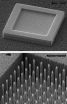
(Press-News.org) Scientists have developed a new method of replacing missing teeth with a bioengineered material generated from a person's own gum cells. Current implant-based methods of whole tooth replacement fail to reproduce a natural root structure and as a consequence of the friction from eating and other jaw movement, loss of jaw bone can occur around the implant. The research is led by Professor Paul Sharpe, an expert in craniofacial development and stem cell biology at King's College London and published in the Journal of Dental Research.
Research towards achieving the aim of producing bioengineered teeth – bioteeth – has largely focussed on the generation of immature teeth (teeth primordia) that mimic those in the embryo that can be transplanted as small cell 'pellets' into the adult jaw to develop into functional teeth.
Remarkably, despite the very different environments, embryonic teeth primordia can develop normally in the adult mouth and thus if suitable cells can be identified that can be combined in such a way to produce an immature tooth, there is a realistic prospect bioteeth can become a clinical reality. Subsequent studies have largely focussed on the use of embryonic cells and although it is clear that embryonic tooth primordia cells can readily form immature teeth following dissociation into single cell populations and subsequent recombination, such cell sources are impractical to use in a general therapy.
Professor Sharpe says: 'What is required is the identification of adult sources of human epithelial and mesenchymal cells that can be obtained in sufficient numbers to make biotooth formation a viable alternative to dental implants.'
In this new work, the researchers isolated adult human gum tissue from patients at the Dental Institute at King's College London, grew more of it in the lab, and then combined it with the cells of mice that form teeth. By transplanting this combination of cells into mice the researchers were able to grow hybrid human/mouse teeth containing dentine and enamel, as well as viable roots.
Professor Sharpe concludes: 'Epithelial cells derived from adult human gum tissue are capable of responding to tooth inducing signals from embryonic tooth mesenchyme in an appropriate way to contribute to tooth crown and root formation and give rise to relevant differentiated cell types, following in vitro culture.
'These easily accessible epithelial cells are thus a realistic source for consideration in human biotooth formation. The next major challenge is to identify a way to culture adult human mesenchymal cells to be tooth-inducing, as at the moment we can only make embryonic mesenchymal cells do this.'
###
CONTACT
Katherine Barnes
International PR Manager
King's College London
NOTES TO EDITORS
The research was funded by the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and King's College London, UK.
Adult Human Gingival Epithelial Cells as a Source for Whole-tooth Bioengineering
Journal of Dental Research 2013
Copy of the paper available on request
About King's College London (http://www.kcl.ac.uk)
King's College London is one of the top 30 universities in the world (2011/12 QS World University Rankings), and the fourth oldest in England. A research-led university based in the heart of London, King's has more than 25,000 students (of whom more than 10,000 are graduate students) from nearly 140 countries, and some 6,500 employees. King's is in the second phase of a £1 billion redevelopment programme which is transforming its estate.
King's has an outstanding reputation for providing world-class teaching and cutting-edge research. In the 2008 Research Assessment Exercise for British universities, 23 departments were ranked in the top quartile of British universities; over half of our academic staff work in departments that are in the top 10 per cent in the UK in their field and can thus be classed as world leading. The College is in the top seven UK universities for research earnings and has an overall annual income of nearly £450 million.
King's has a particularly distinguished reputation in the humanities, law, the sciences (including a wide range of health areas such as psychiatry, medicine, nursing and dentistry) and social sciences including international affairs. It has played a major role in many of the advances that have shaped modern life, such as the discovery of the structure of DNA and research that led to the development of radio, television, mobile phones and radar. It is the largest centre for the education of healthcare professionals in Europe; no university has more Medical Research Council Centres.
About the National Institute for Health Research (http://www.nihr.ac.uk)
The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) is funded by the Department of Health to improve the health and wealth of the nation through research. Since its establishment in April 2006, the NIHR has transformed research in the NHS. It has increased the volume of applied health research for the benefit of patients and the public, driven faster translation of basic science discoveries into tangible benefits for patients and the economy, and developed and supported the people who conduct and contribute to applied health research. The NIHR plays a key role in the Government's strategy for economic growth, attracting investment by the life-sciences industries through its world-class infrastructure for health research. Together, the NIHR people, programmes, centres of excellence and systems represent the most integrated health research system in the world. The views expressed in this news release are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health. END
Biological tooth replacement -- a step closer
Scientists have developed a new method of replacing missing teeth with a bioengineered material generated from a person's own gum cells
2013-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Weight loss may prevent, treat osteoarthritis in obese patients
2013-03-09
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Weight loss may prevent and significantly alleviate the symptoms of osteoarthritis, a progressive disease of the joints known as "wear and tear" arthritis, according to a literature review appearing in the March 2013 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (JAAOS).
According to the article, obesity actually may trigger the biomechanical and inflammatory changes that cause osteoarthritis, and the pain and loss of mobility associated with the condition.
"There's a clear link between obesity and osteoarthritis, and the link is ...
New player in electron field emitter technology makes for better imaging and communications
2013-03-09
Scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Maryland, College Park, have built a practical, high-efficiency nanostructured electron source. Described in the journal Nanotechnology*, this new, patent-pending technology could lead to improved microwave communications and radar, and more notably to new and improved X-ray imaging systems for security and health-care applications.
While thermionic electron sources such as the hot filaments inside cathode ray tubes have largely been replaced by LEDs and liquid crystals for display ...
NIST quantum refrigerator offers extreme cooling and convenience
2013-03-09
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have demonstrated a solid-state refrigerator that uses quantum physics in micro- and nanostructures to cool a much larger object to extremely low temperatures.
What's more, the prototype NIST refrigerator, which measures a few inches in outer dimensions, enables researchers to place any suitable object in the cooling zone and later remove and replace it, similar to an all-purpose kitchen refrigerator. The cooling power is the equivalent of a window-mounted air conditioner cooling a building the size ...
New NIST time code to boost reception for radio-controlled clocks
2013-03-09
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is changing the way it broadcasts time signals that synchronize radio-controlled "atomic" clocks and watches to official U.S. time in ways that will enable new radio-controlled timepieces to be significantly more robust and reliable.
This new time broadcast protocol will not only improve the performance of new radio-controlled clocks and watches, but will encourage the development of new timekeeping products that were not practical with the old broadcast system because of local interference or other limitations. ...
Study shows confidence builds better exercise habits for cancer survivors
2013-03-09
HOUSTON - Endometrial cancer survivors are more likely to complete physical activity, and for longer durations, when their daily self-efficacy is higher, according to a study published online in the journal Health Psychology – a publication of the American Psychology Association.
"Sedentary behavior is associated with increased cancer risk, including endometrial cancer," said Karen Basen-Engquist, Ph.D., professor in the Department of Behavioral Science at MD Anderson and lead investigator on the study. "When cancer survivors exercise, it not only improves their physical ...
NIST panel expands recommendations for use of electronic health records in pediatrics
2013-03-09
To speed development and adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) for pediatrics, a group of experts from industry, academia and government convened by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has focused its attention on three key audiences—records-system vendors and developers, small-group pediatric medical practices and children's hospitals.
In a paper* in The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety, the panel of medical, human factors engineering and software-usability experts detail how specific recommendations from a recent guide ...
Why a hereditary anemia is caused by genetic mutation in mechanically sensitive ion channel
2013-03-09
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A genetic mutation that alters the kinetics of an ion channel in red blood cells has been identified as the cause behind a hereditary anemia, according to a paper (http://bit.ly/13LgCzc) published this month in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by University at Buffalo scientists and colleagues.
The research team was led by Frederick Sachs, PhD, SUNY Distinguished Professor in the UB Department of Physiology and Biophysics, who discovered in the 1980s that some ion channels are mechanosensitive, that is, they convert mechanical stress ...
Temp-controlled 'nanopores' may allow detailed blood analysis
2013-03-09
Tiny biomolecular chambers called nanopores that can be selectively heated may help doctors diagnose disease more effectively if recent research by a team at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Wheaton College, and Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU) proves effective. Though the findings* may be years away from application in the clinic, they may one day improve doctors' ability to search the bloodstream quickly for indicators of disease—a longstanding goal of medical research.
The team has pioneered work on the use of nanopores—tiny chambers ...
Some biologists shun new media
2013-03-09
Although biologists think that "new media" such as blogs and online social networks have an important influence on public opinion and political decisions, they aren't much inclined to use them themselves to stay informed about developments in science. Rather, they prefer traditional outlets such as newspapers and television. That seems, at least, to be the implication of a study published in the April issue of BioScience.
The study, by Joachim Allgaier of the Jülich Research Center in Germany and four coauthors, examined the opinions of 257 neuroscientists working in ...
UTHealth researchers say more rapid test for Group B strep successful
2013-03-09
HOUSTON – (March 8, 2013) – A more rapid laboratory test for pregnant women to detect potentially deadly Group B strep (GBS) has been successful at identifying GBS colonization in six and a half hours, according to the results of a study from The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
The more rapid test could be helpful for the 13 percent of patients who experience pre-term labor before they are screened for GBS, which usually occurs between 35 and 37 weeks of gestation. The current standard test takes 48 hours. Antibiotics can be administered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Biological tooth replacement -- a step closerScientists have developed a new method of replacing missing teeth with a bioengineered material generated from a person's own gum cells