Discards ban could impact seabird populations
2013-03-14
(Press-News.org) The European Parliament recently voted to scrap the controversial discards policy, which has seen fishermen throwing thousands of edible fish and fish waste back into the sea because they have exceeded their quotas.
Scientists at Plymouth University believe this could have a negative impact on some seabirds, which have become used to following the fishing vessels and are increasingly reliant on their discards.
But they say others could return to using foraging as their sole source of food, as long as there are sufficient numbers of fish to meet their needs.
Dr Stephen Votier, Associate Professor in Marine Ecology at Plymouth University, led a recent study examining seabirds' foraging habits. He said: "Policy changes can have unforeseen consequences, and the recent decision on the EU discards policy will pose challenges for a number of species. Many seabirds have come to rely to some extent on fishing vessels for food and globally, commercial capture fisheries generate huge quantities of discards. However, we believe there is a level of resilience among seabirds which means they will be able to overcome these challenges."
The Plymouth University study focused on populations of northern gannets on Grassholm Island, in Wales, with tiny cameras and GPS trackers being attached to birds to monitor their foraging habits.
The cameras captured more than 20,000 images, allowing scientists for the first time to analyse where the birds had flown to source food, precisely what they had fed on, and other details such as their sex and reproductive status.
The findings showed 42% of birds regularly targeted fishing vessels, as well as searching for naturally occurring prey, while a gender breakdown showed 81% of male gannets used fishing vessels to source food and 30% of female birds did so.
Dr Votier added: "We have used cutting-edge technology to reveal the private lives of seabirds at sea – in this instance how they interact with fisheries – and the findings suggest scavenging is more common in this species than previously thought. This suggests a discard ban may have a significant impact on gannet behaviour, particularly so for males. But a continued reliance on 'natural' foraging shows the ability to switch away from discards, but only if there is sufficient forage fish to meet their needs in the absence of a discard subsidy."
###
The research study, which also involved scientists from the Plymouth Marine Laboratory and the Centre d'Etudes Biologiques de Chize in France, was conducted under licence from the Countryside Council for Wales and the British Trust for Ornithology.
It received funding from the National Environment Research Council, and the full findings are published in the latest issue of the PLOS ONE scientific journal.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chemical chameleon tamed
2013-03-14
How you get the chameleon of the molecules to settle on a particular "look" has been discovered by RUB chemists led by Professor Dominik Marx. The molecule CH5+ is normally not to be described by a single rigid structure, but is dynamically flexible. By means of computer simulations, the team from the Centre for Theoretical Chemistry showed that CH5+ takes on a particular structure once you attach hydrogen molecules. "In this way, we have taken an important step towards understanding experimental vibrational spectra in the future", says Dominik Marx. The researchers report ...
New research discovers the emergence of Twitter 'tribes'
2013-03-14
A project led by scientists from Royal Holloway University in collaboration with Princeton University, has found evidence of how people form into tribe-like communities on social network sites such as Twitter.
In a paper published in EPJ Data Science, they found that these communities have a common character, occupation or interest and have developed their own distinctive languages.
"This means that by looking at the language someone uses, it is possible to predict which community he or she is likely to belong to, with up to 80% accuracy," said Dr John Bryden from ...
What do American bullfrogs eat when they're away from home? Practically everything!
2013-03-14
American bullfrogs are native to eastern North America but have been transported by people to many other parts of the globe, and other parts of North America, where they have readily established populations and become an invasive alien menace to native ecosystems. In the largest study of its kind to date, the stomach contents of over 5,000 invasive alien American bullfrogs from 60 lakes and ponds on southern Vancouver Island were examined to identify the native and exotic animals that they had preyed upon. The study was published in the open access journal NeoBiota.
Over ...
The mysterious GRIN3A and the cause of schizophrenia
2013-03-14
Philadelphia, PA, March 14, 2013 – Since the 1960s, psychiatrists have been hunting for substances made by the body that might accumulate in abnormally high levels to produce the symptoms associated with schizophrenia. In particular, there was a search for chemicals that might be related to the hallucinogens phencyclidine (PCP) or lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), which could explain the emergence of psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia. This "auto-intoxication" hypothesis led investigators on a wild goose chase where substances, including the "Pink Spot" and the "Frohman ...
Testing can improve learning among young and old people
2013-03-14
Testing can improve learning among young and old people alike, according to new research from Rice University.
The study found that regardless of their age, intelligence or whether they work or attend college, people appear to learn more by taking tests rather than merely rereading or studying information. The research was published in the March 2013 edition of Psychology and Aging.
"There is a significant body of research examining the benefits of testing among young students," said Ashley Meyer '09, the study's lead author. Currently a cognitivepsychologist with the ...
Hovering is a bother for bees: Fast flight is more stable
2013-03-14
Amsterdam, March 14, 2013 - Bumblebees are much more unstable when they hover than when they fly fast, according to new research published this month in the Journal of Theoretical Biology.
The authors of the paper, Na Xu and Mao Sun from Beijing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics in China, used a mathematical model to analyze the way bumblebees fly at different speeds, showing that the bumblebee is unstable when it hovers and flies slowly, and becomes neutral or weakly stable at medium and high flight speeds.
The instability at hovering and low speed is mainly ...
Smoking linked with worse urothelial cancer prognosis in patients, especially women
2013-03-14
Smoking significantly increases individuals' risk of developing serious forms of urothelial carcinoma and a higher likelihood of dying from the disease, particularly for women. That is the conclusion of a recent study published in BJU International. While the biological mechanisms underlying this gender difference are unknown, the findings indicate that clinicians and society in general should focus on smoking prevention and cessation to safeguard against deadly cancers of the bladder, ureters, and renal pelvis, especially in females.
To evaluate the gender-specific effects ...
A better understanding of the impacts of grazing sheep
2013-03-14
This press release is available in Spanish.
A U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientist is giving guidance to growers in Montana and the Dakotas on how grazing sheep when fields are left fallow will affect soil quality.
Grazing sheep and other livestock was once common in the region before fertilizers were introduced in the 1950s. While fertilizers increased yields, they also have increased nitrogen runoff and leaching, made soils more acidic, and contributed to greenhouse gas emissions, according to Upendra Sainju, a soil scientist with the Agricultural Research ...
A new method for measuring the flow of traffic a street has to bear by measuring atmospheric noise
2013-03-14
Researchers from the University of Granada and the Carlos III University of Madrid have patented a new method to measure the flow of motorized traffic that a specific street carries each day, by measuring solely the levels of atmospheric noise. This pioneer system, unique in the world, is an alternative, or a complement, to other methods currently used to measure traffic flow, such as image counting or magnetic discharge levels.
This method, designed by the University of Granada, allows a differentiation between the flow of cars, LGVs, HGVs and motorbikes/scooters along ...
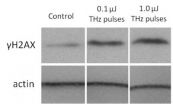
Intense terahertz pulses cause DNA damage but also induce DNA repair
2013-03-14
Terahertz (THz) radiation, a slice of the electromagnetic spectrum that occupies the middle ground between microwaves and infrared light, is rapidly finding important uses in medical diagnostics, security, and scientific research. As scientists and engineers find evermore practical uses for this form of radiation, questions persist about its potential human health risks.
New research performed on lab-grown human skin suggests that short but powerful bursts of THz radiation may both cause DNA damage and increase the production of proteins that help the body fight cancer. ...