(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
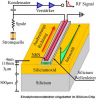
Scientists at Aalto University, Finland, have demonstrated results that show a huge improvement in the light absorption and the surface passivation on highly absorbing silicon nanostructures. This has been achieved by applying atomic layer coating. The results advance the development of devices that require high sensitivity light response such as high efficiency solar cells.
This method provides extremely good surface passivation. Simultaneously, it reduces the reflectance further at all wavelengths. These results are very promising considering the use of black silicon (b-Si) surfaces on solar cells to increase the efficiency to completely new levels, tells Päivikki Repo, a researcher at Aalto University.
More effective surface passivation methods than those used in the past have been needed to make black silicon a viable material for commercial applications. Good surface passivation is crucial in photonic applications such as solar cells. So far, the poor charge carrier transport properties attributed to nanostructured surfaces have been more detrimental for the final device operation than the gain obtained from the reduced reflectance.
Black silicon can also be used in other technologies than solar cells. Numerous applications suggested for b-Si include drug analysis.
Black silicon (b-Si) has been a subject of great interest in various fields including photovoltaics for its ability to reduce the surface reflectance even below 1 per cent. However, many b-Si applications - especially solar cells - suffer from increased surface recombination resulting in poor spectral response. This is particularly problematic at short wavelengths.
INFORMATION:
The research has just been published in the Journal of Photovoltaics. The research is carried out by Aalto University, Finland, together with experts from Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE.
Further information: Research Scientist Päivikki Repo, Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering
e-mail. paivikki.repo@aalto.fi tel. +358 504361156
Link to images: http://aalto.digtator.fi:80/public/85632eacc889.aspx
Link to article: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6264075
full citation: Effective Passivation of Black Silicon Surfaces by Atomic Layer Deposition
P. Repo, A. Haarahiltunen, L. Sainiemi, M. Yli-Koski, H. Talvitie, M. C. Schubert, and H. Savin pp. 90-94.
in IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, JPV January 2013
DOI: 10.1109/JPHOTOV.2012.2210031
Black silicon can take efficiency of solar cells to new levels
2013-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
DNA and quantum dots: All that glitters is not gold
2013-01-25
A team of researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has shown that by bringing gold nanoparticles close to the dots and using a DNA template to control the distances, the intensity of a quantum dot's fluorescence can be predictably increased or decreased.* This breakthrough opens a potential path to using quantum dots as a component in better photodetectors, chemical sensors and nanoscale lasers.
Anyone who has tried to tune a radio knows that moving their hands toward or away from the antenna can improve or ruin the reception. Although ...
More than 1 brain behind E=mc2
2013-01-25
Two American physicists outline the role played by Austrian physicist Friedrich Hasenöhrl in establishing the proportionality between the energy (E) of a quantity of matter with its mass (m) in a cavity filled with radiation. In a paper about to be published in EPJ H, Stephen Boughn from Haverford College in Pensylvannia and Tony Rothman from Princeton University in New Jersey argue how Hasenöhrl's work, for which he now receives little credit, may have contributed to the famous equation E=mc2.
According to science philosopher Thomas Kuhn, the nature of scientific progress ...
National Cancer Centre Singapore scientists discover p53 mutation hinders cancer treatment response
2013-01-25
Reducing the level of mutant p53 gene increases susceptibility to treatment
Scientists from the National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS) have discovered the workings of the gene that has been hindering treatment response in cancer patients. This discovery was made after 5 years of studying the mutant form of the p53 gene, the major tumor suppressor in humans, which is generally found mutated in over 50% of all type of human cancers.
The dominant-negative (DN) effect of the mutant p53 gene in cancers was found to affect the outcome of cancer treatment modalities. DN effect ...
Evolution inspires more efficient solar cell design
2013-01-25
The sun's energy is virtually limitless, but harnessing its electricity with today's single-crystal silicon solar cells is extremely expensive — 10 times pricier than coal, according to some estimates. Organic solar cells — polymer solar cells that use organic materials to absorb light and convert it into electricity — could be a solution, but current designs suffer because polymers have less-than-optimal electrical properties.
Researchers at Northwestern University have now developed a new design for organic solar cells that could lead to more efficient, less expensive ...
Quantum communication: Each photon counts
2013-01-25
This press release is available in German.
The detector combines near-unity detection efficiency with high timing resolution and has a very low error rate. The results have been published by Nature Communications (doi:10.1038/ncomms2307).
Ultrafast, efficient, and reliable single-photon detectors are among the most sought-after components in photonics and quantum communication, which have not yet reached maturity for practical application. Physicist Dr. Wolfram Pernice of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), in cooperation with colleagues at Yale University, ...
NIST's 'nanotubes on a chip' may simplify optical power measurements
2013-01-25
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has demonstrated a novel chip-scale instrument made of carbon nanotubes that may simplify absolute measurements of laser power, especially the light signals transmitted by optical fibers in telecommunications networks.
The prototype device, a miniature version of an instrument called a cryogenic radiometer, is a silicon chip topped with circular mats of carbon nanotubes standing on end.* The mini-radiometer builds on NIST's previous work using nanotubes, the world's darkest known substance, to make an ultraefficient, ...
Analysis of Greenland ice cores adds to historical record and provide glimpse into climate's future
2013-01-25
A new study that provides surprising details on changes in Earth's climate from more than 100,000 years ago indicates that the last interglacial--the period between "ice ages"--was warmer than previously thought and may be a good analog for future climate, as greenhouse gases increase in the atmosphere and global temperatures rise.
The research findings also indicate that melting of the massive West Antarctic ice sheet may have contributed more to sea-level rise at that time than melting of the Greenland ice sheet.
The new results from the North Greenland Eemian Ice ...
Emotional stress reduces effectiveness of prostate cancer therapies in animal model
2013-01-25
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Jan. 25, 2013 – Not surprisingly, a cancer diagnosis creates stress. And patients with prostate cancer show higher levels of anxiety compared to other cancer patients.
A new study by researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center indicates that stress is not just an emotional side effect of the diagnosis; it also can reduce the effectiveness of prostate cancer drugs and accelerate the development of prostate cancer.
The findings are published in the February issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The Wake Forest Baptist team, headed ...
INRS develops a nanohybrid with remarkable properties using a new laser-plasma process
2013-01-25
Montreal, January 25, 2013 – By achieving the synthesis of a novel nanohybrid structure by means of the pulsed laser ablation (PLA) technique, Professor My Ali El Khakani and his team paved the way for a new generation of optoelectronic materials. The combination of carbon nanotubes and lead sulfide (PbS) nanoparticles was performed using an effective and relatively simple process that offers considerable latitude for creating other nanohybrids for a variety of applications. The INRS Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre researcher's work, published in the ...
No more 'empty nest:' middle-aged adults face family pressure on both sides
2013-01-25
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The "empty nest" of past generations, in which the kids are grown up and middle-aged adults have more time to themselves, has been replaced in the United States by a nest that's full – kids who can't leave, can't find a job and aging parents who need more help than ever before.
According to a new study by researchers at Oregon State University, what was once a life stage of new freedoms, options and opportunities has largely disappeared.
An economic recession and tough job market has made it hard on young adults to start their careers and families. ...