Standard water treatment eliminates enveloped viruses -- like the coronavirus
2021-02-03
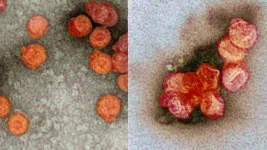
Among the many avenues that viruses can use to infect humans, drinking water may pose only a tiny risk for spreading certain viruses like the novel coronavirus. However, in cases where there is unauthorized wastewater disposal or other events of inadvertent mixing of wastewater with water sources, the possibility of transmission through drinking water remains unknown.
Using a surrogate of the coronavirus that only infects bacteria, researchers at Texas A&M University have now presented strong evidence that existing water purification plants can easily reduce vast quantities of the virus thereby protecting our household water from such contagions. In particular, the researchers showed that the water purification step called coagulation could alone get rid of 99.999% of ...
The business of bees
2021-02-03
The economic value of insect pollinators was $34 billion in the U.S. in 2012, much higher than previously thought, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and Penn State University. The team also found that areas that are economically most reliant on insect pollinators are the same areas where pollinator habitat and forage quality are poor.
"Pollinators like bees play an extremely important role in agriculture," explained senior author Vikas Khanna, Wellington C. Carl Faculty Fellow and associate professor of civil and environmental engineering at Pitt's Swanson School of Engineering. "The insects that pollinate farmers' crops underpin our ecosystem biodiversity and function, ...
Preventive anti-clotting therapy does not boost survival of critically ill COVID patients
2021-02-03
BOSTON - Although abnormal blood clotting has been identified as one of the primary causes of death from COVID-19, early treatment in an intensive care unit (ICU) with therapeutic anticoagulation (anti-clotting) for adults who are critically ill with COVID-19 does not appear to improve chances of survival, and could do more harm than good by increasing the risk for major bleeding, a multicenter research group cautions.
"In patients critically ill with COVID-19, therapeutic dose anticoagulation started early in the ICU stay was not associated with improved survival,"says Hanny Al-Samkari, MD, an investigator in the Division of Hematology/Oncology at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and lead author ...
Most vulnerable often overlooked in clinical trials of new treatments for COVID-19
2021-02-03
Studies examining the effectiveness of treatments for COVID-19 often do not include the very populations hardest hit by the disease, according to a new review by University of Chicago Medicine researchers.
The findings, based on an analysis of all US COVID-19 treatment trials registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, were published Jan. 27 in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
"This study highlights the blind spot in how clinical trials are done in the United States," said senior author Neda Laiteerapong, MD, MS, a general internist and associate director of the Center for Chronic Disease Research and Policy at the University of Chicago. "Researchers, hospitals and pharmaceutical ...
Scientists discover plants' roadblock to specialty oil production
2021-02-03
UPTON, NY - Hundreds of naturally occurring specialty fatty acids (building blocks of oils) have potential for use as raw materials for making lubricants, plastics, pharmaceuticals, and more--if they could be produced at large scale by crop plants. But attempts to put genes for making these specialty building blocks into crops have had the opposite effect: Seeds from plants with genes added to make specialty fatty acids accumulated dramatically less oil. No one knew why.
Now two teams of biochemists working on separate aspects of oil synthesis at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory have converged to discover the mechanism behind the oil-production slowdown. As described in the journal Plant Physiology, they crossbred model plants and conducted detailed ...
Moffitt researchers discover mechanism that regulates anti-tumor activity of immune cells
2021-02-03
TAMPA, Fla. -- The prognosis of ovarian cancer is poor, with an estimated five-year survival of only 40% for advanced disease, the stage at which most ovarian carcinomas are diagnosed. These poor outcomes are partly due to the lack of effective therapies for advanced disease and recurrence. Immunotherapies hold promise for many types of cancer; however, studies have shown that patients with ovarian cancer do not have strong responses to existing drugs. In a new article published in Nature, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers demonstrate why some ...
Minority patients miss out on cystic fibrosis drugs due to genetic test limitations
2021-02-03
There is an impassioned debate taking place in medicine on whether race-based considerations should be a factor in research, diagnoses, or treatments. Those on one side assert that race should be ignored entirely because it is a societal construct with no biological basis, and accordingly many hospitals are abandoning long-established "race corrections" in medical algorithms and diagnostics. Others, like Meghan McGarry, MD, MS, assistant professor of pediatrics at UC San Francisco, say that we can't completely ignore race, precisely because science is rarely free of societal influence - the structural inequality ...
Discoveries at the edge of the periodic table: first ever measurements of einsteinium
2021-02-03
Since element 99 - einsteinium - was discovered in 1952 at the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) from the debris of the first hydrogen bomb, scientists have performed very few experiments with it because it is so hard to create and is exceptionally radioactive. A team of Berkeley Lab chemists has overcome these obstacles to report the first study characterizing some of its properties, opening the door to a better understanding of the remaining transuranic elements of the actinide series.
Published in the journal Nature, the study, "Structural and Spectroscopic Characterization of an Einsteinium Complex," was co-led by Berkeley Lab scientist Rebecca Abergel and Los ...
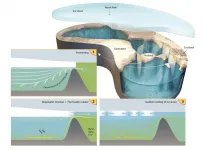
The Arctic Ocean was covered by a shelf ice and filled with freshwater
2021-02-03
The Arctic Ocean was covered by up to 900 m thick shelf ice and was filled entirely with freshwater at least twice in the last 150,000 years. This surprising finding, reported in the latest issue of the journal Nature, is the result of long-term research by scientists from the Alfred Wegener Institute and the MARUM. With a detailed analysis of the composition of marine deposits, the scientists could demonstrate that the Arctic Ocean as well as the Nordic Seas did not contain sea-salt in at least two glacial periods. Instead, these oceans were filled with large amounts of freshwater under a thick ice shield. This water could then be released into the North Atlantic in very short periods of time. Such sudden freshwater inputs could explain rapid climate oscillations for which no satisfying ...
Emergency department visits for mental health, overdose and violence before, during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-02-03
What The Study Did: Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were used to look at changes in emergency department visits for mental health, suicide attempts, drug and opioid overdoses and outcomes of violence before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Kristin M. Holland, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4402)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
COVID-19 outcomes among individuals living with, without HIV in New York State
2021-02-03
What The Study Did: COVID-19 outcomes including hospitalization and in-hospital death were compared between people living with or without diagnosed HIV in New York State.
Authors: Eli S. Rosenberg, Ph.D., of the State University of New York in Rensselaer, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37069)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Soil bacteria hormone discovery provides fertile ground for new antibiotics
2021-02-03
Mechanism for control of antibiotic production in soil bacteria is visualised for the first time by scientists at University of Warwick and Monash University
Research reported in Nature could lead to improved manufacturing of existing antibiotics, and open up opportunities to discover new ones
The majority of clinically used antibiotics are derived from soil bacteria, but can be hard to find because their production is switched off in laboratory cultures
The discovery of how hormone-like molecules turn on antibiotic production in soil bacteria could unlock the untapped opportunities for medicines that are under our very feet.
An international team of scientists working at the University of Warwick, UK, and Monash ...
Personalized screening to identify teens with high suicide risk
2021-02-03
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - The suicide rate among American adolescents has rose drastically over the last decade, but many at-risk youths aren't receiving the mental health services they need.
In fact, one of the greatest challenges is identifying the young people who need the most help.
Now, researchers have developed a personalized system to better detect suicidal youths. The novel, universal screening tool helps caregivers reliably predict an adolescent's suicide risk - alerting them to which ones need follow-up interventions - according to Michigan Medicine-led findings published in JAMA Psychiatry.
"Too many young people are dying by suicide and many at high risk go completely unrecognized and untreated," says lead author Cheryl King, Ph.D., ...
Epigenomic map reveals circuitry of 30,000 human disease regions
2021-02-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Twenty years ago this month, the first draft of the human genome was publicly released. One of the major surprises that came from that project was the revelation that only 1.5 percent of the human genome consists of protein-coding genes.
Over the past two decades, it has become apparent that those noncoding stretches of DNA, originally thought to be "junk DNA," play critical roles in development and gene regulation. In a new study published today, a team of researchers from MIT has published the most comprehensive map yet of this noncoding DNA.
This map provides in-depth annotation of epigenomic marks -- modifications indicating which genes are turned on or off in different types of cells -- across 833 tissues and cell types, a significant increase over ...
Two studies shed light on how, where body can add new fat cells
2021-02-03
DALLAS - Feb. 3, 2021 - Gaining more fat cells is probably not what most people want, although that might be exactly what they need to fight off diabetes and other diseases. How and where the body can add fat cells has remained a mystery - but two new studies from UT Southwestern provide answers on the way this process works.
The studies, both published online today in Cell Stem Cell, describe two different processes that affect the generation of new fat cells. One reports how fat cell creation is impacted by the level of activity in tiny organelles inside cells called mitochondria. The other outlines a process that prevents new fat cells from developing in one fat storage area in ...
Increased risk of dying from COVID for people with severe mental disorders
2021-02-03
People with severe mental disorders have a significantly increased risk of dying from COVID-19. This has been shown in a new study from Umeå University and Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. Among the elderly, the proportion of deaths due to COVID-19 was almost fourfold for those with severe mental disorders compared to non-mentally ill people in the same age.
"We see a high excess mortality due to COVID-19 among the elderly with severe mental disorders, which gives us reason to consider whether this group should be given priority for vaccines," says Martin Maripuu, associate professor at Umeå University.
In the current study, the researchers studied data covering the entire Swedish population over the age of 20 during the period from 11 March to 15 June 2020. Among citizens ...
CABI study updates safer options for fall armyworm control in Africa
2021-02-03
CABI scientists have updated the first major study of potential biological controls that could be used in the fight against the devastating fall armyworm in Africa. The research offers new insight into evidence of their efficacy in the field and increased availability as commercial products.
Indeed, the review, published in the Journal of Applied Entomology, includes many biocontrol products which are now featured in the CABI BioProtection Portal - a free web-based tool that enables users to discover information about registered biocontrol and biopesticide products around the world.
The fall armyworm ...
"Ghost particle" ML model permits full quantum description of the solvated electron
2021-02-03
The behavior of the solvated electron e-aq has fundamental implications for electrochemistry, photochemistry, high-energy chemistry, as well as for biology--its nonequilibrium precursor is responsible for radiation damage to DNA--and it has understandably been the topic of experimental and theoretical investigation for more than 50 years.
Though the hydrated electron appears to be simple--it is the smallest possible anion as well as the simplest reducing agent in chemistry--capturing its physics is...hard. They are short lived and generated in small quantities and so impossible to concentrate and isolate. Their structure is therefore impossible to capture with direct experimental observation such as diffraction methods or NMR. Theoretical modelling has turned out to ...
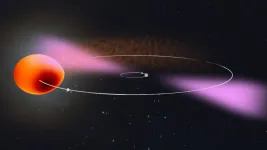
True identity of mysterious gamma-ray source revealed
2021-02-03
An international research team including members from The University of Manchester has shown that a rapidly rotating neutron star is at the core of a celestial object now known as PSR J2039?5617
The international collaboration used novel data analysis methods and the enormous computing power of the citizen science project Einstein@Home to track down the neutron star's faint gamma-ray pulsations in data from NASA's Fermi Space Telescope. Their results show that the pulsar is in orbit with a stellar companion about a sixth of the mass of our Sun. The pulsar is slowly but surely evaporating this star. The team also found that the companion's orbit varies slightly and unpredictably over time. Using their search ...
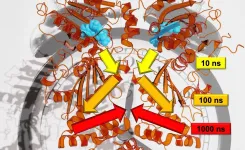
Hierarchical dynamics
2021-02-03
Consider for a moment a tree swaying in the wind. How long does it take for the movement of a twig to reach the trunk of the tree? How is this motion actually transmitted through the tree? Researchers at the University of Freiburg are transferring this kind of question to the analysis of proteins - which are the molecular machinery of cells. A team of researchers lead by Prof. Dr. Thorsten Hugel of the Institute of Physical Chemistry, and Dr. Steffen Wolf and Prof. Dr. Gerhard Stock of the Institute of Physics are investigating how the signals that cause structural changes in proteins travel from one site to another. They are also trying to ...
CDDEP's report 'The State of the World's Antibiotics' highlights the growing threat of AMR
2021-02-03
Washington, DC / New Delhi, India - Researchers at CDDEP have released, The State of the World's Antibiotics in 2021, which presents extensive data on global antimicrobial use and resistance as well as drivers and correlates of antimicrobial resistance, based on CDDEP's extensive research and data collection through ResistanceMap, a global repository that has been widely used by researchers, policymakers, and the media.
Since the first State of the World's Antibiotics report in 2015, antimicrobial resistance has leveled off in some high-income countries but continues to rise in many low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where access to antibiotics has risen with increases in gross ...
Fish in warming Scottish seas grow faster but reach a smaller size
2021-02-03
Researchers have found new evidence that global warming is affecting the size of commercial fish species, documenting for the first time that juvenile fish are getting bigger, as well as confirming that adult fish are getting smaller as sea temperatures rise. The findings are published in the British Ecological Society's Journal of Applied Ecology.
The researchers from the University of Aberdeen looked at four of the most important commercial fish species in the North Sea and the West of Scotland: cod, haddock, whiting and saithe. They found that juvenile fish in the North Sea and on the West of Scotland have been getting bigger while adult fish have been getting smaller. These changes ...
Ostriches challenged by temperature fluctuations
2021-02-03
The world's largest bird, the ostrich, has problems reproducing when the temperature deviates by 5 degrees or more from the ideal temperature of 20 °C. The research, from Lund University in Sweden, is published in Nature Communications.
The results show that the females lay up to 40 percent fewer eggs if the temperature has fluctuated in the days before laying eggs. Both male and female production of gametes is also negatively affected.
"Many believe that ostriches can reproduce anywhere, but they are actually very sensitive to changes in temperature. Climate change means that temperatures will fluctuate even more, and that could be a challenge for the ostrich", says Mads Schou, researcher at Lund ...
Maternal mental health needs attention during COVID-19 lockdowns
2021-02-03
Mothers are at increased risk of mental health problems as they struggle to balance the demands of childcare and remote working in COVID-19 lockdowns, according to new research from an international team of researchers.
The findings, published in the journal Psychological Medicine, were drawn from a comprehensive, online survey of mothers in China, Italy and the Netherlands.
Changes to their working lives, family strife and loss of social networks emerged as common factors affecting the mental health of mothers in all three countries.
The study was carried out by a team from Radboud University, ...
Quantum tunneling in graphene advances the age of terahertz wireless communications
2021-02-03
Scientists from MIPT, Moscow Pedagogical State University and the University of Manchester have created a highly sensitive terahertz detector based on the effect of quantum-mechanical tunneling in graphene. The sensitivity of the device is already superior to commercially available analogs based on semiconductors and superconductors, which opens up prospects for applications of the graphene detector in wireless communications, security systems, radio astronomy, and medical diagnostics. The research results are published in a high-rank journal Nature Communications.
Information transfer in wireless networks is based on transformation of a high-frequency continuous electromagnetic wave into a discrete sequence of bits. This technique is known as signal modulation. ...
[1] ... [2671]
[2672]
[2673]
[2674]
[2675]
[2676]
[2677]
[2678]
2679
[2680]
[2681]
[2682]
[2683]
[2684]
[2685]
[2686]
[2687]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.