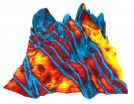
(Press-News.org) Nearly the entire genetic landscape of the most common form of brain tumor can be explained by abnormalities in just five genes, an international team of researchers led by Yale School of Medicine scientists report online in the Jan. 24 edition of the journal Science. Knowledge of the genomic profile of the tumors and their location in the brain make it possible for the first time to develop personalized medical therapies for meningiomas, which currently are only managed surgically.
Meningioma tumors affect about 170,000 patients in the United States. They are usually benign but can turn malignant in about 10 percent of cases. Even non-cancerous tumors can require surgery if they affect the surrounding brain tissue and disrupt neurological functions.
Approximately half of the tumors have already been linked to a mutation or deletion of a gene called neurofibromin 2, or NF2. The origins of the rest of the meningiomas had remained a mystery.
The Yale team conducted genomic analyses of 300 meningiomas and found four new genetic suspects, each of which yields clues to the origins and treatment of the condition. Tumors mutated with each of these genes tend to be located in different areas of the brain, which can indicate how likely they are to become malignant.
"Combining knowledge of these mutations with the location of tumor growth has direct clinical relevance and opens the door for personalized therapies," said Murat Gunel, the Nixdorff-German Professor of Neurosurgery, professor of genetics and of neurobiology, and senior author of the study. Gunel is also a member of Yale Cancer Center's Genetics and Genomics Research Program.
For instance, two of the mutations identified — SMO and AKT1 — have been linked to various cancers. SMO mutations had previously been found in basal cell carcinoma and are the target of an already approved drug for that form of skin cancer. Another, KLF4, activates a suite of genes and is known for its role in inducing stem cell formation, even in cells that have fully differentiated into a specific tissue type. Mutations in a TRAF7, a gene not previously associated with cancer, were found in approximately one-fourth of tumors. Meningiomas with these mutations are found in the skull base and are unlikely to become cancerous. In contrast, NF2 mutant tumors that flank the brain's hemispheres are more likely to progress to malignancy, especially in males.
Doctors may be able to use targeted chemotherapy on patients with non-NF2 mutations, especially those with recurrent or invasive meningiomas and those who are surgically at high risk. Individualized chemotherapies could also spare patients irradiation treatment, a risk factor for progression of these generally benign tumors. Gunel said it may also be possible to extend these approaches to more malignant tumors.
###
Funding for the study was provided by Gregory M. Kiez and Mehmet Kutman Foundation. END
Genetic landscape of common brain tumors holds key to personalized treatment
2013-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New Year brings (potentially) good news for conservation of species on Earth
2013-01-25
Claims that most species will go extinct before they can be discovered have been debunked in the latest issue of Science, by researchers from The University of Auckland, Griffith University, and the University of Oxford.
The scientists show that the claims are based on two key misconceptions: an over-estimation of how many species may exist on Earth, and the erroneous belief that the number of taxonomists (people who describe and identify species) is declining.
"Our findings are potentially good news for the conservation of global biodiversity," says lead author Associate ...
Organic ferroelectric molecule shows promise for memory chips, sensors
2013-01-25
At the heart of computing are tiny crystals that transmit and store digital information's ones and zeroes. Today these are hard and brittle materials. But cheap, flexible, nontoxic organic molecules may play a role in the future of hardware.
A team led by the University of Washington in Seattle and the Southeast University in China discovered a molecule that shows promise as an organic alternative to today's silicon-based semiconductors. The findings, published this week in the journal Science, display properties that make it well suited to a wide range of applications ...
HIV-like viruses in non-human primates have existed much longer than previously thought
2013-01-25
Viruses similar to those that cause AIDS in humans were present in non-human primates in Africa at least 5 million years ago and perhaps up to 12 million years ago, according to study published January 24 in the Open Access journal PLOS Pathogens by scientists at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. Until now, researchers have hypothesized that such viruses originated much more recently.
HIV-1, the virus responsible for AIDS, infiltrated the human population in the early 20th century following multiple transmissions of a similar chimpanzee virus known as SIVcpz. Previous ...
Bats split on family living
2013-01-25
For the tiny Daubenton's bat, the attractions of family life seem to vary more with altitude than with the allure of the opposite sex.
For more than a decade, a team led by Professor John Altringham from the University of Leeds' School of Biology has studied a population of several hundred bats along a 50-km stretch of the River Wharfe. They monitored roosts in Ilkley and Addingham, upstream in the market town of Grassington and higher still in the villages of Kettlewell and Buckden.
The researchers found that all Daubenton's bats in nursery roosts in lowland areas ...
Extinction rates not as bad as feared ... for now
2013-01-25
Concerns that many animals are becoming extinct, before scientists even have time to identify them, are greatly overstated according Griffith University researcher, Professor Nigel Stork.
Professor Stork has taken part in an international study, the findings of which have been detailed in "Can we name Earth's species before they go extinct?" published in the journal Science.
Deputy Head of the Griffith School of Environment, Professor Stork said a number of misconceptions have fuelled these fears, and there is no evidence that extinction rates are as high as some have ...
Organizing human specimen collections: Getting the best out of biobanks
2013-01-25
The diversity of biobanks, collections of human specimens from a variety of sources, raises questions about the best way to manage and govern them, finds a study published in BioMed Central's open access journal Genome Medicine. The research highlights difficulties in standardizing these collections and how to make these samples available for research.
Biobanks have been around for decades, storing hundreds of millions of human specimens. But there has been a dramatic increase in the number of biobanks in the last ten years, since the human genome sequencing project. ...
Immune cell suicide alarm helps destroy escaping bacteria
2013-01-25
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Cells in the immune system called macrophages normally engulf and kill intruding bacteria, holding them inside a membrane-bound bag called a vacuole, where they kill and digest them.
Some bacteria thwart this effort by ripping the bag open and then escaping into the macrophage's nutrient-rich cytosol compartment, where they divide and could eventually go on to invade other cells.
But research from the University of North Carolina School of Medicine shows that macrophages have a suicide alarm system, a signaling pathway to detect this escape into ...
Out-of-pocket costs for breast cancer probably manageable for most Canadian women
2013-01-25
Out-of-pocket costs resulting from breast cancer care in the year following diagnosis are likely manageable for most women, but some women are at a higher risk of experiencing the financial burden that comes from those costs in Canadian breast cancer patients, according to a study published January 24 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
While extensive information about the level of out-of-pocket costs after early breast cancer diagnosis has been unavailable until now, the costs resulting from the disease and the effects the costs have on family financial ...
Fruit and vegetable intake is associated with lower risk of ER- breast cancer
2013-01-25
There is no association between total fruit and vegetable intake and risk of overall breast cancer, but vegetable consumption is associated with a lower risk of estrogen receptor-negative (ER-) breast cancer, according to a study published January 24 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
The intake of fruits and vegetables has been hypothesized to lower breast cancer risk, however the existing evidence is inconclusive. There are many subtypes of breast cancer including ER- and ER positive (ER+) tumors and each may have distinct etiologies. Since ER- tumors, ...
Spotting fetal growth problems early could cut UK stillbirths by 600 a year
2013-01-25
The authors say spotting it early could substantially reduce the risk, and this needs to become a cornerstone of safety and effectiveness in antenatal care.
Stillbirth rates in the United Kingdom are among the highest in developed countries. They have often been considered unexplained and unavoidable, and their rates have changed little over the last two decades.
Recently, doctors have found that many stillborn babies fail to reach their growth potential, prompting a renewed focus on what causes fetal growth restriction. So a team of researchers at the West Midlands ...