(Press-News.org) Researchers at Plymouth University, UK, believe that findings from fieldwork along the North Yorkshire coast reveal strong parallels between the Early Jurassic era of 180 million years ago and current climate predictions over the next century.
Through geology and palaeontology, they've shown how higher temperatures and lower oxygen levels caused drastic changes to marine communities, and that while the Jurassic seas eventually recovered from the effects of global warming, the marine ecosystems that returned were noticeably different from before.
The results of the Natural Environment Research Council-funded project are revealed for the first time in this month's PLOS ONE scientific journal.
Professor Richard Twitchett, from the University's School of Geography, Earth and Environmental Sciences, and a member of its Marine Institute, said: "Our study of fossil marine ecosystems shows that if global warming is severe enough and lasts long enough it may cause the extinction of marine life, which irreversibly changes the composition of marine ecosystems."
Professor Twitchett, with Plymouth colleagues Dr Silvia Danise and Dr Marie-Emilie Clemence, undertook fieldwork between Whitby and Staithes, studying the different sedimentary rocks and the marine fossils they contained. This provided information about the environmental conditions on the sea floor at the time the rocks were laid down.
The researchers, working with Dr Crispin Little from the University of Leeds, were then able to correlate the ecological data with published data on changes in temperature, sea level and oxygen concentrations.
Dr Danise said: "Back in the laboratory, we broke down the samples and identified all of the fossils, recording their relative abundance much like a marine biologist would do when sampling a modern environment. Then we ran the ecological analyses to determine how the marine seafloor community changed through time."
The team found a 'dead zone' recorded in the rock, which showed virtually no signs of life and contained no fossils. This was followed by evidence of a return to life, but with new species recorded.
Professor Twitchett added: "The results show in unprecedented detail how the fossil Jurassic communities changed dramatically in response to a rise in sea level and temperature and a decline in oxygen levels.
"Patterns of change suffered by these Jurassic ecosystems closely mirror the changes that happen when modern marine communities are exposed to declining levels of oxygen. Similar ecological stages can be recognised in the fossil and modern communities despite differences in the species present and the scale of the studies."
The NERC project – 'The evolution of modern marine ecosystems: environmental controls on their structure and function' – runs until March 2015, and is one of four funded under their Coevolution of Life and the Planet research programme.
INFORMATION:
Jurassic records warn of risk to marine life from global warming
2013-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Towards a new moth perfume
2013-02-19
A single mutation in a moth gene has been shown to be able to produce an entirely new scent. This has been shown in a new study led by researchers from Lund University in Sweden. In the long run, the researchers say that the results could contribute to tailored production of pheromones for pest control.
Male moths can pick up the scent of a female moth from a distance of several hundred metres. The females produce sexual pheromones – scent substances that guide the males to them. There are around 180 000 species of moth and butterfly in the world, and most of them communicate ...
Radio telescope, GPS use ionosphere to detect nuclear tests
2013-02-19
WASHINGTON--U.S. Naval Research Laboratory radio astronomer, Joseph Helmboldt, Ph.D., and researchers at Ohio State University Department of Civil, Environmental and Geodetic Engineering analyzed radio telescope interferometry and Global Positioning Satellite (GPS) data recorded of the ionosphere during one of the last underground nuclear explosions (UNEs) in the U.S., codenamed Hunters Trophy.
Situated in the Plains of San Agustin, 50 miles west of Socorro, New Mexico, twenty-seven 25-meter parabolic dish antennas collectively make up the National Radio Astronomy Observatory's ...
Private Security Industry must be made transparent and accountable, study concludes
2013-02-19
The true cost of war is being masked by the secretive and largely unaccountable activities of a private security industry, according to a new study.
These invisible costs of war – both in terms of casualties and financial resources – are not reported and are hard to find because contractors are not subject to the same reporting structures and laws as the regular military, and many of their activities are protected from Freedom of Information requests.
Private security firms – usually run by former senior figures in the military, civil service or politics – are increasingly ...
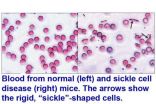
Could an old antidepressant treat sickle cell disease?
2013-02-19
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — An antidepressant drug used since the 1960s may also hold promise for treating sickle cell disease, according to a surprising new finding made in mice and human red blood cells by a team from the University of Michigan Medical School.
The discovery that tranylcypromine, or TCP, can essentially reverse the effects of sickle cell disease was made by U-M scientists who have spent more than three decades studying the basic biology of the condition, with funding from the National Institutes of Health.
Their findings, published in Nature Medicine, pave ...
Buying ad time just got easier
2013-02-19
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Today's consumers switch between media forms so often – from TV to laptops to smart phones – that capturing their attention with advertising has gone, as one CEO explained, from shooting fish in a barrel to shooting minnows.
Now, a Michigan State University business scholar and colleagues have developed the most accurate model yet for targeting those fast-moving minnows. The research-based model predicts when during the day people use the varying forms of media and even when they are using two or more at a time, an increasingly common practice known ...
Could a computer on the police beat prevent violence?
2013-02-19
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — As cities across America work to reduce violence in tight budget times, new research shows how they might be able to target their efforts and police attention – with the help of high-powered computers and loads of data.
In a newly published paper, University of Michigan Medical School researchers and their colleagues have used real police data from Boston to demonstrate the promise of computer models in zeroing in on violent areas.
They combined and analyzed information in small geographic units, on police reports, drug offenses, and alcohol availability ...
Russian fireball largest ever detected by CTBTO's infrasound sensors
2013-02-19
Infrasonic waves from the meteor that broke up over Russia's Ural mountains last week were the largest ever recorded by the CTBTO's International Monitoring System. Infrasound is low frequency sound with a range of less than 10 Hz. The blast was detected by 17 infrasound stations in the CTBTO's network, which tracks atomic blasts across the planet. The furthest station to record the sub-audible sound was 15,000km away in Antarctica.
The origin of the low frequency sound waves from the blast was estimated at 03:22 GMT on 15 February 2013. People cannot hear the low frequency ...
Researchers create semiconductor 'nano-shish-kebabs' with potential for 3-D technologies
2013-02-19
Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed a new type of nanoscale structure that resembles a "nano-shish-kebab," consisting of multiple two-dimensional nanosheets that appear to be impaled upon a one-dimensional nanowire. But looks can be deceiving, as the nanowire and nanosheets are actually a single, three-dimensional structure consisting of a single, seamless series of germanium sulfide (GeS) crystals. The structure holds promise for use in the creation of new, three-dimensional (3-D) technologies.
The researchers believe this is the first engineered ...
Theory of crystal formation complete again
2013-02-19
Exactly how a crystal forms from solution is a problem that has occupied scientists for decades. Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e), together with researchers from Germany and the USA, are now presenting the missing piece. This classical theory of crystal formation, which occurs widely in nature and in the chemical industry, was under fire for some years, but is saved now. The team made this breakthrough by detailed study of the crystallization of the mineral calcium phosphate –the major component of our bones. The team published their findings yesterday ...
New study shows how seals sleep with only half their brain at a time
2013-02-19
TORONTO, ON – A new study led by an international team of biologists has identified some of the brain chemicals that allow seals to sleep with half of their brain at a time.
The study was published this month in the Journal of Neuroscience and was headed by scientists at UCLA and the University of Toronto. It identified the chemical cues that allow the seal brain to remain half awake and asleep. Findings from this study may explain the biological mechanisms that enable the brain to remain alert during waking hours and go off-line during sleep.
"Seals do something biologically ...