilated space, chlorine levels could be high enough to cause lung injury.
University of Louisville scientist Gary Hoyle, Ph.D., School of Public Health and Information Sciences ...
Closest sun-like star may have planets
2012-12-19
Washington, D.C.— An international team of scientists, including Carnegie's Paul Butler, has discovered that Tau Ceti, one of the closest and most Sun-like stars, may have five planets. Their work is published by Astronomy & Astrophysics and is available online.
At a distance of twelve light years and visible with a naked eye in the evening sky, Tau Ceti is the closest single star with the same spectral classification as our Sun. Its five planets are estimated to have masses between two and six times the mass of the Earth--making it the lowest-mass planetary system yet ...
NTU study finds ways to prevent muscle loss, obesity and diabetes
2012-12-19
A research study from Nanyang Technological University (NTU) has yielded important breakthroughs on how the body loses muscle, paving the way for new treatments for aging, obesity and diabetes.
The study found that by inhibiting a particular molecule produced naturally in the body, muscle loss due to aging or illnesses can be prevented. Blocking the same molecule will also trigger the body to go into a 'fat-burning mode' which will fight obesity and also treat the common form of diabetes.
The exciting discoveries have led NTU scientists to embark on joint clinical research ...
Successful results against human leishmaniasis with a more efficient and economic vaccine
2012-12-19
A research coordinated by the UAB has succeeded in testing a vaccine against leishmaniasis. The vaccine was tested with the best animal model existing, the golden hamster, and can be produced at low costs by using insect larvae. The research, published in the latest edition of PLoS ONE, is an important step towards the fight against a disease which causes the death of 70,000 people each year in developing countries and of countless dogs, which also suffer from this disease and are its natural reservoir.
Leishmaniasis is one of the main health problems existing at global ...
A mathematical formula to decipher the geometry of surfaces like that of cauliflower
2012-12-19
This press release is available in Spanish.
VIDEO:
This is a cauliflower.
Click here for more information.
The scientists have found a formula that describes how the patterns found in a multitude of natural structures are formed. "We have found a model that describes, in detail, the evolution in time and in space of cauliflower-type fractal morphologies for nanoscopic systems", explains ...
Geo-engineering against climate change
2012-12-19
Numerous geo-engineering schemes have been suggested as possible ways to reduce levels of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and so reduce the risk of global warming and climate change. One such technology involves dispersing large quantities of iron salts in the oceans to fertilize otherwise barren parts of the sea and trigger the growth of algal blooms and other photosynthesizing marine life. Photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide as its feedstock and when the algae die they will sink to the bottom of the sea taking the locked in carbon with them.
Unfortunately, ...
Better approach to treating deadly melanoma identified by scientists
2012-12-19
Scientists at The University of Manchester have identified a protein that appears to hold the key to creating more effective drug treatments for melanoma, one of the deadliest cancers.
Researchers funded by Cancer Research UK have been looking at why new drugs called "MEK inhibitors", which are currently being tested in clinical trials, aren't as effective at killing cancer cells as they should be.
They discovered that MITF - a protein that helps cells to produce pigment but also helps melanoma cells to grow and survive - is able to provide cancer cells with a resistance ...
Fast-acting enzymes with 2 fingers: Protein structurally and dynamically explained
2012-12-19
Researchers at the RUB and from the MPI Dortmund have uncovered the mechanism that
switches off the cell transport regulating proteins. They were able to resolve in detail how the central switch protein Rab is down-regulated with two "protein fingers" by its interaction partners. The structural and dynamic data is reported by the researchers led by Prof. Dr. Klaus Gerwert (Chair of Biophysics, RUB) and Prof. Dr. Roger S. Goody (Max Planck Institute for Molecular Physiology, Dortmund, Germany) in the Online Early Edition of the journal PNAS. "Unlike in the cell growth protein ...