(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
This video, created from a sequence of images from the Hubble Space Telescope, shows a pulse of light emanating from the protostellar object LRLL 54361. Most if not all of...
Click here for more information.
Two of NASA's great observatories, the Spitzer and Hubble space telescopes, have teamed up to uncover a mysterious infant star that behaves like a strobe light.
Every 25.34 days, the object, designated LRLL 54361, unleashes a burst of light. Although a similar phenomenon has been observed in two other young stellar objects, this is the most powerful such beacon seen to date.
The heart of the fireworks is hidden behind a dense disk and envelope of dust. Astronomers propose the light flashes are caused by periodic interactions between two newly formed stars that are binary, or gravitationally bound to each other. LRLL 54361 offers insights into the early stages of star formation when lots of gas and dust is being rapidly accreted, or pulled together, to form a new binary star.
Astronomers theorize the flashes are caused by material suddenly being dumped onto the growing stars, known as protostars. A blast of radiation is unleashed each time the stars get close to each other in their orbits. This phenomenon, called pulsed accretion, has been seen in later stages of star birth, but never in such a young system or with such intensity and regularity.
"This protostar has such large brightness variations with a precise period that it is very difficult to explain," said James Muzerolle of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md. His paper recently was published in the science journal Nature.
Discovered by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, LRLL 54361 is a variable object inside the star-forming region IC 348, located 950 light-years from Earth. Data from Spitzer revealed the presence of protostars. Based on statistical analysis, the two stars are estimated to be no more than a few hundred thousand years old.
The Spitzer infrared data, collected repeatedly during a period of seven years, showed unusual outbursts in the brightness of the suspected binary protostar. Surprisingly, the outbursts recurred every 25.34 days, which is a very rare phenomenon.
Astronomers used NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to confirm the Spitzer observations and reveal the detailed stellar structure around LRLL 54361. Hubble observed two cavities above and below a dusty disk. The cavities are visible by tracing light scattered off their edges. They likely were blown out of the surrounding natal envelope of dust and gas by an outflow launched near the central stars. The disk and the envelope prevent the suspected binary star pair from being observed directly. By capturing multiple images over the course of one pulse event, the Hubble observations uncovered a spectacular movement of light away from the center of the system, an optical illusion known as a light echo.
Muzerolle and his team hypothesized the pair of stars in the center of the dust cloud move around each other in a very eccentric orbit. As the stars approach each other, dust and gas are dragged from the inner edge of a surrounding disk. The material ultimately crashes onto one or both stars, which triggers a flash of light that illuminates the circumstellar dust. The system is rare because close binaries account for only a few percent of our galaxy's stellar population. This is likely a brief, transitory phase in the birth of a star system.
Muzerolle's team next plans to continue monitoring LRLL 54361 using other facilities including the European Space Agency's Herschel Space Telescope. The team hopes to eventually obtain more direct measurements of the binary star and its orbit.
INFORMATION:
For related images and video, visit:
http://hubblesite.org/news/2013/04
For more information on Hubble visit:
http://www.nasa.gov/hubble
http://hubblesite.org/
For more information on Spitzer, visit:
http://www.nasa.gov/spitzer
NASA telescopes discover strobe-like flashes in a suspected binary protostar
2013-02-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The amazing amphibians and reptiles of the Philippine island Luzon
2013-02-08
A recent study of the amphibians and reptiles of Sierra Madre Mountain Range, northeastern Luzon, reveals a preliminary enumeration of more than 100 species that contribute to the unique biodiversity of the region. At present, the Luzon region's herpetological range stands at more than 150 species. Out of these, a total of 49 amphibian species have been documented, 44 of which are native and a remarkable 32 endemic. In the world of reptiles, Luzon can boast with 106 native species, 76 of which are unique to this region.
The catalogue published in the open access journal ...
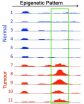
Colon cancer exhibits a corresponding epigenetic pattern in mice and humans
2013-02-08
Tumourigenesis is driven by genetic alterations and by changes in the epigenome, for instance by the addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases in the DNA. A deeper understanding of the interaction between the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms is critical for the selection of tumour biomarkers and for the future development of therapies. Human tumour specimens and cell lines however contain a plethora of genetic and epigenetic changes, which complicate data analysis. In contrast, certain mouse tumour models contain only a single genetic mutation and allow the analysis ...
Study identifies liver gene that regulates cholesterol and fat blood levels
2013-02-08
Researchers have identified a microRNA liver gene, miR-27b, which regulates lipid (cholesterol or fat) levels in the blood. This regulator gene controls multiple genes involved in dyslipidemia—abnormal blood cholesterol levels that can contribute to heart disease. Study details published in the February issue of Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), describe a new in silico approach to identify the significance of microRNAs in regulating disease-related gene pathways.
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed in ...
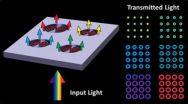
Boston College researchers' unique nanostructure produces novel 'plasmonic halos'
2013-02-08
CHESTNUT HILL, MA (February 7, 2013) – Using the geometric and material properties of a unique nanostructure, Boston College researchers have uncovered a novel photonic effect where surface plasmons interact with light to form "plasmonic halos" of selectable output color. The findings appear in the journal Nano Letters.
The novel nanostructure proved capable of manipulating electron waves known as surface plasmon polaritons, or SPPs, which were discovered in the 1950s but of late have garnered the attention of scientists for their potential applications in fields that ...
Specific warning signs of complications in colorectal surgical patients released
2013-02-08
Chicago (February 7, 2013): Colorectal surgical patients are often discharged from the hospital with vague guidance on how to recognize complications, but researchers at the Michael DeBakey Veterans Administration (VA) Medical Center and Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, aim to change that scenario. A health services research team convened a panel of surgical experts to develop a list of postoperative complication signs that should prompt colorectal surgical patients to call their surgeons or go to an emergency room. The study on the development of this early patient-centered ...
Dickkopf makes fountain of youth in the brain run dry
2013-02-08
The hippocampus – a structure of the brain whose shape resembles that of a seahorse – is also called the "gateway" to memory. This is where information is stored and retrieved. Its performance relies on new neurons being continually formed in the hippocampus over the entire lifetime. "However, in old age, production of new neurons dramatically decreases. This is considered to be among the causes of declining memory and learning ability", Prof. Dr. Ana Martin-Villalba, a neuroscientist, explains.
Martin-Villalba, who heads a research department at the German Cancer Research ...
Scientists find key to growth of 'bad' bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease
2013-02-08
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Scientists have long puzzled over why "bad" bacteria such as E. coli can thrive in the guts of those with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), causing serious diarrhea. Now UC Davis researchers have discovered the answer—one that may be the first step toward finding new and better treatments for IBD.
The researchers discovered a biological mechanism by which harmful bacteria grow, edge out beneficial bacteria and damage the gut in IBD. This new understanding, published in the Feb. 8 issue of Science, may help researchers develop new treatments for ...
Experimental gene therapy treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy offers hope for youngster
2013-02-08
Jacob Rutt is a bright 11-year-old who likes to draw detailed maps in his spare time. But the budding geographer has a hard time with physical skills most children take for granted -- running and climbing trees are beyond him, and even walking can be difficult. He was diagnosed with a form of muscular dystrophy known as Duchenne when he was two years old.
The disease affects about 1 in 3,500 newborns -- mostly boys -- worldwide. It usually becomes apparent in early childhood, as weakened skeletal muscles cause delays in milestones such as sitting and walking. Children ...
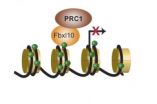
Protein paves the way for correct stem cell differentiation
2013-02-08
A single embryonic stem cell can develop into more than 200 specialized cell types that make up our body. This maturation process is called differentiation and is tightly regulated. If the regulation is lost, specialized cells cannot develop correctly during development. In adulthood, the specialized cells may forget their identity and develop into cancer cells. Research from BRIC, University of Copenhagen, has identified a crucial role of the molecule Fbxl10 in differentiation of embryonic stem cells and suggests the molecule as a new potential target for cancer therapy.
"Our ...
USC research finds certain contraceptive may pose risk of Type 2 diabetes for obese women
2013-02-08
Highlights of this news release:
Six-month study finds that progestin-releasing contraceptives show a slight negative impact on metabolic markers, raising the risk for type 2 diabetes.
Contraceptive implants under the skin increase the risk more than uterine implants.
Longer and larger studies are needed to see if metabolic changes are temporary or long-term.
LOS ANGELES – A first-of-its-kind study by researchers at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California (USC) indicates that healthy, obese, reproductive-age women who use long-acting ...