Lesbian, gay, bisexual medical students are more likely to experience burnout, study finds
2021-02-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Studies have shown that nearly half of all medical students in the U.S. report symptoms of burnout, a long-term reaction to stress characterized by emotional exhaustion, cynicism and feelings of decreased personal accomplishment. Beyond the personal toll, the implications for aspiring and practicing physicians can be severe, from reduced quality of care to increased risk of patient safety incidents.
According to a new study published on Tuesday, Feb. 2, in JAMA Network Open, students who identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual ...
1 in 10 college women experience period poverty, more likely to experience depression
2021-02-02
Period poverty, a lack of access to menstrual hygiene products, and other unmet menstrual health needs can have far-reaching consequences for women and girls in the United States and globally.
New research led by George Mason University's College of Health and Human Services found that more than 14% of college women experienced period poverty in the past year, and 10% experienced period poverty every month. Women who experienced period poverty every month (68%) or in the past year (61.2%) were more likely to experience moderate or severe depression than those who did not experience period poverty (43%).
Dr. Jhumka Gupta, an associate professor at George Mason University was senior author of the study published in BMC Women's Health. ...
U of M study shows enhanced accuracy of CMV detection method in newborn screening
2021-02-02
MINNEAPOLIS- February 2, 2021 - In Minnesota, there are currently about END ...
Automated imaging detects and tracks brain protein involved in Alzheimer's disease
2021-02-02
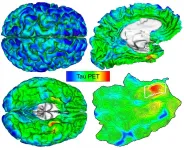
BOSTON - Amyloid-beta and tau are the two key abnormal protein deposits that accumulate in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease, and detecting their buildup at an early stage may allow clinicians to intervene before the condition has a chance to take hold. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has now developed an automated method that can identify and track the development of harmful tau deposits in a patient's brain. The research, which is published in END ...
Opioid prescriptions remained elevated two years after critical care
2021-02-02
Nearly 11 percent of people admitted to an intensive care unit in Sweden between 2010 and 2018 received opioid prescriptions on a regular basis for at least six months and up to two years after discharge. That is according to a study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet published in Critical Care Medicine. The findings suggest some may become chronic opioid users despite a lack of evidence of the drugs' long-term effectiveness and risks linked to increased mortality.
"We know that the sharp rise in opioid prescriptions in the U.S. has contributed to a deadly opioid crisis there," says first author Erik von Oelreich, PhD student in the Department of Physiology and ...
Decision-support tool could reduce unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions for child diarrhoea
2021-02-02
A decision-support tool that could be accessed via mobile devices may help clinicians in lower-resource settings avoid unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions for children with diarrhoea, a study published today in eLife shows.
The preliminary findings suggest that incorporating real-time environmental, epidemiologic, and clinical data into an easy-to-access, electronic tool could help clinicians appropriately treat children with diarrhoea even when testing is not available. This could help avoid the overuse of antibiotics, which contributes to the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria.
"Diarrhoea is a common condition among children ...
International research network identifies triggers for severe course of liver cirrhosis
2021-02-02
FRANKFURT. Chronic liver disease and even cirrhosis can go unnoticed for a long time because many patients have no symptoms: the liver suffers silently. When the body is no longer able to compensate for the liver's declining performance, the condition deteriorates dramatically in a very short time: tissue fluid collects in the abdomen (ascites), internal bleeding occurs in the oesophagus and elsewhere, and the brain is at risk of being poisoned by metabolic products. This acute decompensation of liver cirrhosis can develop into acute-on-chronic liver failure with inflammatory reactions throughout the body and failure of several organs.
In the PREDICT study, led ...
Good customer service can lead to higher profits, even for utilities without competition
2021-02-02
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. - In Lily Tomlin's classic SNL comedy sketch, her telephone operator "Ernestine" famously delivers the punchline, "We don't care. We don't have to. We're the Phone Company." But new research finds that satisfied customers mean increased profits even for public utilities that don't face competition.
Little is known about effect of customer satisfaction at utilities. As a result, utility managers are often unsure how much to invest in customer service - if anything at all. The issue also is of interest to regulators responsible for protecting consumers.
The study, in ...
Finding rare birds is never a picnic, contrary to popular Patagonia belief
2021-02-02
CORVALLIS, Ore. - One of birdwatching's most commonly held and colorfully named beliefs, the Patagonia Picnic Table Effect, is more a fun myth than a true phenomenon, Oregon State University research suggests.
Owing its moniker to an Arizona rest area, the Patagonia Picnic Table Effect, often shortened to PPTE, has for decades been cited as a key driver of behavior, and rare-species-finding success, among participants in the multibillion-dollar recreational birding business - an industry that has gotten even stronger during a pandemic that's shut down so many other activities.
But a study led by an OSU College of Science ...
Beyond qubits: Sydney takes next big step to scale up quantum computing
2021-02-02
Scientists and engineers at the University of Sydney and Microsoft Corporation have opened the next chapter in quantum technology with the invention of a single chip that can generate control signals for thousands of qubits, the building blocks of quantum computers.
"To realise the potential of quantum computing, machines will need to operate thousands if not millions of qubits," said Professor David Reilly, a designer of the chip who holds a joint position with Microsoft and the University of Sydney.
"The world's biggest quantum computers currently operate with just 50 or so qubits," he said. "This small scale is partly because of limits to the physical architecture that control the qubits."
"Our ...
Not too big, not too small: Goldilocks analogy found in maze navigation
2021-02-02
New research from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) has found a surprising randomness for how fluids choose their path around obstacles that depends on their spacing. This has important implications for a range of scenarios - from oil recovery and groundwater remediation, to understanding the movement of fluids through biological systems. The research was published in Physical Review Letters.
Scientists from OIST's Micro/Bio/Nanofluidics Unit created a tiny set up comprised of two microscopic cylinders, each around the width of a human hair, placed side-by-side in a channel. This created a choice of three possible paths for a fluid to take past the pair of obstacles. A viscoelastic fluid, which is like that ...
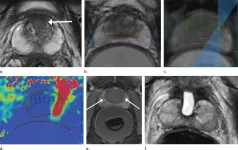
Ultrasound technique treats prostate cancer with minimal side effects
2021-02-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. - A technique that delivers high-intensity focused ultrasound to targeted tissue under MRI guidance effectively treats intermediate-risk prostate cancer with minimal side effects, according to a study published in Radiology.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men, aside from non-melanoma skin cancers. Common treatments to the entire gland, such as surgery and radiation therapy, are effective in eliminating the cancer, but they often leave patients with incontinence and sexual dysfunction.
A class of treatments called focal therapy offers an alternative for some men with intermediate-risk disease that is still confined to the prostate. In focal therapy, the cancer is ablated, or destroyed, by either ...
Age groups that sustain resurging COVID-19 epidemics in the United States
2021-02-02
By late summer 2020, the resurgence of COVID-19 in the United States was largely driven by adults between the ages of 20 and 49, a new study finds. The results indicate that in locations where novel highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 lineages have not yet established, additional interventions among adults of these ages could bring resurgent COVID-19 epidemics under control and avert deaths. Following initial declines in the number of reported SARS-CoV-2 infections and deaths - a result largely attributed to non-pharmaceutical interventions - a resurgence in transmission of COVID-19 occurred in the United States and Europe beginning in August 2020. Understanding the age demographics that drove this is crucial. For example, between August ...
Tracking cells with omnidirectional visible laser particles
2021-02-02
Laser particles are micrometre and nanometre lasers in the form of particles dispersible in aqueous solution, which have attracted considerable interest in the life sciences as a promising new optical probe. Laser particles emit highly bright light with extremely narrow spectral bandwidth. By transferring laser particles into live cells as shown in Figure 1, individual cells in a heterogeneous population can be tracked using each intracellular particle's specific spectral fingerprint as an optically readable barcode. However, laser particles emit directional light (Figure 2) and freely tumble inside living cells, their orientation varying randomly over time. Therefore optical readout of these labels results ...
Ergodicity of turbulence measurements upon complex terrain in Loess Plateau
2021-02-02
Loess Plateau possesses a particular loess physiognomy with numerous ravines and slopes, and tableland is a typical landform in it. Together, the ununiform in both topographic undulation and land coverage compose the ununiform, complex underlying surface on Loess Plateau. This provides a special platform for research of turbulence above the complex underlying surface.
As the front-edge problem encountered in the atmospheric boundary layer thesis, the turbulence research for complex underlying surface has drawn extensive attention recently. Local similarity has already proven that under certain condition, theories of turbulence based on the uniform underlying surface can also be applied to which for the ununiform underlying surface. ...
NTU Singapore team develops portable device that creates 3D images of skin in 10 minutes
2021-02-02
A team from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a portable device that produces high-resolution 3D images of human skin within 10 minutes.
The team said the portable skin mapping (imaging) device could be used to assess the severity of skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis.
3D skin mapping could be useful to clinicians, as most equipment used to assess skin conditions only provide 2D images of the skin surface. As the device also maps out the depth of the ridges and grooves of the skin at up to 2mm, it could also help with monitoring wound healing.
The device presses a specially devised film onto the subject's skin to obtain an imprint of up to 5 by 5 centimetres, which is then ...
A fine-grained view of dust storms
2021-02-02
A satellite-based dataset generated by KAUST researchers has revealed the dynamics of dust storm formation and movements over the last decade in the Arabian Peninsula. Analysis of this long-term dataset reveals the connection between the occurrence of extreme dust events and regional atmospheric conditions, a finding that could help improve weather forecasting and air-quality models.
Dust storms occur when strong winds lift tiny particles of sand into the atmosphere. These events often span several miles and can have an enormous impact on daily life, from damaging buildings and disrupting air traffic to triggering respiratory illnesses and other health problems.
The Arabian Peninsula is a global hotspot of extreme dust events, with storms occurring ...
Curtin study finds native bees under threat from growing urbanization
2021-02-02
Residential gardens are a poor substitute for native bushland and increasing urbanisation is a growing threat when it comes to bees, Curtin University research has found.
Published in 'Urban Ecosystems', the research looked at bee visits to flowers, which form pollination networks across different native bushland and home garden habitats.
Lead author, Forrest Foundation Scholar Miss Kit Prendergast, from Curtin's School of Molecular and Life Sciences said the findings highlight the need to prevent destruction of remaining bushland and preserve native vegetation, in order to protect sustainable bee communities and their pollination services.
"Our study involved spending hundreds of hours at 14 sites on the Swan Coastal Plain at Perth, Western Australia, ...
Recycling face masks into roads to tackle COVID-generated waste
2021-02-02
Researchers have shown how disposable face masks could be recycled to make roads, in a circular economy solution to pandemic-generated waste.
Their study shows that using the recycled face mask material to make just one kilometre of a two-lane road would use up about 3 million masks, preventing 93 tonnes of waste from going to landfill.
Developed by researchers at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, the new road-making material is a mix of shredded single-use face masks and processed building rubble designed to meet civil engineering safety standards. ...
"Genetic SD-card": Scientists obtained new methods to improve the genome editing system
2021-02-02
Researchers from Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) in collaboration with colleagues from Belgium take a step in the development of genome editing technology. Currently it is possible to deliver genetic material of different sizes and structures to organs and tissues. This is the key to eliminating DNA defects and treating more patients. The project is guided by Professor Gleb Sukhorukov and supported by the Russian Science Foundation. Research results were published in Particle & Particle Systems Characterization journal.
An international research group developed a polymer ...
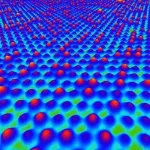
Fine tuned: adjusting the composition and properties of semiconducting 2D alloys
2021-02-02
Semiconducting 2D alloys could be key to overcoming the technical limitations of modern electronics. Although 2D Si-Ge alloys would have interesting properties for this purpose, they were only predicted theoretically. Now, scientists from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology have realized the first experimental demonstration. They have also shown that the Si to Ge ratio can be adjusted to fine tune the electronic properties of the alloys, paving the way for novel applications.
Alloys--materials composed of a combination of different elements or compounds--have played a crucial role in the technological development of humans since the Bronze Age. Today, ...
What did the Swiss eat during the Bronze Age?
2021-02-02
The Bronze Age (2200 to 800 BC) marked a decisive step in the technological and economic development of ancient societies. People living at the time faced a series of challenges: changes in the climate, the opening up of trade and a degree of population growth. How did they respond to changes in their diet, especially in Western Switzerland? A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, and Pompeu Fabra University (UPF) in Spain has for the first time carried out isotopic analyses on human and animal skeletons together with plant remains. The scientists discovered that manure use had become widespread over time to improve crop harvests in response to demographic growth. The researchers also found that there had ...
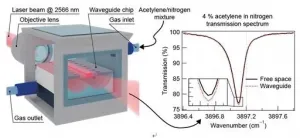
Air-guiding in solid-core optical waveguides: A solution for on-chip trace gas spectroscopy
2021-02-02
Optical waveguides suspended in air are capable to beat free-space laser beams in light-analyte interaction even without complex dispersion engineering. This phenomenon has been predicted more than 20 years ago, yet never observed in experiment.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Jana Jágerská from Department of Science and Technology, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, and co-workers have devised a mid-infrared free standing solid core optical waveguide which pushes the light interaction with the surrounding air beyond what has been reported up until now: 107 % interaction strength compared to that of a free-space beam has been demonstrated.
"The guided mode of our thin waveguide ...
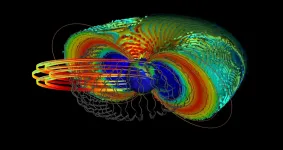
How do electrons close to Earth reach almost the speed of light?
2021-02-02
New study found that electrons can reach ultra-relativistic energies for very special conditions in the magnetosphere when space is devoid of plasma.
Recent measurements from NASA's Van Allen Probes spacecraft showed that electrons can reach ultra-relativistic energies flying at almost the speed of light. Hayley Allison, Yuri Shprits and collaborators from the German Research Centre for Geosciences have revealed under which conditions such strong accelerations occur. They had already demonstrated in 2020 that during solar storm plasma waves play a crucial role for that. However, it was previously unclear why such high electron energies are not achieved ...
Inspiring leadership, resilience and new challenges: The keys to efficient work teams
2021-02-02
The COVID-19 pandemic has upended many parts of daily life, one of them being our work life. Research carried out by the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) has studied the factors that help make efficient work teams. The explanation is multidimensional and multilevel.
"Inspiring leadership builds employees' resilience and willingness to undertake new challenges," said Pilar Ficapal Cusi, professor at the UOC's Faculty of Economics and Business and one of the authors of the study, which was published in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
Viewed from the group and organizational perspective, "the shared vision, the team's belief in its own creative effectiveness, the ability to reflect openly about how their members connect to adapt ...
[1] ... [2676]
[2677]
[2678]
[2679]
[2680]
[2681]
[2682]
[2683]
2684
[2685]
[2686]
[2687]
[2688]
[2689]
[2690]
[2691]
[2692]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.