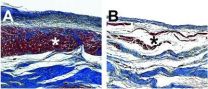
(Press-News.org) University of California, San Diego bioengineers have demonstrated in a study in pigs that a new injectable hydrogel can repair damage from heart attacks, help the heart grow new tissue and blood vessels, and get the heart moving closer to how a healthy heart should. The results of the study were published Feb. 20 in Science Translational Medicine and clear the way for clinical trials to begin this year in Europe. The gel is injected through a catheter without requiring surgery or general anesthesia -- a less invasive procedure for patients.
There are an estimated 785,000 new heart attack cases in the United States each year, with no established treatment for repairing the resulting damage to cardiac tissue. Lead researcher Karen Christman, a professor in the Department of Bioengineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, said the gel forms a scaffold in damaged areas of the heart, encouraging new cell growth and repair. Because the gel is made from heart tissue taken from pigs, the damaged heart responds positively, creating a harmonious environment for rebuilding, rather than setting off a chain of adverse immune system defenses.
"While more people today are initially surviving heart attacks, many will eventually go into heart failure," said Christman. "Our data show that this hydrogel can increase cardiac muscle and reduce scar tissue in the region damaged by the heart attack, which prevents heart failure. These results suggest this may be a novel minimally invasive therapy to prevent heart failure after a heart attack in humans."
The hydrogel is made from cardiac connective tissue that is stripped of heart muscle cells through a cleansing process, freeze-dried and milled into powder form, and then liquefied into a fluid that can be easily injected into the heart. Once it hits body temperature, the liquid turns into a semi-solid, porous gel that encourages cells to repopulate areas of damaged cardiac tissue and to improve heart function, according to Christman. The material is also biocompatible; animals treated with the hydrogel suffered no adverse affects such as inflammation, lesions or arrhythmic heart beating, according to safety experiments conducted as part of the study. Further tests with human blood samples showed that the gel had no effect on the blood's clotting ability, which underscores the biocompatibility of the treatment for use in humans.
San Diego-based startup, Ventrix, Inc., which Christman co-founded, has licensed the technology for development and commercialization. Christman also serves on the company's board. "We are excited and encouraged by the results of the study leading to a novel regenerative medicine solution for cardiac repair. The technology offers the potential for a longer and better quality of life for millions of heart attack sufferers," said Adam Kinsey, the CEO of Ventrix.
INFORMATION:
Video available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=COTh-nAQifs&feature=player_embedded
New injectable hydrogel encourages regeneration and improves functionality after a heart attack
2013-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers find multiple tests needed to detect infection in low birth-weight newborns
2013-02-21
New research by Case Western Reserve University School of Dental Medicine and Yale University School of Medicine finds that cultures commonly used to detect bacterial infections in low birth-weight newborns with early onset sepsis may actually overlook some germs.
The research done at Case Western Reserve supports the need for multiple detection methods, such as DNA genomic analyses and other independent culture technologies, to identify bacteria that culturing may miss, said Yiping Han, professor of Periodontics and Reproductive Biology at the Case Western Reserve dental ...
Digital processing system avoids 17.4 million drug errors in US in 1 year
2013-02-21
Processing a prescription through an electronic ordering system can halve the likelihood of a drug error, and avert more than 17 million such incidents in US hospitals in one year alone, indicates research published online in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.
And if much more widely adopted than at present, the system has the potential to cut out 50 million drug errors a year, calculate the researchers.
The US Institute of Medicine estimates that, on average, at least one mistake will be made with a hospital patient's medication every day.
Computerised ...
Myth that UK supply of innovative new pharma drugs is drying up
2013-02-21
The widely held belief that the UK supply of innovative new medicines has conspicuously dwindled in recent decades, is not borne out by the evidence, reveals research published in the online journal BMJ Open.
In fact, the reverse may be true, the figures suggest.
The prevailing view is that pharmaceutical industry innovation has been in decline, with fewer new drugs launched in recent decades than before—despite more cash being pumped into research and development—prompting a good deal of hand-wringing, say the authors.
They wanted to find out whether this view was ...
Bullied children can suffer lasting psychological harm as adults
2013-02-21
DURHAM, NC – Bullied children grow into adults who are at increased risk of developing anxiety disorders, depression and suicidal thoughts, according to a study led by researchers at Duke Medicine.
The findings, based on more than 20 years of data from a large group of participants initially enrolled as adolescents, are the most definitive to date in establishing the long-term psychological effects of bullying.
Published online Feb. 20, 2013, in JAMA Psychiatry, the study belies a common perception that bullying, while hurtful, inflicts a fleeting injury that victims ...
Scrap 'unwinnable' drugs war and divert funds into curbing global antibiotic misuse
2013-02-21
Governments around the world should stop squandering resources fighting an "unwinnable war" against illegal drugs, such as cocaine and heroin. Instead, they should use the cash to curb antibiotic misuse, which poses a far more serious threat to human health, claims a leading ethicist in the Journal of Medical Ethics.
Dr Jonny Anomaly, of Duke University, Durham in North Carolina, USA, says that concerted collective action is needed to tackle the excessive and casual prescribing of antibiotics, which has led to a worrying rise in resistance to these medicines.
"Government ...
Human heart tissue development slower than other mammals
2013-02-21
The walls of the human heart are a disorganised jumble of tissue until relatively late in pregnancy despite having the shape of a fully functioning heart, according to a pioneering study.
A University of Leeds-led team developing the first comprehensive model of human heart development using observations of living foetal hearts found surprising differences from existing animal models.
Although they saw four clearly defined chambers in the foetal heart from the eighth week of pregnancy, they did not find organised muscle tissue until the 20th week, much later than expected.
Developing ...
'I'm not just fat, I'm old!'
2013-02-21
Similar to talking about being fat, talking about being old is an important an indicator of body dissatisfaction, shows research in BioMed Central's open access journal Journal of Eating Disorders.
Body dissatisfaction is known to be correlated with, and predictive of, physical and mental health problems including binge eating, emotional eating, stress, low self-esteem, depression, and use of unhealthy weight control behaviours. High levels of talking about weight and being fat, 'fat talk', is known to be a good indicator of body dissatisfaction.
In order to see if ...
Bracelet-like device controls chronic acid reflux, study finds
2013-02-21
VIDEO ALERT: Audio and video resources, including excerpts from an interview with Dr. C. Daniel Smith describing the device and procedure, are available on the Mayo Clinic News Network.
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — A bracelet-like device with magnetic beads can control the chronic digestive disorder gastroesophageal reflux disease, according to a study published online today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The device encircles the valve at the junction of the esophagus and stomach and helps it stay closed when a person is not eating or drinking. It eased symptoms ...
Using 3-D printing and injectable molds, bioengineered ears look and act like the real thing
2013-02-21
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell bioengineers and physicians have created an artificial ear – using 3-D printing and injectable molds – that looks and acts like a natural ear, giving new hope to thousands of children born with a congenital deformity called microtia.
In a study published online Feb. 20 in PLOS ONE, Cornell biomedical engineers and Weill Cornell Medical College physicians described how 3-D printing and injectable gels made of living cells can fashion ears that are practically identical to a human ear. Over a three-month period, these flexible ears grew cartilage ...
Building trust for online health research
2013-02-21
Status updates, patient forums, blog comments – among the incredible amount of personal information on the Web is a potential trove of health data. Bioethicists writing in Science Translational Medicine acknowledge the value of this resource but argue that to be ethically acceptable for use in research, traditional models of informed consent must be adapted to suit the dynamic online environment.
"Context is crucial to what people reveal about themselves on the Web, and it should be central to how informed consent is obtained," says co-author Jeffrey Kahn, PhD, MPH, the ...