(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Alberta are leading a charge among Canada's obesity experts and calling on the federal government to ban food and beverage ads that target children.
Kim Raine, a professor with the Centre for Health Promotion Studies in the School of Public Health at the U of A, says governments need to take action to stem the rising obesity epidemic. The only exception to a proposed food and beverage marketing ban would be for approved public health campaigns that promote healthy eating.
"Restricting marketing is not going to be a cure for childhood obesity, but it's one step in a multi-pronged approach to creating an environment where the healthy choice is the easy choice," said Raine, lead author of new consensus recommendations calling for the ban.
"Right now, it's the flashy, highly marketed, 'fun,' high-sugar and high-fat foods that are the easy choice. Kids see them and want them, and parents' efforts to encourage their kids to eat a healthy diet are undermined."
The recommendations were developed by leading Canadian and international obesity experts at an obesity conference held in Montreal in 2011. They were published last month in the peer-reviewed Journal of Public Health Policy, in an early online release.
More than five million Canadians are considered obese, including 500,000 children, and the number of kids who are overweight or obese has more than doubled since the early 1980s.
That's a trend Raine says cannot continue without overloading the health-care system—80 per cent of costs are associated with obesity-related chronic diseases such as heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, stroke, high blood pressure and certain cancers. Obese children are more likely to become obese adults, she said, meaning the rates of these preventable chronic diseases are only going to rise.
"Without investing in strong prevention efforts, like the proposed ban, the health system is not sustainable," she said.
Raine and the consensus panel said there are important lessons to be drawn from the ban on tobacco advertising to minors, which has helped cut smoking rates. The rest of the country can also learn from Quebec, which since 1980 has banned all marketing to children under 13 years old—legislation that withstood a Supreme Court challenge in 1989.
The panel, which also included U of A researchers Timothy Caulfield and John C. Spence, is also calling on government to create a regulatory body that would ensure children are protected from exposure to food ads. The body would be required to create minimum standards for food marketing, monitor companies for compliance and impose penalties when necessary.
Though some may view marketing bans as a heavy-handed approach, Raine notes the food industry has deep pockets that governments and public health advocates cannot come close to matching. Food advertisements appear not only on TV and in schools, but also on the Internet; in video games; through sponsorships, product placements, emails and brand mascots; and even through viral marketing.
"It really is about trying to set a more level playing field because the healthy choices aren't being promoted well. They're getting buried, they're getting lost in an ocean of flashy marketing."
INFORMATION:
The panel's work was funded by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
END
The discovery of the Rosetta Stone resolved a longstanding puzzle, permitting the translation of Egyptian hieroglyphs into Ancient Greek.
John Chaput, a researcher at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute has been hunting for a biological Rosetta Stone—an enzyme allowing DNA's 4-letter language to be written into a simpler (and potentially more ancient) molecule that may have existed as a genetic pathway to DNA and RNA in the prebiotic world.
Research results, which recently appeared in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, demonstrate that DNA sequences ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A key advance, newly reported by chemists from Brown and Yale Universities, could lead to a cheaper and more sustainable way to make acrylate, an important commodity chemical used to make materials from polyester fabrics to diapers.
Chemical companies churn out billions of tons of acrylate each year, usually by heating propylene, a compound derived from crude oil. "What we're interested in is enhancing both the economics and the sustainability of how acrylate is made," said Wesley Bernskoetter, assistant professor of chemistry at ...
When babies are deprived of oxygen before birth, brain damage and disorders such as cerebral palsy can occur. Extended cooling can prevent brain injuries, but this treatment is not always available in developing nations where advanced medical care is scarce. To address this need, Johns Hopkins undergraduates have devised a low-tech $40 unit to provide protective cooling in the absence of modern hospital equipment that can cost $12,000.
The device, called the Cooling Cure, aims to lower a newborn's temperature by about 6 degrees F for three days, a treatment that has been ...
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — A new University of Florida study of nearly 5,000 Haiti bird fossils shows contrary to a commonly held theory, human arrival 6,000 years ago didn't cause the island's birds to die simultaneously.
Although many birds perished or became displaced during a mass extinction event following the first arrival of humans to the Caribbean islands, fossil evidence shows some species were more resilient than others. The research provides range and dispersal patterns from A.D. 600 to 1600 that may be used to create conservation plans for tropical mountainous regions, ...
Scientists have confirmed that the pathogen that causes Lyme Disease—unlike any other known organism—can exist without iron, a metal that all other life needs to make proteins and enzymes. Instead of iron, the bacteria substitute manganese to make an essential enzyme, thus eluding immune system defenses that protect the body by starving pathogens of iron.
To cause disease, Borrelia burgdorferi requires unusually high levels of manganese, scientists at Johns Hopkins University (JHU), Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), and the University of Texas reported. Their ...
The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) has issued a new white paper, "Enhancing the role of case-oriented peer review to improve quality and safety in radiation oncology: Executive Summary," that recommends increased peer review within the radiation therapy treatment process and among members of the radiation oncology team in order to increase quality assurance and safety, according to the manuscript published as an article in press online in Practical Radiation Oncology (PRO), the official clinical practice journal of ASTRO. The executive summary and supplemental ...
Martin Gartzman sat in his dentist's waiting room last fall when he read a study in Education Next that nearly brought him to tears.
A decade ago, in his former position as chief math and science officer for Chicago Public Schools, Gartzman spearheaded an attempt to decrease ninth-grade algebra failure rates, an issue he calls "an incredibly vexing problem." His idea was to provide extra time for struggling students by having them take two consecutive periods of algebra.
Gartzman had been under the impression that the double-dose algebra program he had instituted had ...
Though we all desire relief -- from stress, work, or pain -- little is known about the specific emotions underlying relief. New research from the Association for Psychological Science explores the psychological mechanisms associated with relief that occurs after the removal of pain, also known as pain offset relief.
This new research shows that healthy individuals and individuals with a history of self-harm display similar levels of relief when pain is removed, which suggests that pain offset relief may be a natural mechanism that helps us to regulate our emotions.
Feeling ...
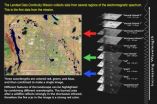
Turning on new satellite instruments is like opening new eyes. This week, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) released its first images of Earth, collected at 1:40 p.m. EDT on March 18. The first image shows the meeting of the Great Plains with the Front Ranges of the Rocky Mountains in Wyoming and Colorado. The natural-color image shows the green coniferous forest of the mountains coming down to the dormant brown plains. The cities of Cheyenne, Fort Collins, Loveland, Longmont, Boulder and Denver string out from north to south. Popcorn clouds dot the plains while ...
Teaching bystander Cardiac Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) strategically to the general public offers the greatest potential to make the biggest overall impact on survival in out of hospital cardiac arrests in Europe, reported a main session on Resuscitation Science at the European Society of Cardiology's EuroHeart Care Congress, which took place in Glasgow, 22 to 23 March, 2013.
"The reality is that four out of five cardiac arrests happen at home, and unless the public are trained in resuscitation many people die before emergency services get to them," said Mary Hannon. ...