(Press-News.org) When fruit flies sense parasitic wasps in their environment, they lay their eggs in an alcohol-soaked environment, essentially forcing their larvae to consume booze as a drug to combat the deadly wasps.
The discovery by biologists at Emory University is being published in the journal Science on Friday, February 22.
"The adult flies actually anticipate an infection risk to their children, and then they medicate them by depositing them in alcohol," says Todd Schlenke, the Emory evolutionary geneticist whose lab led the research. "We found that this medicating behavior was shared by diverse fly species, adding to the evidence that using toxins in the environment to medicate offspring may be common across the animal kingdom."
Adult fruit flies detect the wasps by sight, and appear to have much better vision than previously realized, he adds. "Our data indicate that the flies can visually distinguish the relatively small morphological differences between male and female wasps, and between different species of wasps."
The experiments were led by Balint Zacsoh, who recently graduated from Emory with a degree in biology and still works in the Schlenke lab. The team also included Emory graduate student Zachary Lynch and postdoc Nathan Mortimer.
The larvae of the common fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, eat the rot, or fungi and bacteria, that grows on overripe, fermenting fruit. They have evolved a certain amount of resistance to the toxic effects of the alcohol levels in their natural habitat, which can range up to 15 percent.
Tiny, endoparasitoid wasps are major killers of fruit flies. The wasps inject their eggs inside the fruit fly larvae, along with venom that aims to suppress their hosts' cellular immune response. If the flies fail to kill the wasp egg, a wasp larva hatches inside the fruit fly larva and begins to eat its host from the inside out.
Last year, the Schlenke lab published a study showing how fruit fly larvae infected with wasps prefer to eat food high in alcohol. This behavior greatly improves the survival rate of the fruit flies because they have evolved high tolerance of the toxic effects of the alcohol, but the wasps have not.
"The fruit fly larvae raise their blood alcohol levels, so that the wasps living in their blood will suffer," Schlenke says. "When you think of an immune system, you usually think of blood cells and immune proteins, but behavior can also be a big part of an organism's immune defense."
For the latest study, the researchers asked whether the fruit fly parents could sense when their children were at risk for infection, and whether they then sought out alcohol to prophylactically medicate them.
Adult female fruit flies were released in one mesh cage with parasitic wasps and another mesh cage with no wasps. Both cages had two petri dishes containing yeast, the nourishment for lab-raised fruit flies and their larvae. The yeast in one of the petri dishes was mixed with 6 percent alcohol, while the yeast in the other dish was alcohol free. After 24 hours, the petri dishes were removed and the researchers counted the eggs that the fruit flies had laid.
The results were dramatic. In the mesh cage with parasitic wasps, 90 percent of the eggs laid were in the dish containing alcohol. In the cage with no wasps, only 40 percent of the eggs were in the alcohol dish.
"The fruit flies clearly change their reproductive behavior when the wasps are present," Schlenke says. "The alcohol is slightly toxic to the fruit flies as well, but the wasps are a bigger danger than the alcohol."
The fruit flies strains used in the experiments have been bred in the lab for decades. "The flies that we work with have not seen wasps in their lives before, and neither have their ancestors going back hundreds of generations," Schlenke says. "And yet, the flies still recognize these wasps as a danger when they are put in a cage with them."
Further experiments showed that the flies are extremely discerning about differences in the wasps. They preferred to lay their eggs in alcohol when female wasps were present, but not if only male wasps were in the cage.
Theorizing that the flies were reacting to pheromones, the researchers conducted experiments using two groups of mutated fruit flies. One group lacked the ability to smell, and another group lacked sight. The flies unable to smell, however, still preferred to lay their eggs in alcohol when female wasps were present. The blind flies did not make the distinction, choosing the non-alcohol food for their offspring, even in the presence of female wasps.
"This result was a surprise to me," Schlenke says. "I thought the flies were probably using olfaction to sense the female wasps. The small, compound eyes of flies are believed to be more geared to detecting motion than high-resolution images."
The only obvious visual differences between the female and male wasps, he adds, is that the males have longer antennae, slightly smaller bodies, and lack an ovipositor.
Further experimentation showed that the fruit flies can distinguish different species of wasps, and will only choose the alcohol food in response to wasp species that infect larvae, not fly pupae. "Fly larvae usually leave the food before they pupate," Schlenke explains, "so there is likely little benefit to laying eggs at alcoholic sites when pupal parasites are present."
The researchers also connected the exposure to female parasitic wasps to changes in a fruit fly neuropeptide.
Stress, and the resulting reduced level of neuropeptide F, or NPF, has previously been associated with alcohol-seeking behavior in fruit flies. Similarly, the level of a homologous neuropeptide in humans, NPY, is associated with alcoholism.
"We found that when a fruit fly is exposed to female parasitic wasps, this exposure reduces the level of NPF in the fly brain, causing the fly to seek out alcoholic sites for oviposition," Schlenke says. "Furthermore, the alcohol-seeking behavior appears to remain for the duration of the fly's life, even when the parasitic wasps are no longer present, an example of long-term memory."
Finally, Drosophila melanogaster is not unique in using this offspring medication behavior. "We tested a number of fly species," Schlenke says, "and found that each fly species that uses rotting fruit for food mounts this immune behavior against parasitic wasps. Medication may be far more common in nature than we previously thought."
###
Emory University is known for its demanding academics, outstanding undergraduate experience, highly ranked professional schools and state-of-the-art research facilities. Emory encompasses nine academic divisions as well as the Carlos Museum, The Carter Center, the Yerkes National Primate Research Center and Emory Healthcare, Georgia's largest and most comprehensive health care system. END
Fruit flies force their young to drink alcohol -- for their own good
Fruit fly study adds to evidence that using toxins in the environment to medicate offspring may be common across the animal kingdom
2013-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Light from silicon nanocrystal LEDs
2013-02-22
This press release is available in German.
Silicon nanocrystals have a size of a few nanometers and possess a high luminous potential. Scientists of KIT and the University of Toronto/Canada have now succeeded in manufacturing silicon-based light-emitting diodes (SiLEDs). They are free of heavy metals and can emit light in various colors. The team of chemists, materials researchers, nanoscientists, and opto-electronic experts presents its development in the "Nano Letters" journal (DOI: 10.1021/nl3038689).
Silicon dominates in microelectronics and photovoltaics ...
Has evolution given humans unique brain structures?
2013-02-22
Our ancestors evolutionarily split from those of rhesus monkeys about 25 million years ago. Since then, brain areas have been added, have disappeared or have changed in function. This raises the question, 'Has evolution given humans unique brain structures?'. Scientists have entertained the idea before but conclusive evidence was lacking. By combining different research methods, we now have a first piece of evidence that could prove that humans have unique cortical brain networks.
Professor Vanduffel explains: "We did functional brain scans in humans and rhesus monkeys ...
Controversial dam removals founded on value conflicts
2013-02-22
Researchers at Umeå University in Sweden conclude that public opposition to dam removal is not based on knowledge deficiency, as is sometimes argued in dam removal science. It is instead a case of different understandings and valuation of the environment and the functions it provides. The findings are now published in the journal Ecology and Society.
Dam removal is an increasingly common practice as old splash dams and small hydropower dams have become obsolete. Although the removal of these dams has ecological benefits by restoring rivers to their former courses, local ...
Reforming US research ethics: Alex John London calls for system that works for all stakeholders
2013-02-22
PITTSBURGH—At a time when the U.S. government is contemplating changes to federal guidelines governing research with humans, serious questions are being raised about the role of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in overseeing such research. Particularly, vocal critics have cited lost time, money and even lives under a system that they claim consumes scarce resources and stifles academic freedom. In response, defenders of the IRB system point to the need to protect research participants from abuse.
Carnegie Mellon University's Alex John London, an internationally renowned ...
Genomic detectives crack the case of the missing heritability
2013-02-22
Despite years of research, the genetic factors behind many human diseases and characteristics remain unknown. The inability to find the complete genetic causes of family traits such as height or the risk of type 2 diabetes has been called the "missing heritability" problem.
A new study by Princeton University researchers, however, suggests that missing heritability may not be missing after all — at least not in yeast cells, which the researchers used as a model for studying the problem. Published in the journal Nature, the results suggest that heritability in humans ...
Researchers find appointed justices outperform elected counterparts
2013-02-22
State supreme court justices who don't face voters are generally more effective than their elected counterparts, according to research led by Princeton University political scientists.
The research combines data about almost 6,000 state supreme court rulings nationwide between 1995 and 1998 with a new theoretical model to reach the conclusions that appointed justices generally bring a higher quality of information to the decision-making process, are more likely to change their preconceived opinions about a case, and are less likely to make errors than elected justices.
"Judges ...
1 week and counting: Don't cut the research that fuels the US economy
2013-02-22
WASHINGTON, DC – With only one week left before sequestration is to take effect, America's research community sustained its call for an end to the across-the-board cuts to discretionary spending that will severely restrict the nation's ability to invest in the basic scientific research that drives innovation and produces economic growth. Sequestration will reduce federal funding for scientific research by nearly $95 billion over the next nine years, which will result in a reduction of U.S. GDP by at least $203 billion. The net impact will be 200,000 fewer jobs per year ...
Israel rocket attacks increase miscarriage likelihood -- Ben-Gurion U. research study
2013-02-22
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, February 21, 2013 -- Rocket attacks in Sderot, Israel significantly increase the likelihood of miscarriages, according to a new study by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) researchers.
The study, published in the January issue of Psychosomatic Medicine Journal of Bio-behavioral Medicine, compared 1,341 pregnancies of women (exposed group) who resided in Sderot, an area exposed to frequent rocket fire, with 2,143 pregnancies of women who lived in Kiryat Gat (unexposed group), which is out of range of missiles. Among women residing in the exposed ...
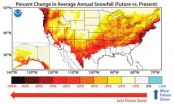
Forecast is for more snow in polar regions, less for the rest of us
2013-02-22
A new climate model predicts an increase in snowfall for the Earth's polar regions and highest altitudes, but an overall drop in snowfall for the globe, as carbon dioxide levels rise over the next century.
The decline in snowfall could spell trouble for regions such as the western United States that rely on snowmelt as a source of fresh water.
The projections are the result of a new climate model developed at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) and analyzed by scientists at GFDL and Princeton University. ...
The lifetime journeys of manure-based microbes
2013-02-22
This press release is available in Spanish.
Studies at the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) are shedding some light on the microbes that dwell in cattle manure—what they are, where they thrive, where they struggle, and where they can end up.
This research, which is being conducted by Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientists at the agency's Agroecosystems Management Research Unit in Lincoln, Neb., supports the USDA priority of ensuring food safety. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific research agency.
In one project, ARS microbiologist Lisa Durso ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Fruit flies force their young to drink alcohol -- for their own goodFruit fly study adds to evidence that using toxins in the environment to medicate offspring may be common across the animal kingdom