(Press-News.org) Voracious absences at the center of galaxies, black holes shape the growth and death of the stars around them through their powerful gravitational pull and explosive ejections of energy.
"Over its lifetime, a black hole can release more energy than all the stars in a galaxy combined," said Roger Blandford, director of the Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology and a member of the U.S. National Academy of Science. "Black holes have a major impact on the formation of galaxies and the environmental growth and evolution of those galaxies."
Gravitational forces grow so strong close to a black hole that even light cannot escape from within, hence the difficulty in observing them directly. Scientists infer facts about black holes by their influence on the astronomical objects around them: the orbit of stars and clumps of detectable energy.
With this information in hand, scientists create computer models to understand the data and to make predictions about the physics of distant regions of space. However, models are only as good as their assumptions.
"All tests of general relativity in the weak gravity field limit, like in our solar system, fall directly along the lines of what Einstein predicted," explained Jonathan McKinney, an assistant professor of physics at the University of Maryland at College Park. "But there is another regime—which has yet to be tested, and which is the hardest to test—that represents the strong gravitational field limit. And according to Einstein, gravity is strongest near black holes."
This makes black holes the ultimate experimental testing grounds for Einstein's theory of general relativity.
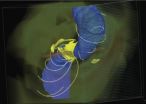
While black holes cannot be observed, they are typically accompanied by other objects with distinctive features that can be seen, including accretion disks, which are circling disks of superhot matter on our side of the black hole's "event horizon"; and relativistic jets, high-powered streams of ionized gases that shoot hundreds of thousands of light years across the sky.
In a paper published in Science in January 2013, McKinney, Tchekhovskoy and Blandford predicted the formation of accretion disks and relativistic jets that warp and bend more than previously thought, shaped both by the extreme gravity of the black hole and by powerful magnetic forces generated by its spin. Their highly detailed models of the black hole environment contribute new knowledge to the field.
For decades, a simplistic view of the accretion disks and polar jets reigned. It was widely believed that accretion disks sat like flat plates along the outer edges of black holes and that jets shot straight out perpendicularly. However, new 3D simulations performed on the powerful supercomputers of the National Science Foundation's Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE) and NASA overturned this oversimplified view of jets and disks.
The simulations show that the jet is aligned with the black hole's spin near the black hole but that it gradually gets pushed by the disk material and becomes parallel to (but offset from) the disk's rotational axis at large distances. The interaction between the jet and disk leaves a warp in the accretion disk density.
"An important aspect that determines jet properties is the strength of the magnetic field threading the black hole," said Alexander Tchekhovskoy, a post-doctoral fellow at the Princeton Center for Theoretical Science. "While in previous works it was a free parameter, in our series of works the field is maximum: it is as strong as a black hole's gravity pull on the disk."
In the simulations, the twisting energy grows so strong that it actually powers the jet. In fact, the jet can reorient the accretion disk, rather than the other way around, as was thought previously.
"People had thought that the disk was the dominant aspect," McKinney said. "It was the dog and the jet was the wagging tail. But we found that the magnetic field builds up to become stronger than gravity, and then the jet becomes the dog and the disk becomes the wagging tail. Or, one can say the dog is chasing its own tail, because the disk and jet are quite balanced, with the disk following the jet — it's the inverse situation to what people thought."
What does this have to do with Einstein and his theory of general relativity?
Astronomers are closer than ever to being able to see the details of the jets and accretion disks around black holes. In a September 2012 paper in Science, Sheperd Doeleman of MIT reported the first images of the jet-launching structure near the supermassive black hole, M87, at the center of a neighboring galaxy, captured using the Event Horizon Telescope, a very long baseline interferometry (VLBI) array composed of four telescopes at three geographical locations. It constituted a small sliver of a vast skyscape, yet the results give astronomers like McKinney, Tchekhovskoy and Blandford the hope that they will get their first comprehensive glimpse into the black hole's neighborhood in the next three to five years.
"We'll see the gases swirl around the black hole and other optical effects that will be signatures of a black holes in spacetime that one can look out for," said Blandford.
The observations will either match models like theirs, or they will be different. Both outcomes will tell researchers a lot.
"If you don't have an accurate model and anything can happen as far as you understand, then you're not going to be able to make any constraints and prove one way or another whether Einstein was right," McKinney explained. "But if you have an accurate model using Einstein's equations, and you observe a black hole that is very different from what you expected, then you can begin to say that he may be wrong."
The model Blandford and others generated using supercomputing simulations will help serve that comparative role. But they need to add one crucial element to make the simulations meaningful: a way of translating the physics of the black hole system into a visual signal as it would be seen from the vantage point of our telescopes, billions of light years away.
"We're in the process of making our simulations shine, so they can be compared with observations," McKinney said, "not only to test our ideas of how these disks and jets work, but ultimately to test general relativity."
INFORMATION:
Journey to the limits of spacetime
Black hole simulations on XSEDE supercomputers present new view of jets and accretion disks
2013-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Baylor University researchers study barriers, resources to physical activity in Texas towns
2013-02-21
WACO, Texas (Feb. 20, 2013) —Obesity, diabetes and other ailments plague impoverished communities at higher rates than the general United States population. In rural Texas border towns, or colonias, Mexican-American residents are at an even greater risk for chronic health problems.
Physical activity has shown to reduce the risks for chronic health problems, but "few Mexican-American and lower-income Americans, including children, engage in physical activity that bring about health benefits," according to a study conducted by Baylor University and Texas A&M University ...
How human language could have evolved from birdsong
2013-02-21
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- "The sounds uttered by birds offer in several respects the nearest analogy to language," Charles Darwin wrote in "The Descent of Man" (1871), while contemplating how humans learned to speak. Language, he speculated, might have had its origins in singing, which "might have given rise to words expressive of various complex emotions."
Now researchers from MIT, along with a scholar from the University of Tokyo, say that Darwin was on the right path. The balance of evidence, they believe, suggests that human language is a grafting of two communication forms ...
Facing disaster while averting tragedy
2013-02-21
This press release is available in French.
Montreal, February 21, 2013 – Nobody can foresee disaster, but changing climate conditions are prompting smart communities increasingly to prepare for them with solid emergency response plans and protocols. Images as recent as those from the 2011 wildfire in Slave Lake, Alberta or as distant as those from the 1998 ice storm in Eastern Ontario and Quebec are distressing reminders that no area is immune from devastation, and reinforce the need to be prepared.
Yet while emergency responses may originate through official channels, ...
Antioxidants in your diet may not reduce risk of stroke or dementia
2013-02-21
MINNEAPOLIS – Contrary to other research, a new study found that the total level of antioxidants in people's diets is not related to their risk of developing stroke or dementia. The study is published in the February 20, 2013, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Antioxidants such as lycopene, beta-carotene and vitamins C and E are found in many foods.
"These results are interesting because other studies have suggested that antioxidants may help protect against stroke and dementia," said study author Elizabeth E. Devore, ...
New research on migratory behavior of oceanic whitetip sharks can help shape conservation strategies
2013-02-21
STONY BROOK, NY, February 20, 2013–As the nations of the world prepare to vote on measures to restrict international trade in endangered sharks in early March, a team of researchers has found that one of these species – the oceanic whitetip shark – regularly crosses international boundaries. Efforts by individual nations to protect this declining apex predator within their own maritime borders may therefore need to be nested within broader international conservation measures.
The research team, which included researchers from Microwave Telemetry, Inc., the Cape Eleuthera ...
Study advances LSUHSC research, shows fish oil component reduces brain damage in newborns
2013-02-21
New Orleans, LA – Research conducted by a team of scientists from Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons and Dr. Nicolas Bazan, Boyd Professor and Director of the Neuroscience Center of Excellence at LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, found the novel use of a component of fish oil reduced brain trauma in newborn mice. The study reports that neonatal brain damage decreased by about 50% when a triglyceride lipid emulsion containing docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) was injected within two hours of the onset of ischemic stroke. The paper, n-3 Fatty Acid Rich ...
Omega-3 lipid emulsions markedly protect brain after stroke in mouse study
2013-02-21
New York, NY (February 20, 2013) — Triglyceride lipid emulsions rich in an omega-3 fatty acid injected within a few hours of an ischemic stroke can decrease the amount of damaged brain tissue by 50 percent or more in mice, reports a new study by researchers at Columbia University Medical Center.
The results suggest that the emulsions may be able to reduce some of the long-term neurological and behavioral problems seen in human survivors of neonatal stroke and possibly of adult stroke, as well. The findings were published today in the journal PLoS One.
Currently, clot-busting ...
Creeping epidemic of obesity hits Asia Pacific region
2013-02-21
Sophia Antipolis, 21 February 2013: Over eating, sedentary lifestyles, cultural attitudes, and lack of prevention programmes are to blame for the rising epidemic of obesity in the Asia Pacific region. Overweight and obesity has quadrupled in China and societies still label people of healthy weight as poor.
Prevention will be an important theme at the 19th Asian Pacific Congress of Cardiology held 21-24 February 2013 in Pattaya, Thailand. Experts from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) will lead a one day collaborative programme on 23 February.
Professor Kui-Hian ...
Organic tomatoes accumulate more vitamin C, sugars than conventionally grown fruit
2013-02-21
Tomatoes grown on organic farms accumulate higher concentrations of sugars, vitamin C and compounds associated with oxidative stress compared to those grown on conventional farms, according to research published February 20 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Maria Raquel Alcantara Miranda and colleagues from the Federal University of Ceara, Brazil.
In their study, the researchers compared the weights and biochemical properties of tomatoes from organic and conventional farms. They found that tomatoes grown on organic farms were approximately 40% smaller than those ...
People with disabilities at greater risk of violence and subsequent mental ill-health
2013-02-21
People with disabilities are at a greater risk of being the victims of violence and of suffering mental ill health when victimized, according to research published February 20 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Hind Khalifeh and colleagues from University College London and King's College London.
A recent World Report on Disability highlighted violence as a leading cause of morbidity among disabled people. The research published today is the first to assess the extent to which people with disabilities experience different kinds of violence and the associated health ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Journey to the limits of spacetimeBlack hole simulations on XSEDE supercomputers present new view of jets and accretion disks