(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, PA, March 14, 2013 – Since the 1960s, psychiatrists have been hunting for substances made by the body that might accumulate in abnormally high levels to produce the symptoms associated with schizophrenia. In particular, there was a search for chemicals that might be related to the hallucinogens phencyclidine (PCP) or lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), which could explain the emergence of psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia. This "auto-intoxication" hypothesis led investigators on a wild goose chase where substances, including the "Pink Spot" and the "Frohman Factor", were isolated from people with schizophrenia and implicated in their illness, but these findings were later discredited.
The mysterious GRIN3A is a new version of the hunt for an intrinsic mechanism that produces schizophrenia-like symptoms. GRIN3A is a gene that codes for the GluN3A subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate-type (NMDA) receptor, a target for the neurotransmitter glutamate in the brain. Functional NMDA receptors usually have two GluN1 subunits and two GluN2 subunits. The ability of glutamate to activate these receptors is blocked by PCP and the anesthetic/hallucinogen, ketamine. When the GluN3A subunit is incorporated, it prevents the NMDA receptor from being activated by glutamate, almost as if the receptor had been blocked by PCP.
It is unclear why the brain needs this mechanism for normal brain development and function, hence the mystery surrounding GRIN3A. One piece of evidence supporting a link between GluN3A and schizophrenia is the finding that GluN3A levels are elevated in the post-mortem brain tissue from people who had been diagnosed with schizophrenia.
In this issue of Biological Psychiatry, Japanese researchers led by Dr. Takeo Yoshikawa provide new support for this hypothesis by implicating variation in GRIN3A in the heritable risk for schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia is thought to have a substantial genetic background which is, to some extent, population-specific. Genome-wide searches have revealed many common genomic variants with weak effects, but the remaining "missing heritability" is largely unknown. Scientists theorize that it may be partly explained by rare variants with large effect.
To identify genetic variants with larger effect sizes, Yoshikawa and his colleagues examined genetic data from several Asian populations. They identified a rare variant in GRIN3A with study-wide significance.
"This discovery is important, because the 'NMDA receptor hypothesis' for schizophrenia is a common disease model," said Yoshikawa. "We propose a novel point of therapeutic intervention in the NMDA receptor signaling system for schizophrenia."
Dr. John Krystal, Editor of Biological Psychiatry, commented, "The notion that a genetic trait that acts like PCP in the brain produces schizophrenia is a very attractive but over-simplistic hypothesis. It is that the biology of schizophrenia is much more complicated than this single factor. Nonetheless, perhaps this study of GRIN3A brings us another step closer to understanding glutamate abnormalities in schizophrenia."
###
The article is "A Population-Specific Uncommon Variant in GRIN3A Associated with Schizophrenia" by Atsushi Takata, Yoshimi Iwayama, Yasuhisa Fukuo, Masashi Ikeda, Tomo Okochi, Motoko Maekawa, Tomoko Toyota, Kazuo Yamada, Eiji Hattori, Tetsuo Ohnishi, Manabu Toyoshima, Hiroshi Ujike, Toshiya Inada, Hiroshi Kunugi, Norio Ozaki, Shinichiro Nanko, Kazuhiko Nakamura, Norio Mori, Shigenobu Kanba, Nakao Iwata, Tadafumi Kato, and Takeo Yoshikawa (doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.10.024). The article appears in Biological Psychiatry, Volume 73, Issue 6 (March 15, 2013), published by Elsevier.
Notes for Editors
Full text of the article is available to credentialed journalists upon request; contact Rhiannon Bugno at +1 214 648 0880 or Biol.Psych@utsouthwestern.edu. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Takeo Yoshikawa at +81 48 467 5968 or takeo@brain.riken.jp.
The authors' affiliations, and disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available in the article.
John H. Krystal, M.D., is Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry at the Yale University School of Medicine and a research psychiatrist at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. His disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available here.
About Biological Psychiatry
Biological Psychiatry is the official journal of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, whose purpose is to promote excellence in scientific research and education in fields that investigate the nature, causes, mechanisms and treatments of disorders of thought, emotion, or behavior. In accord with this mission, this peer-reviewed, rapid-publication, international journal publishes both basic and clinical contributions from all disciplines and research areas relevant to the pathophysiology and treatment of major psychiatric disorders.
The journal publishes novel results of original research which represent an important new lead or significant impact on the field, particularly those addressing genetic and environmental risk factors, neural circuitry and neurochemistry, and important new therapeutic approaches. Reviews and commentaries that focus on topics of current research and interest are also encouraged.
Biological Psychiatry is one of the most selective and highly cited journals in the field of psychiatric neuroscience. It is ranked 5th out of 129 Psychiatry titles and 16th out of 243 Neurosciences titles in the Journal Citations Reports® published by Thomson Reuters. The 2011 Impact Factor score for Biological Psychiatry is 8.283.
ABOUT ELSEVIER
Elsevier is a world-leading publisher of scientific, technical and medical information products and services. The company works in partnership with the global science and health communities to publish more than 2,000 journals, including The Lancet and Cell, and close
to 20,000 book titles, including major reference works from Mosby and Saunders. Elsevier's online solutions include SciVerse ScienceDirect, SciVerse Scopus, Reaxys, MD Consult and Nursing Consult, which enhance the productivity of
science and health professionals, and the SciVal suite and MEDai's Pinpoint Review, which help research and health care institutions deliver better outcomes more cost-effectively.
A global business headquartered in Amsterdam, Elsevier employs 7,000 people worldwide. The company is part of Reed Elsevier Group PLC, a world-leading publisher and information provider, which is jointly owned by Reed Elsevier PLC and Reed Elsevier NV. The ticker symbols are REN (Euronext Amsterdam), REL (London Stock Exchange), RUK and ENL (New York Stock Exchange).
Testing can improve learning among young and old people alike, according to new research from Rice University.
The study found that regardless of their age, intelligence or whether they work or attend college, people appear to learn more by taking tests rather than merely rereading or studying information. The research was published in the March 2013 edition of Psychology and Aging.
"There is a significant body of research examining the benefits of testing among young students," said Ashley Meyer '09, the study's lead author. Currently a cognitivepsychologist with the ...
Amsterdam, March 14, 2013 - Bumblebees are much more unstable when they hover than when they fly fast, according to new research published this month in the Journal of Theoretical Biology.
The authors of the paper, Na Xu and Mao Sun from Beijing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics in China, used a mathematical model to analyze the way bumblebees fly at different speeds, showing that the bumblebee is unstable when it hovers and flies slowly, and becomes neutral or weakly stable at medium and high flight speeds.
The instability at hovering and low speed is mainly ...
Smoking significantly increases individuals' risk of developing serious forms of urothelial carcinoma and a higher likelihood of dying from the disease, particularly for women. That is the conclusion of a recent study published in BJU International. While the biological mechanisms underlying this gender difference are unknown, the findings indicate that clinicians and society in general should focus on smoking prevention and cessation to safeguard against deadly cancers of the bladder, ureters, and renal pelvis, especially in females.
To evaluate the gender-specific effects ...
This press release is available in Spanish.
A U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientist is giving guidance to growers in Montana and the Dakotas on how grazing sheep when fields are left fallow will affect soil quality.
Grazing sheep and other livestock was once common in the region before fertilizers were introduced in the 1950s. While fertilizers increased yields, they also have increased nitrogen runoff and leaching, made soils more acidic, and contributed to greenhouse gas emissions, according to Upendra Sainju, a soil scientist with the Agricultural Research ...
Researchers from the University of Granada and the Carlos III University of Madrid have patented a new method to measure the flow of motorized traffic that a specific street carries each day, by measuring solely the levels of atmospheric noise. This pioneer system, unique in the world, is an alternative, or a complement, to other methods currently used to measure traffic flow, such as image counting or magnetic discharge levels.
This method, designed by the University of Granada, allows a differentiation between the flow of cars, LGVs, HGVs and motorbikes/scooters along ...
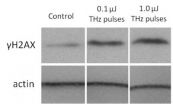
Terahertz (THz) radiation, a slice of the electromagnetic spectrum that occupies the middle ground between microwaves and infrared light, is rapidly finding important uses in medical diagnostics, security, and scientific research. As scientists and engineers find evermore practical uses for this form of radiation, questions persist about its potential human health risks.
New research performed on lab-grown human skin suggests that short but powerful bursts of THz radiation may both cause DNA damage and increase the production of proteins that help the body fight cancer. ...
The beetle family Cerambycidae, also known as long-horned beetles or longicorns, is characterized by emblematic extremely long antennae, which are usually longer than the total body length of the animal. The family is rather rich in diversity with more than 20 000 species known, distributed worldwide. Some representatives of these bizarre-shaped beetles, are also known as serious pests with their wood-feeding larvae causing extensive damage to living trees or untreated lumber. The beetles from this family are mainly associated with leaf litter habitats, where the specimens ...
New Rochelle, NY, March 14, 2013—A woman's health status before pregnancy is critical for the health and wellbeing of the fetus and mother-to-be. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has set Healthy People 2020 national objectives for women of reproductive age, and young women are making important gains toward achieving some of those health goals, while some trends are less encouraging, as reported in a study published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on ...
(WASHINGTON)-Transplants of blood-forming stem cells from umbilical cord blood may be an effective alternative to transplants of matched donor bone marrow stem cells to treat children with a rare, debilitating disease known as Hurler's syndrome (HS), according to results of a study published online today in Blood, the Journal of the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
HS is an inherited metabolic disease characterized by the lack of a critical metabolic enzyme (lysosomal α-L-iduronidase) that breaks down long chains of sugar molecules in the body. In the absence ...
TORONTO, ON – Both daughters and sons from divorced families are significantly more likely to initiate smoking in comparison to their peers from intact families, shows a new analysis of 19,000 Americans.
This University of Toronto study, published online this month in the journal Public Health, shows that men who experienced parental divorce before they turned 18 had 48-per-cent higher odds of ever smoking 100 or more cigarettes than men whose parents did not divorce. Women from divorced families were also at risk, with 39-per-cent higher odds of smoking in comparison ...