(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. – Research at Oregon State University has found that one particular omega-3 fatty acid has a powerful effect in preventing liver inflammation and fibrosis – common problems that are steadily rising along with the number of Americans who are overweight.
The American Liver Foundation has estimated that about 25 percent of the nation's population, and 75 percent of those who are obese, have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. This early-stage health condition can sometimes progress to more serious, even fatal diseases, including nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, as well as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
The study, published online in the Journal of Nutrition, was one of the first to directly compare the effects of two of the omega-3 fatty acids often cited for their nutritional value, DHA and EPA.
In research with laboratory animals, it found that EPA had comparatively little effect on preventing the fibrosis, or scarring, that's associated with NASH. However, DHA supplementation reduced the proteins involved in liver fibrosis by more than 65 percent.
"A reduction of that magnitude in the actual scarring and damage to the liver is very important," said Donald Jump, a principal investigator with the Linus Pauling Institute at OSU and a professor in the College of Public Health and Human Sciences.
"Many clinical trials are being done with omega-3 fatty acids related to liver disease," Jump said. "Our studies may represent the first to specifically compare the capacity of EPA versus DHA to prevent NASH. It appears that DHA, which can also be converted to EPA in the human body, is one of the most valuable for this purpose."
The issues have taken center stage as the weight of Americans continues to rise, with a related increase in the incidence of fatty liver disease and liver damage.
NASH is a progressive form of liver disease that is associated with chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, resulting from excess fat storage in the liver. Chronic inflammation can eventually lead to fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer. While management of lifestyle, including weight loss and exercise, is one approach to control the onset and progression of fatty liver disease, other approaches are needed to prevent and treat it.
About 30-40 percent of people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progress to NASH, which in turn can result in cirrhosis, a major risk factor for liver cancer. While this research studied the prevention of fatty liver disease, Jump said, ongoing studies are examining the capacity of DHA to be used in NASH therapy.
The levels of omega-3 oils needed vary with the health concern, officials say.
"Omega-3 fatty acids are typically recommended for the prevention of cardiovascular disease," Jump said. "Recommended intake levels of omega-3 fatty acids in humans for disease prevention are around 200-500 milligrams of combined DHA and EPA per day."
Levels used in therapy to lower blood triglycerides, also a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, are higher, about 2-4 grams of combined EPA and DHA per day. The OSU studies with mice used DHA at levels comparable to the triglyceride therapies.
"DHA was more effective than EPA at attenuating inflammation, oxidative stress, fibrosis and hepatic damage," the researchers wrote in their conclusion. "Based on these results, DHA may be a more attractive dietary supplement than EPA for the prevention and potential treatment of NASH in obese humans."
###
This work was the result of a four-year study supported by the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, as well as the National Institutes of Health. Co-authors on the paper included Christopher M. Depner and Kenneth A. Philbrick, both graduate students in the Nutrition Graduate Program at OSU.
Some omega-3 oils better than others for protection against liver disease
2013-02-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tendency to fear is strong political influence
2013-02-05
It's no secret that fear is a mechanism often used in political campaigns to steer public opinion on hot-button issues like immigration and war. But not everyone is equally predisposed to be influenced by such a strategy, according to new research by Rose McDermott, professor of political science, and colleagues published in the American Journal of Political Science.
By examining the different ways that fear manifests itself in individuals and its correlation to political attitudes, the researchers found that people who have a greater genetic liability to experience higher ...
Vitamin D, omega-3 may help clear amyloid plaques found in Alzheimer's
2013-02-05
A team of academic researchers has pinpointed how vitamin D3 and omega-3 fatty acids may enhance the immune system's ability to clear the brain of amyloid plaques, one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease.
In a small pilot study published in the Feb. 5 issue of the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, the scientists identified key genes and signaling networks regulated by vitamin D3 and the omega-3 fatty acid DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) that may help control inflammation and improve plaque clearance.
Previous laboratory work by the team helped clarify key mechanisms ...
JSCM publishes issue on NIDRR-funded project on practice-based evidence in SCI rehabilitation
2013-02-05
West Orange, NJ. February 4, 2013. The final phase of the SCIRehab Project (Phase 3) was published in the November 2012 issue of the Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine (JSCM). Nine papers comprised the Special Issue: Relationship of Inpatient Rehabilitation Interventions to Outcomes Following Spinal Cord Injury. Guest editors: J. Scott Richards, Gale Whiteneck, Daniel Lammertse, Marcel Dijkers, and Julie Gassaway. Key article available for free download via ingentaconnect.com: Whiteneck G, Gassaway J. The SCIRehab Project: What rehabilitation interventions are most strongly ...
Enigmatic 'ribbon' of energy discovered by NASA satellite explained
2013-02-05
DURHAM, N.H. -- After three years of puzzling over a striking "ribbon" of energy and particles discovered by NASA's Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) at the edge of our solar system, scientists may be on the verge of cracking the mystery.
In a paper published Feb. 4, 2013, in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers, including lead author Nathan Schwadron of the University of New Hampshire, propose a "retention theory" that for the first time explains all the key observations of this astrophysical enigma.
"If the theory is correct," Schwadron notes, "the ribbon can ...
Scientists discover protein that allows safe recycling of iron from old red blood cells
2013-02-05
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – Humans survive by constantly recycling iron, a metal that is an essential component of red blood cells, but which is toxic outside of those cells. More than 90 percent of the iron in an adult human's 25 trillion life-sustaining red blood cells is recycled from worn-out cells.
Almost 50 years ago scientists first began hypothesizing that our bodies must have a special protein 'container' to safely transport heme -- the form of iron found in living things – during the breakdown and recycling of old red blood cells and other types of heme metabolism. ...
Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for Feb. 5, 2013
2013-02-05
1. Being Physically Fit Earlier in Life May Lower Risk for Dementia Later in Life
Having a higher fitness level at midlife seems to be associated with lower hazards of developing Alzheimer disease and other types of dementia later in life. Between 1970 and 2009, researchers at a community health clinic utilized an exercise treadmill test to assess the baseline fitness levels of 19,458 non-elderly, community-dwelling adults who were in generally good health. The researchers reviewed Medicare data for the patients who became eligible to receive benefits between January ...
New study shows that gases work with particles to promote cloud formation
2013-02-05
New York, NY—January 30, 2013—Researchers at Columbia Engineering and Georgia Institute of Technology have published a study in the online Early Edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) showing—for the first time—that certain volatile organic gases can promote cloud formation in a way never considered before by atmospheric scientists. The study will be published the week of February 4, 2013.
"This is the first time gases have been shown to affect cloud formation in this way," says V. Faye McNeill, Associate Professor in Chemical Engineering at ...
Hoodoos -- key to earthquakes?
2013-02-05
Please cite the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA) as the source of this information.
In the absence of long-term instrumental data, fragile rock formations, called hoodoos, may be key to understanding seismic hazard risk. In this study, researchers consider two hoodoos in Red Rock Canyon region to put limits on expected intensity of ground motion from earthquakes along the Garlock fault.
Hoodoos can be found in desert regions and are highly susceptible to erosion that makes their age uncertain. Despite that uncertainty, existing unfractured hoodoos, ...
Osaka Basin map: Identifies high-rise buildings at risk from quakes
2013-02-05
Please cite the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA) as the source of this information.
The Osaka Basin, Japan is home to many high-rise buildings that sit atop its thick soft sediments, vulnerable to long-period strong ground motions that last minutes. A new map created by Japanese researchers is intended to guide engineers and city planners in new construction and identifies existing buildings with the potential of resonance vibration.
The Osaka Basin in western Japan is surrounded by short mountain ranges, affected by large (M 8+) interplate earthquakes ...
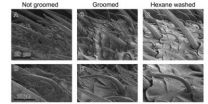
Grooming helps insects keep their senses sharpened
2013-02-05
Like a self-absorbed teenager, insects spend a lot of time grooming.
In a study that delves into the mechanisms behind this common function, North Carolina State University researchers show that insect grooming – specifically, antennal cleaning – removes both environmental pollutants and chemicals produced by the insects themselves.
The findings, published online this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show that grooming helps insects maintain acute olfactory senses that are responsible for a host of functions, including finding food, ...