(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO -- A commonly used erectile dysfunction drug, sildenafil, doesn't help patients who have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, a condition in which the heart's lower chambers are stiff and cannot relax and fill fully between beats. That is the finding of the RELAX study, presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session and simultaneously published in The Journal of the American Medical Association. The study's lead author called the results disappointing.
Sildenafil, a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, had shown encouraging results in smaller studies and in animal models.
In this study, researchers looked at the drug's effect on maximum exercise ability as assessed by peak oxygen consumption and on how far people could walk in six minutes, their clinical status and their heart structure and function. They found no benefit, says lead author Margaret Redfield, M.D., heart failure specialist and researcher at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
"It was surprising and a disappointment, and it was contradictory to our hypothesis," says
Dr. Redfield. "There are few options for help for these patients, and we hoped we would find something."
When the heart does not pump blood well, heart failure symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue and weakness can result.
The RELAX study is the first multicenter trial to look at the effect of therapy with sildenafil on this condition, also known as diastolic heart failure. The study was a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of 216 stable outpatients with heart failure (with an ejection fraction of greater than 50 percent) with reduced exercise capacity; the median age was 69. Participants were enrolled during a 3.5-year period from the nine U.S. centers including Mayo Clinic that make up the Heart Failure Clinical Research Network and 17 other centers in the United States and Canada.
"This was a very complex study and criteria for study participants were very strict," Dr. Redfield says. "But it's most likely that we didn't see the results we hoped for because this type of heart failure just does not respond to this drug."
###
The RELAX study was funded by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant HL84907 (original) and grant HL110262 (this grant cycle). The institute also funds the Heart Failure Clinical Research Network.
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit worldwide leader in medical care, research and education for people from all walks of life. For more information, visit http://www.mayoclinic.org/about and http://www.mayoclinic.org/news.
Journalists can become a member of the Mayo Clinic News Network for the latest health, science and research news and access to video, audio, text and graphic elements that can be downloaded or embedded.
Common erectile dysfunction drug not helpful for heart failure patients, study finds
2013-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Astronomers conduct first remote reconnaissance of another solar system
2013-03-12
Researchers have conducted a remote reconnaissance of a distant solar system with a new telescope imaging system that sifts through the blinding light of stars. Using a suite of high-tech instrumentation and software called Project 1640, the scientists collected the first chemical fingerprints, or spectra, of this system's four red exoplanets, which orbit a star 128 light years away from Earth. A detailed description of the planets—showing how drastically different they are from the known worlds in the universe—was accepted Friday for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. ...
Creating indestructible self-healing circuits
2013-03-12
PASADENA, Calif.—Imagine that the chips in your smart phone or computer could repair and defend themselves on the fly, recovering in microseconds from problems ranging from less-than-ideal battery power to total transistor failure. It might sound like the stuff of science fiction, but a team of engineers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), for the first time ever, has developed just such self-healing integrated chips.
The team, made up of members of the High-Speed Integrated Circuits laboratory in Caltech's Division of Engineering and Applied Science, ...
Epigenetics mechanism may help explain effects of mom's nutrition on her children's health
2013-03-12
This press release is available in Spanish.
Pioneering studies by U. S. Department of Agriculture-funded research molecular geneticist Robert A. Waterland are helping explain how the foods that soon-to-be-moms eat in the days and weeks around the time of conception—or what's known as periconceptional nutrition–may affect the way genes function in her children, and her children's health.
In an early study, Waterland and co-investigators examined gene function of 50 healthy children living in rural villages in the West African nation of The Gambia. The study has shaped ...
Study shows how one insect got its wings
2013-03-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have delved deeper into the evolutionary history of the fruit fly than ever before to reveal the genetic activity that led to the development of wings – a key to the insect's ability to survive.
The wings themselves are common research models for this and other species' appendages. But until now, scientists did not know how the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, first sprouted tiny buds that became flat wings.
A cluster of only 20 or so cells present in the fruit fly's first day of larval life was analyzed to connect a gene known to be active ...
Study predicts lag in summer rains over parts of US and Mexico
2013-03-12
A delay in the summer monsoon rains that fall over the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico is expected in the coming decades according to a new study in the Journal of Geophysical Research. The North American monsoon delivers as much as 70 percent of the region's annual rainfall, watering crops and rangelands for an estimated 20 million people.
"We hope this information can be used with other studies to build realistic expectations for water resource availability in the future," said study lead author, Benjamin Cook, a climate scientist with joint appointments ...
Study shows on-pump bypass comparable to off-pump at year mark
2013-03-12
SAN FRANCISCO (March 11, 2013) — Patients who underwent heart bypass surgery without a heart- lung machine did as well one year later as patients whose hearts were connected to a pump during surgery in a study presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session.
CORONARY, an international, multicenter trial of on-pump (with a heart-lung machine) versus off-pump bypass surgery, enrolled 4,752 patients already scheduled to undergo a bypass procedure. The study is the largest to compare the two approaches.
For the primary endpoint of ...
University of Maryland School of Medicine discovers adaptations to explain strategies for survival on Mars
2013-03-12
Research from the University of Maryland School of Medicine has revealed key features in proteins needed for life to function on Mars and other extreme environments. The researchers, funded by NASA, studied organisms that survive in the extreme environment of Antarctica. They found subtle but significant differences between the core proteins in ordinary organisms and Haloarchaea, organisms that can tolerate severe conditions such as high salinity, desiccation, and extreme temperatures. The research gives scientists a window into how life could possibly adapt to exist on ...
Similar outcomes in older patients with on- or off-pump bypass
2013-03-12
SAN FRANCISCO (March 11, 2013) — Older patients did as well after undergoing coronary bypass surgery off-pump as they did with the more costly "on-pump" procedure using a heart-lung machine to circulate blood and oxygen through the body during surgery, according to research presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session.
This large, multicenter trial—the German Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in Elderly Patients, called GOPCABE—was the first to evaluate on-pump versus off-pump bypass surgery among patients aged 75 or older. ...
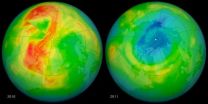
NASA pinpoints causes of 2011 Arctic ozone hole
2013-03-12
A combination of extreme cold temperatures, man-made chemicals and a stagnant atmosphere were behind what became known as the Arctic ozone hole of 2011, a new NASA study finds.
Even when both poles of the planet undergo ozone losses during the winter, the Arctic's ozone depletion tends to be milder and shorter-lived than the Antarctic's. This is because the three key ingredients needed for ozone-destroying chemical reactions —chlorine from man-made chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), frigid temperatures and sunlight— are not usually present in the Arctic at the same time: the ...
NASA's SDO observes Earth, lunar transits in same day
2013-03-12
On March 2, 2013, NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) entered its semiannual eclipse season, a period of three weeks when Earth blocks its view of the sun for a period of time each day. On March 11, however, SDO was treated to two transits. Earth blocked SDO's view of the sun from about 2:15 to 3:45 a.m. EDT. Later in the same day, from around 7:30 to 8:45 a.m. EDT, the moon moved in front of the sun for a partial eclipse.
When Earth blocks the sun, the boundaries of Earth's shadow appear fuzzy, since SDO can see some light from the sun coming through Earth's atmosphere. ...