(Press-News.org) A new and experimental anti-clotting drug, cangrelor, proved better than the commonly used clopidogrel and was significantly more effective at preventing blood clots in a large trial of patients who underwent coronary stent procedures. These data, from the phase III CHAMPION PHOENIX study, were presented at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Researchers report that the new drug, which is administered intravenously, reduced the odds of complications from stenting procedures. Specifically, those who received cangrelor had a lower combined incidence of death, myocardial infarction, ischemia-driven revascularization, or stent thrombosis at 48 hours after randomization.
"We are very excited about the potential for this new medication to reduce complications in patients receiving coronary stents for a wide variety of indications. In addition to being much quicker to take effect and more potent than currently available treatment options, this intravenous drug is reversible and has a fast offset of action, which could be an advantage if emergency surgery is needed." said Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, lead author of the study, director of the Integrated Interventional Cardiovascular Program at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) and chief of cardiology at VA Boston Healthcare System, as well as professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School.
In this randomized double-blind trial, researchers compared the novel IV drug cangrelor against the oral clopidogrel standard of care in approximately 11,000 patients at 153 centers around the world. The study included a wide selection of patients with different types of heart attack, angina, and other conditions for which people undergo percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), as long as they did not have high risk for bleeding or recent exposure to other anti-clotting drugs.
Researchers report significantly better performance by cangrelor compared with clopidogrel:
A 22 percent reduction in the odds of death, myocardial infarction, ischemia-driven revascularization, or stent thrombosis at 48 hours after randomization: 4.7 percent vs. 5.9 percent
A 38 percent reduction in the odds of stent thrombosis at 48 hours: 0.8 percent vs. 1.4 percent
Both treatment arms showed a quite low, statistically comparable incidence in severe bleeding at 48 hours: 0.16 percent vs. 0.11 percent.
Coronary artery stents are used in the majority of patients who undergo percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a common medical procedure used to treat arteries in the heart that have become narrowed or blocked due to coronary artery disease, which affects an estimated 14 million Americans. During this procedure, patients are regularly given oral doses of an anti-clotting agent to prevent blood clotting. Both cangrelor and clopidogrel interfere with the P2Y12 receptor, a platelet-surface protein that helps regulate blood clotting.
"We are encouraged by these compelling results, especially as it relates to the safety data, and believe that this drug has the potential to offer dramatic benefits to our patients" said Robert A. Harrington, M.D., chairman of medicine at Stanford University School of Medicine and co-chair of the study.
The company plans to file for approval with the Food and Drug Administration using data from CHAMPION PHOENIX and the earlier BRIDGE trial.
### The Medicines Company sponsored the CHAMPION PHOENIX trial and provided a research grant to the Duke Clinical Research Institute for the statistical analyses and event adjudication. Both Bhatt and Harrington reported receiving institutional grants from The Medicines Company. Harrington reported receiving grants and travel support to attend meetings for the trial from the company.
Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) is a 793-bed nonprofit teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School and a founding member of Partners HealthCare. BWH has more than 3.5 million annual patient visits, is the largest birthing center in New England and employs more than 15,000 people. The Brigham's medical preeminence dates back to 1832, and today that rich history in clinical care is coupled with its national leadership in patient care, quality improvement and patient safety initiatives, and its dedication to research, innovation, community engagement and educating and training the next generation of health care professionals. Through investigation and discovery conducted at its Biomedical Research Institute (BRI), BWH is an international leader in basic, clinical and translational research on human diseases, involving nearly 1,000 physician-investigators and renowned biomedical scientists and faculty supported by $640 million in funding. For the last 19 years, BWH ranked second in research funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) among independent hospitals. BWH continually pushes the boundaries of medicine, including building on its legacy in organ transplantation by performing the first face transplants in the U.S. in 2011. BWH is also home to major landmark epidemiologic population studies, including the Nurses' and Physicians' Health Studies, OurGenes and the Women's Health Initiative. For more information and resources, please visit BWH's online newsroom.
New anti-clotting drug more effective than current treatment
Cangrelor, a novel intravenous anti-clotting medication, proves better across a broad population of patients receiving coronary stent procedures
2013-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Magnet ingestion by young children serious and growing problem
2013-03-11
Physicians and parents must be aware of the growing danger of magnet ingestion by children because magnets can adhere to each other and cause life-threatening problems such as bowel perforations, a new case study illustrates in CMAJ.
"Modern magnet technology has transformed what was once an esoteric subtype of foreign-body ingestion into a common and lethal threat," writes Dr. Daniel Rosenfield, Department of Paediatrics, The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids), with coauthors.
In the past, magnet ingestion generally could be treated with a wait-and-see approach, ...
Therapies for ALL and AML targeting MER receptor hold promise of more effect with less side-effect
2013-03-11
Two University of Colorado Cancer Center studies show that the protein receptor Mer is overexpressed in many leukemias, and that inhibition of this Mer receptor results in the death of leukemia cells – without affecting surrounding, healthy cells.
The first study, published today in the journal Oncogene, worked with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), for which current chemotherapies offer a cure rate of only about 55 percent.
"In about 2/3 of all AML patients and about 90 percent of adult AML patients, we found that the Mer receptor was upregulated. Mer receptor protein ...
EARTH: Well-healed faults produce high-frequency earthquake waves
2013-03-11
Alexandria, VA – Much like our voices create sound waves with a variety of low and high pitches, or frequencies, earthquakes produce seismic waves over a broad spectrum. The seismic waves' frequencies determine, in part, how far they travel and how damaging they are to human-made structures. However, the inaccessibility of fault zones means that very little is known about why and how earthquakes produce different frequencies. With the help of a new tabletop model, scientists have now identified how a process known as fault healing can shape seismic waves and potentially ...
BGI Tech develops novel 'Ultra-Deep de novo' assembly solution for heterozygous genomes
2013-03-11
Shenzhen, China, March 11, 2013- BGI Tech Solutions Co., Ltd., also referred to as "BGI Tech", introduced today its novel assembly solution for facilitating heterozygous genomes research. This marks another technological breakthrough for BGI in heterozygous genome assembly after the completed genome sequencing of oyster, diamondback moth and pear.
The availability of a reference genome for a species is the cornerstone for the in-depth understanding of its biological secrets and commercial values. However, a major obstacle that prevents scientists to easily crack the genome ...
Gun retailers take a hard line on illegal firearm sales, UC Davis survey finds
2013-03-11
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) —A scientific survey of more than 1,600 gun retailers in the U.S. has found that gun buyers frequently try to make illegal purchases and that gun retailers take a dim view of fellow sellers who engage in illegal activity — regardless of whether they are actively breaking the law or simply looking the other way.
The survey, conducted in 2011 by Garen Wintemute, professor of emergency medicine and director of the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program, is believed to be the first scientific study of a large group of gun retailers to determine ...
An Internet for robots
2013-03-11
Researchers of five European universities have developed a cloud-computing platform for robots. The platform allows robots connected to the Internet to directly access the powerful computational, storage, and communications infrastructure of modern data centers - the giant server farms behind the likes of Google, Facebook, and Amazon - for robotics tasks and robot learning.
With the development of the RoboEarth Cloud Engine the team continues their work towards creating an Internet for robots. The new platform extends earlier work on allowing robots to share knowledge ...
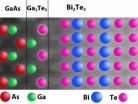
Researchers solve riddle of what has been holding 2 unlikely materials together
2013-03-11
For years, researchers have developed thin films of bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) – which converts heat into electricity or electricity to cooling – on top of gallium arsenide (GaAs) to create cooling devices for electronics. But while they knew it could be done, it was not clear how – because the atomic structures of those unlikely pair of materials do not appear to be compatible. Now researchers from North Carolina State University and RTI International have solved the mystery, opening the door to new research in the field.
"We've used state-of-the-art technology to solve ...
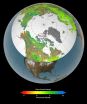
Amplified greenhouse effect shifts north's growing seasons
2013-03-11
Vegetation growth at Earth's northern latitudes increasingly resembles lusher latitudes to the south, according to a NASA-funded study based on a 30-year record of land surface and newly improved satellite data sets.
An international team of university and NASA scientists examined the relationship between changes in surface temperature and vegetation growth from 45 degrees north latitude to the Arctic Ocean. Results show temperature and vegetation growth at northern latitudes now resemble those found 4 degrees to 6 degrees of latitude farther south as recently as 1982.
"Higher ...
Nerve damage may underlie widespread, unexplained chronic pain in children
2013-03-11
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have described what may be a newly identified disease that appears to explain some cases of widespread chronic pain and other symptoms in children and young adults. Their report that will appear in the April issue of the journal Pediatrics, and has received early online release, finds that most of a group of young patients seen at the MGH for chronic, unexplained pain had test results indicating small-fiber polyneuropathy, a condition not previously reported in children. The MGH investigators call this new syndrome juvenile-onset ...
Study: Antibiotics are unique assassins
2013-03-11
In recent years, a body of publications in the microbiology field has challenged all previous knowledge of how antibiotics kill bacteria. "A slew of papers came out studying this phenomenon, suggesting that there is a general mechanism of killing by antibiotics," said Kim Lewis, Northeastern University Distinguished Professor in the Department of Biology and director of Northeastern's Antimicrobial Discovery Center.
The standard thinking at the time was that the three main classes of bactericidal antibiotics each had a unique way of killing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] New anti-clotting drug more effective than current treatmentCangrelor, a novel intravenous anti-clotting medication, proves better across a broad population of patients receiving coronary stent procedures