(Press-News.org) National Science Foundation- (NSF) funded researchers at Amherst College in Massachusetts and the University of Texas at Austin have described a new technique based in particle physics that might one day reveal, in more detail than ever before, the composition and characteristics of the deep Earth.
There's just one catch: the technique relies on a fifth force of nature that has not yet been detected, but some particle physicists think it might exist. The fifth force would be in addition to gravity, the weak and strong nuclear forces and electromagnetism.
Physicists call this fifth force a long-range spin-spin interaction. As theorized, the fifth force would rely on the building blocks of atoms (electrons, protons and neutrons), separated over vast distances, to "feel" each other's presence.
If it does exist, this exotic new force would connect matter at Earth's surface with matter hundreds or even thousands of miles deep within Earth's mantle and could potentially provide new information about the composition and characteristics of deep Earth, which is poorly understood because of its inaccessibility.
"The most rewarding and surprising thing about this project was realizing that particle physics could actually be used to study the deep Earth," says Jung-Fu "Afu" Lin, associate professor at the University of Texas at Austin's Jackson School of Geosciences and co-author of the study appearing this week in the journal Science.
The research was supported by NSF's Geoscience and Mathematical and Physical Science Directorates, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), and the Carnegie/DOE Alliance Center.
This new force could help settle a scientific quandary. When earth scientists previously have tried to model how factors such as iron concentration and physical and chemical properties of matter vary with depth--for example, using the way earthquake rumbles travel through the Earth or through laboratory experiments designed to mimic the intense temperatures and pressures of the deep Earth--they get different answers. The fifth force, assuming it exists, might help reconcile these conflicting lines of evidence.
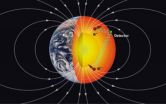
Earth's mantle is a thick geological layer sandwiched between the thin outer crust and central core, made up mostly of iron-bearing minerals. The atoms in these minerals and the subatomic particles making up the atoms have a property called spin.
Spin can be thought of as an arrow that points in a particular direction. It is thought that Earth's magnetic field causes some of the electrons in these mantle minerals to become slightly spin-polarized, meaning the directions in which they spin are no longer completely random, but have some preferred orientation. These electrons have been dubbed "geoelectrons."
The goal of this project was to see whether the scientists could use the proposed long-range spin-spin interaction to detect the presence of these distant geoelectrons.
The researchers, led by Larry Hunter, professor of physics at Amherst College, first created a computer model of Earth's interior to map the expected densities and spin directions of geoelectrons. The model was based in part on insights gained from Lin's laboratory experiments, which measure electron spins in minerals at the high temperatures and pressures of Earth's interior. This map gave the researchers clues about the strength and orientations of interactions they might expect to detect in their laboratory in Amherst, Mass.
Second, the researchers used a specially designed apparatus to search for interactions between geoelectrons deep in the mantle and subatomic particles at Earth's surface. The team's experiments essentially explored whether the spins of electrons, neutrons or protons in various laboratories might have a different energy, depending on the direction with respect to the Earth that they were pointing.
"We know, for example, that a magnet has a lower energy when it is oriented parallel to the geomagnetic field and it lines up with this particular direction--that is how a compass works," Hunter says. "Our experiments removed this magnetic interaction and looked to see if there might be some other interaction with our experimental spins. One interpretation of this 'other' interaction is that it could be a long-range interaction between the spins in our apparatus and the electron spins within the Earth, that have been aligned by the geomagnetic field. This is the long-range spin-spin interaction we were looking for."
Although the apparatus was not able to detect any such interactions, the researchers could at least infer that such interactions, if they exist, must be incredibly weak--no more than a millionth of the strength of the gravitational attraction between the particles. That's useful information as scientists now look for ways to build ever more sensitive instruments to search for the elusive fifth force.
"No one had previously thought about the possible interactions that might occur between the Earth's spin-polarized electrons and precision laboratory spin-measurements," says Hunter.
If the long-range spin-spin interactions are discovered in future experiments, "geoscientists can eventually use such information to reliably understand the geochemistry and geophysics of the planet's interior," says Lin.
INFORMATION:
-NSF-
NSF-funded researchers propose promising new technique for probing Earth's deep interior
Approach is based on theoretical particle physics
2013-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Formation of nanoparticles can now be studied molecule-by-molecule
2013-02-22
The study combines the cycles of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon in the ecosystem, as it shows that the molecular clusters need sulphuric acid, amines and oxygenated organics for growth. When the clusters reach a size of 1.5-2 nm, their growth increases considerably. The measurements were conducted at the University of Helsinki SMEAR II (Station for Measuring Forest Ecosystem-Atmosphere Relations) measurement station in Hyytiälä, southern Finland, which is among the most comprehensive stations in the world for atmosphere and biosphere research.
During the last five years, ...
Fruit flies force their young to drink alcohol -- for their own good
2013-02-22
When fruit flies sense parasitic wasps in their environment, they lay their eggs in an alcohol-soaked environment, essentially forcing their larvae to consume booze as a drug to combat the deadly wasps.
The discovery by biologists at Emory University is being published in the journal Science on Friday, February 22.
"The adult flies actually anticipate an infection risk to their children, and then they medicate them by depositing them in alcohol," says Todd Schlenke, the Emory evolutionary geneticist whose lab led the research. "We found that this medicating behavior ...
Light from silicon nanocrystal LEDs
2013-02-22
This press release is available in German.
Silicon nanocrystals have a size of a few nanometers and possess a high luminous potential. Scientists of KIT and the University of Toronto/Canada have now succeeded in manufacturing silicon-based light-emitting diodes (SiLEDs). They are free of heavy metals and can emit light in various colors. The team of chemists, materials researchers, nanoscientists, and opto-electronic experts presents its development in the "Nano Letters" journal (DOI: 10.1021/nl3038689).
Silicon dominates in microelectronics and photovoltaics ...
Has evolution given humans unique brain structures?
2013-02-22
Our ancestors evolutionarily split from those of rhesus monkeys about 25 million years ago. Since then, brain areas have been added, have disappeared or have changed in function. This raises the question, 'Has evolution given humans unique brain structures?'. Scientists have entertained the idea before but conclusive evidence was lacking. By combining different research methods, we now have a first piece of evidence that could prove that humans have unique cortical brain networks.
Professor Vanduffel explains: "We did functional brain scans in humans and rhesus monkeys ...
Controversial dam removals founded on value conflicts
2013-02-22
Researchers at Umeå University in Sweden conclude that public opposition to dam removal is not based on knowledge deficiency, as is sometimes argued in dam removal science. It is instead a case of different understandings and valuation of the environment and the functions it provides. The findings are now published in the journal Ecology and Society.
Dam removal is an increasingly common practice as old splash dams and small hydropower dams have become obsolete. Although the removal of these dams has ecological benefits by restoring rivers to their former courses, local ...
Reforming US research ethics: Alex John London calls for system that works for all stakeholders
2013-02-22
PITTSBURGH—At a time when the U.S. government is contemplating changes to federal guidelines governing research with humans, serious questions are being raised about the role of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in overseeing such research. Particularly, vocal critics have cited lost time, money and even lives under a system that they claim consumes scarce resources and stifles academic freedom. In response, defenders of the IRB system point to the need to protect research participants from abuse.
Carnegie Mellon University's Alex John London, an internationally renowned ...
Genomic detectives crack the case of the missing heritability
2013-02-22
Despite years of research, the genetic factors behind many human diseases and characteristics remain unknown. The inability to find the complete genetic causes of family traits such as height or the risk of type 2 diabetes has been called the "missing heritability" problem.
A new study by Princeton University researchers, however, suggests that missing heritability may not be missing after all — at least not in yeast cells, which the researchers used as a model for studying the problem. Published in the journal Nature, the results suggest that heritability in humans ...
Researchers find appointed justices outperform elected counterparts
2013-02-22
State supreme court justices who don't face voters are generally more effective than their elected counterparts, according to research led by Princeton University political scientists.
The research combines data about almost 6,000 state supreme court rulings nationwide between 1995 and 1998 with a new theoretical model to reach the conclusions that appointed justices generally bring a higher quality of information to the decision-making process, are more likely to change their preconceived opinions about a case, and are less likely to make errors than elected justices.
"Judges ...
1 week and counting: Don't cut the research that fuels the US economy
2013-02-22
WASHINGTON, DC – With only one week left before sequestration is to take effect, America's research community sustained its call for an end to the across-the-board cuts to discretionary spending that will severely restrict the nation's ability to invest in the basic scientific research that drives innovation and produces economic growth. Sequestration will reduce federal funding for scientific research by nearly $95 billion over the next nine years, which will result in a reduction of U.S. GDP by at least $203 billion. The net impact will be 200,000 fewer jobs per year ...
Israel rocket attacks increase miscarriage likelihood -- Ben-Gurion U. research study
2013-02-22
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, February 21, 2013 -- Rocket attacks in Sderot, Israel significantly increase the likelihood of miscarriages, according to a new study by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) researchers.
The study, published in the January issue of Psychosomatic Medicine Journal of Bio-behavioral Medicine, compared 1,341 pregnancies of women (exposed group) who resided in Sderot, an area exposed to frequent rocket fire, with 2,143 pregnancies of women who lived in Kiryat Gat (unexposed group), which is out of range of missiles. Among women residing in the exposed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] NSF-funded researchers propose promising new technique for probing Earth's deep interiorApproach is based on theoretical particle physics