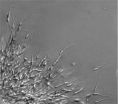
(Press-News.org) NEW YORK (Jan. 14, 2013) -- Scientists at Weill Cornell Medical College have discovered the molecular switch that allows aggressive triple negative breast cancer cells to grow the amoeba-like protrusions they need to crawl away from a primary tumor and metastasize throughout the body. Their findings, published in Cancer Cell, suggest a novel approach for developing agents to treat cancer once it has spread.
"Metastasis can be lethal, and our findings point to potential targeted treatments to stop the spread of this aggressive breast cancer," says the study's senior investigator, Dr. Vivek Mittal, an associate professor of cell and developmental biology and director of the Lehman Brothers Lung Cancer Laboratory at Weill Cornell Medical College.
According to researchers, if such agents were developed, they would perhaps be the first to specifically treat cancer metastasis, importantly in patients whose tumors have already spread. They would also be among the first designed to restore the function of a microRNA (miRNA), a small, non-coding RNA that regulates gene expression, which is crucial to cancer spread. While distinct miRNA "signatures" have been found for many tumor types, including different breast cancers, their specific roles in later steps of cancer metastasis has been unclear, Dr. Mittal says.
In the study, researchers set out to identify a miRNA that impacts metastasis without affecting primary tumor growth, as well as address its underlying molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential against metastatic breast cancer. They discovered that a miRNA known as miR-708 is inhibited in metastatic triple negative breast cancer. They found that miR-708 acts as a metastatic tumor inhibitor, and when its function is restored, the tumors do not spread or form lethal macrometastases.
Silenced miRNA Inhibitor Molecule Can Be Switched Back On
Triple negative breast cancer has the worst outcome of all breast cancer subtypes because of its high recurrence rate and metastatic spread. This is why the research team chose to examine the role of miRNAs in the spread of triple negative breast cancer, which accounts for 15-25 percent of all breast tumors. The cancer is named "triple negative" because its tumor cells do not display two hormone receptors (estrogen and progesterone) or HER2/neu growth factor, which each form the basis of current targeted breast cancer treatments.
Using genome wide miRNA sequencing, Dr. Mittal and his research team found in human samples of triple negative breast cancer that miR-708 was significantly down-regulated with its normal expression curtailed. In both laboratory cells and in animal studies, the researchers identified that the normal role of miR-708 is to suppress the protein neuronatin, which is located on the membrane of a cell's endoplasmic reticulum -- an organelle that stores calcium. Neuronatin helps control how much calcium leaves that organelle.
"It is calcium that provides legs to cancer cells to help them escape a tumor. So miR-708 acts as a suppressor of metastasis by keeping neuronatin in check," Dr. Mittal says. "If miR-708 is itself suppressed, there is an increase in production of neuronatin proteins, which then allows more calcium to leave the endoplasmic reticulum and activate a cascade of genes that turn on migratory pathways leading to metastasis."
Researchers found that delivering synthetic miR-708, carried by bubbles of fat, blocked metastatic outgrowth of triple negative breast cancer cells in the lung of mice. This makes miR-708 a promising therapeutic against metastatic breast cancer. The researchers also discovered that polycomb repressor complex proteins are responsible for silencing miR-708. These proteins remodel the way DNA is packaged in order to epigenetically silence genes.
Dr. Mittal adds that the findings suggest that pharmacological agents now being tested in lymphoma cancer cells may also help to restore miR-708 in triple negative breast cancer. These drugs are designed to inhibit histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2, the member of the polycomb group that directly silences miR-708.
"It is exciting that there are now drugs that can turn off the silencing of these critical genes. They could very well work for this aggressive breast cancer," says Dr. Mittal. "Finding that there may be a way to shut down the spread of an aggressive breast cancer -- which is the only way that triple negative breast cancer can be controlled and lives spared -- is very promising."
"These study results are terrific," says co-author Dr. Linda Vahdat, director of the Breast Cancer Research Program, chief of the Solid Tumor Service and professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College and medical oncologist at the Iris Cantor Women's Health Center at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. "It not only offers us an avenue to treat metastatic triple negative breast cancer in the short-term, but also gives us the roadmap to prevent metastases in the long-run. We are anxious to get this into the clinic and are working as quickly as possible towards that end."
###
The study was funded by the Neuberger Berman Lung Cancer Laboratory, the Robert I. Goldman Foundation and the Cornell Center on the Microenvironment and Metastasis through an award from the National Cancer Institute.
Other study co-authors include Dr. Seongho Ryu, Kevin McDonnell, Dr. Hyejin Choi, Dingcheng Gao, Mary Hahn, Natasha Joshi, Dr. Sun Mi Park, Dr. Raul Catena, Jacqueline Brazin and Dr. Randi B. Silver from Weill Cornell Medical College, and Dr. Yoonkyung Do from Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), School of Nano-Bioscience and Chemical Engineering in Ulsan, Korea.
About Weill Cornell Medical College
Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University's medical school located in New York City, is committed to excellence in research, teaching, patient care and the advancement of the art and science of medicine, locally, nationally and globally. Physicians and scientists of Weill Cornell Medical College are engaged in cutting-edge research from bench to bedside, aimed at unlocking mysteries of the human body in health and sickness and toward developing new treatments and prevention strategies. In its commitment to global health and education, Weill Cornell has a strong presence in places such as Qatar, Tanzania, Haiti, Brazil, Austria and Turkey. Through the historic Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar, the Medical College is the first in the U.S. to offer its M.D. degree overseas. Weill Cornell is the birthplace of many medical advances -- including the development of the Pap test for cervical cancer, the synthesis of penicillin, the first successful embryo-biopsy pregnancy and birth in the U.S., the first clinical trial of gene therapy for Parkinson's disease, and most recently, the world's first successful use of deep brain stimulation to treat a minimally conscious brain-injured patient. Weill Cornell Medical College is affiliated with NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, where its faculty provides comprehensive patient care at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. The Medical College is also affiliated with the Methodist Hospital in Houston. For more information, visit weill.cornell.edu.
Researchers reveal aggressive breast cancer's metastatic path
Weill Cornell study shows triple negative breast cancer metastasis can be halted, potential new therapies on horizon
2013-01-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Medicinal toothbrush tree yields antibiotic to treat TB in new way
2013-01-14
A compound from the South African toothbrush tree inactivates a drug target for tuberculosis in a previously unseen way.
Tuberculosis causes more deaths worldwide than any other bacterial disease. At the same time as rates are increasing, resistance strains are emerging due, in part, to non-compliance with the treatment required. Many current drugs are nearly 50 years old and alternatives are needed to the long, demanding treatment schedules.
The compound under research, diospyrin, binds to a novel site on a well-known enzyme, called DNA gyrase, and inactivates the ...
Cervical cancer screening in less-developed areas should be tailored to local conditions
2013-01-14
The best approach to detecting cervical cancer in HIV-positive women living in research limited countries such as those in Sub-Saharan Africa combines commonly used testing methods tailored to local levels of development and medical infrastructure, according to a study by researchers from and the University of Witwatersrand in South Africa and the University of North Carolina.
The research evaluated the effectiveness of three commonly used screening methods– the pap smear, human papillomavirus testing (HPV) and visual inspection of the cervix with acetic acid (VIA) – among ...
New discovery in autism-related disorder reveals key mechanism in brain development and disease
2013-01-14
A new finding in neuroscience for the first time points to a developmental mechanism linking the disease-causing mutation in an autism-related disorder, Timothy syndrome, and observed defects in brain wiring, according to a study led by scientist Ricardo Dolmetsch and published online yesterday in Nature Neuroscience. These findings may be at the heart of the mechanisms underlying intellectual disability and many other brain disorders.
The present study reveals that a mutation of the disease-causing gene throws a key process of neurodevelopment into reverse. That is, ...
Smoking, high blood pressure and cholesterol can be fatal for hemorrhage survivors
2013-01-14
"It is particularly important for subarachnoid haemorrhage survivors to refrain from smoking and to take care of their blood pressure and cholesterol levels; apart from age, these are the primary factors behind the increased risk of mortality," explains neurosurgeon Miikka Korja from the HUCH's Neurosurgery Department together with professor Jaakko Kaprio from the University of Helsinki's Hjelt Institute.
The most extensive population-based follow-up study ever carried out on the subject, jointly conducted by HUCH, the University of Helsinki, and the Finnish National ...
Depression after heart attack: Threat perception has to be addressed
2013-01-14
"Survivors of heart attacks are three times more likely to develop depression during the first six months after their heart attack, than people with no heart disease. If left untreated this contributes to a worse prognosis, for instance further cardiac events and possibly death. The causes for this high prevalence of depression after heart attacks are still unclear," said Prof. Claus Vögele, Professor of Clinical and Health Psychology at the University of Luxembourg and lead author of the publication entitled "Cardiac Threat Appraisal and Depression after First Myocardial ...
2 new studies show why biodiversity is important for pollination services in California almond
2013-01-14
Agricultural demand for pollination is growing more quickly than the supply of honey bees, the dominant species managed for crop pollination. Increasing the efficiency of pollination represents a way of increasing crop yield without any increase in agricultural intensity or area. A study recently published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences (9 Jan 2013) 1, shows that the pollination effectiveness of honey bees in California almond orchards was greater in the presence of other bees.
Almond is a crop highly dependent on honey bee pollination ...
How does your garden glow?
2013-01-14
Nature's ability to create iridescent flowers has been recreated by mathematicians at The University of Nottingham. The team of researchers have collaborated with experimentalists at the University of Cambridge to create a mathematical model of a plant's petals to help us learn more about iridescence in flowering plants and the role it may play in attracting pollinators.
An iridescent surface appears to change colour as you alter the angle you view it from. It is found in the animal kingdom in insects, inside sea shells and in feathers, and is also seen in some plants. ...
How do happiness and sadness circuits contribute to bipolar disorder?
2013-01-14
Philadelphia, PA, January 14, 2013 – Bipolar disorder is a severe mood disorder characterized by unpredictable and dramatic mood swings between the highs of mania and lows of depression. These mood episodes occur among periods of 'normal mood', termed euthymia.
Prior research has clearly shown that brain emotion circuitry is dysregulated in individuals diagnosed with bipolar disorder. It is thought that these disturbances impair one's ability to control emotion and contribute to mood episodes.
Continuing this line of research, the January 15th issue of Biological Psychiatry ...
Global warming has increased monthly heat records by a factor of 5
2013-01-14
Monthly temperature extremes have become much more frequent, as measurements from around the world indicate. On average, there are now five times as many record-breaking hot months worldwide than could be expected without long-term global warming, shows a study now published in Climatic Change. In parts of Europe, Africa and southern Asia the number of monthly records has increased even by a factor of ten. 80 percent of observed monthly records would not have occurred without human influence on climate, concludes the authors-team of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact ...
Protein identified that can disrupt embryonic brain development and neuron migration
2013-01-14
Interneurons – nerve cells that function as 'dimmers' – play an important role in the brain. Their formation and migration to the cerebral cortex during the embryonic stage of development is crucial to normal brain functioning. Abnormal interneuron development and migration can eventually lead to a range of disorders and diseases, from epilepsy to Alzheimer's. New research by Dr. Eve Seuntjens and Dr. Veronique van den Berghe of the Department of Development and Regeneration (Danny Huylebroeck laboratory, Faculty of Medicine) at KU Leuven (University of Leuven) has identified ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
[Press-News.org] Researchers reveal aggressive breast cancer's metastatic pathWeill Cornell study shows triple negative breast cancer metastasis can be halted, potential new therapies on horizon