A surprising cycle
2021-02-02
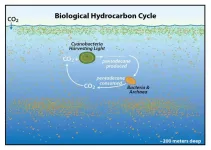
Hydrocarbons and petroleum are almost synonymous in environmental science. After all, oil reserves account for nearly all the hydrocarbons we encounter. But the few hydrocarbons that trace their origin to biological sources may play a larger ecological role than scientists originally suspected.
A team of researchers at UC Santa Barbara and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution investigated this previously neglected area of oceanography for signs of an overlooked global cycle. They also tested how its existence might impact the ocean's response to oil spills.
"We demonstrated that there is a massive and rapid hydrocarbon cycle that occurs in the ocean, and that it is distinct from the ocean's capacity to respond to petroleum input," said Professor David Valentine(link ...
Delaying colonoscopy following abnormal stool test increases risk of colorectal cancer
2021-02-02
A new Veterans Affairs study finds that delays in undergoing colonoscopy following an abnormal stool test increase the risk of a colorectal cancer diagnosis and cancer-related death.
The results appeared online in the journal Gastroenterology in January 2021.
In a retrospective study of more than 200,000 Veterans, the researchers found that patients who received colonoscopy more than 13 months after an abnormal stool blood test were up to 1.3 times more likely to have colorectal cancer, compared with those who had colonoscopy up to three months after the stool test. Odds of an advanced stage of cancer at diagnosis were up to 1.7 times higher when colonoscopy was delayed beyond 16 months.
The findings also ...
The secrets of 3000 galaxies laid bare
2021-02-02
The complex mechanics determining how galaxies spin, grow, cluster and die have been revealed following the release of all the data gathered during a massive seven-year Australian-led astronomy research project.
The scientists observed 13 galaxies at a time, building to a total of 3068, using a custom-built instrument called the Sydney-AAO Multi-Object Integral-Field Spectrograph (SAMI), connected to the 4-metre Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) at Siding Spring Observatory in New South Wales. The telescope is operated by the Australian National University.
Overseen by the ARC Centre of Excellence for All Sky Astrophysics ...
Gene mutations linked to worse outcomes from leukemia in Hispanic and Latino children
2021-02-02
A combination of genetic mutations may explain the higher incidence of and poorer outcomes from pediatric leukemia in Hispanic and Latino children, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. They said a novel therapeutic drug combination - as well as testing for these mutations - may help address the disparity.
Hispanic and Latino children are between 1.2 and 1.75 times more likely to develop B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the most common childhood cancer, than non-Hispanic and Latino children. They also have a 40% higher death rate than their counterparts after correcting for socioeconomic factors. Dr. Sinisa Dovat, a researcher and pediatric ...
Survival tip: Start at normal weight and slowly add pounds
2021-02-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio - People who start adulthood with a body mass index (BMI) in the normal range and move later in life to being overweight - but never obese - tend to live the longest, a new study suggests.
Adults in this category lived longer than even those whose BMI stayed in the normal range throughout their life. Those who started adulthood as obese and continued to add weight had the highest mortality rate.
"The impact of weight gain on mortality is complex. It depends on both the timing and the magnitude of weight gain and where BMI started," said Hui Zheng, lead author of the study and associate ...
Biomedical basis of the Barker hypothesis uncovered
2021-02-02
According to the Barker hypothesis (Hales and Barker 1992) (also referred to as "small baby syndrome"), infants with too low body weight have an increased risk of suffering from cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, diabetes and chronic kidney diseases in adulthood. According to this hypothesis, fetal protective mechanisms enable adaptation to unfavorable intrauterine conditions (chronic oxygen or nutrient deficiency) and allow for fetal survival. At the same time, however, they lead to permanent structural and functional strains and changes into adulthood. The comprehensive study recently published in Nature Communications now clarifies central mechanisms of this phenomenon.
Fetuin-A plays a key role
Under the program of the Swiss National ...
Study shows aspirin before a diagnosis may lower colorectal cancer mortality
2021-02-02
ATLANTA - FEBRUARY 2, 2021 - A new study finds that long-term aspirin use before a diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) may be associated with lower CRC-specific mortality. The report that appears in JNCI: The Journal of the National Cancer Institute, suggests that the findings for pre-diagnosis aspirin use might help reduce CRC mortality in the overall population by limiting metastatic spread of colorectal tumors before diagnosis. Preventing distant metastases leads to fewer deaths from colorectal cancer.
The study, led by Peter T. Campbell, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, used data from men and women enrolled in the American Cancer Society's Cancer Prevention Study-II (CPS-II) Nutrition Cohort who were cancer-free ...
Surgery to heal inflamed gut may create new target for disease
2021-02-02
A surgical procedure meant to counter ulcerative colitis, an immune disease affecting the colon, may trigger a second immune system attack, a new study shows.
The study results revolve around the immune system, the cells and proteins that destroy invading bacteria and viruses. Activating it brings about inflammation, responses like swelling and pain that result from cells homing in on the site of infection or injury. Autoimmune diseases like ulcerative colitis occur when this system mistakenly damages the body's own tissues.
Colon tissue damaged by the disease is routinely addressed with a "J-pouch" procedure wherein a pouch is surgically constructed from nearby, healthy ...
Test for early detection of heart problems reduces risk of heart damage from chemotherapy
2021-02-02
Toronto, ON - Results of a multi-centre, international, clinical trial co-led by Peter Munk Cardiac Centre (PMCC) cardiologist Dr. Dinesh Thavendiranathan point to the benefit of using a more sensitive test to detect heart function issues early, so cancer patients don't have to fight heart failure too.
Unfortunately, for 1 in 20 high-risk patients, treating cancer with certain therapies means the added potential of developing heart failure. The one-year results of the highly anticipated trial compared heart function at the end of anthracycline-based chemotherapy, a treatment that can successfully treat cancer but ...
Racial disparities: Young, Black adults had significantly worse heart transplant outcomes
2021-02-02
DALLAS, Feb. 2, 2021 — Young, Black adults are more than twice as likely to die in the first year after a heart transplant when compared to same-age, non-Black heart transplant recipients, according to new research published today in Circulation: Heart Failure, an American Heart Association journal.
Research has consistently shown that Black heart transplant recipients have a higher risk of death following heart transplantation compared to non-Black recipients. Black patients have higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease at younger ages, and therefore, they may need heart transplants at younger ...
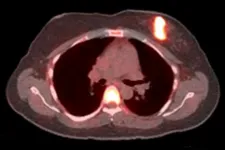
Imaging identifies breast cancer patients unlikely to benefit from hormone therapy
2021-02-02
Hormone therapy commonly is given as a targeted treatment for women whose cancer cells carry receptors for estrogen. But the therapy only works for about half of all patients. Until now, there hasn't been a good way to reliably predict who will benefit and who will not.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown they can distinguish patients likely or unlikely to benefit from hormone therapy using an imaging test that measures the function of the estrogen receptors in their cancer cells. In a small phase 2 clinical trial, the researchers showed that the cancers of all patients with working estrogen receptors remained stable or improved on hormone therapy, and progressed in all women with nonfunctional ...
Tiny 3D structures enhance solar cell efficiency
2021-02-02
A new method for constructing special solar cells could significantly increase their efficiency. Not only are the cells made up of thin layers, they also consist of specifically arranged nanoblocks. This has been shown in a new study by an international research team led by the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), which was published in the scientific journal Nano Letters.
Commercially available solar cells are mostly made of silicon. "Based on the properties of silicon it's not feasible to say that their efficiency can be increased indefinitely," says Dr Akash Bhatnagar, a physicist from the Centre for Innovation Competence (ZIK) "SiLi-nano" at MLU. ...
X-Stop® vs Laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis: Quality of life and cost-effectiveness
2021-02-02
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (FEBRUARY 2, 2021). Researchers in the United Kingdom (UK) conducted a randomized controlled trial in 47 patients with lumbar spinal stenosis to compare treatment outcomes and costs of two competing surgical procedures: insertion of the X-Stop® (Medtronic) interspinous distractor device and open decompression surgery with laminectomy. Both procedures improved the patients' quality of life; however, overall, laminectomy gave patients a better quality of life and was also more cost-effective.
Detailed findings of this study can be found in a new article, "A randomized controlled trial of the X-Stop interspinous ...
NYUAD researchers propose programming to support adolescent mothers in areas of conflict
2021-02-02
Abu Dhabi, UAE, February 2, 2021: Adolescent mothers often fall through the cracks of educational programming. This is highly problematic given that globally an estimated 12 million girls between the ages of 15-19, and 777,000 girls under the age of 15, give birth each year. In populations affected by conflict and displacement, adolescent girls have an increased likelihood of becoming mothers due to various factors, such as disruptions to schooling, the loss of family members, poverty, gender-based violence, and poor access to healthcare and sexual and reproductive services and resources. There is a lack of support programs for these young mothers, and a continuing need for educational programming. ...
South Africa: the rising temperatures will cost up to 20% of per capita GDP
2021-02-02
Temperature rise due to climate change has negatively affected labour productivity in the past decades and will keep damaging it, potentially at a higher extent than what has been estimated in the literature up to now. In South Africa, a future scenario with severe climate change will feature a reduction of per capita GDP of up to 20% by the end of the century, compared to an idealized future without the impacts of a changing climate.
This is what emerges from the study "Climate change and development in South Africa: the impact of rising temperatures on economic productivity and labour availability", coordinated by the ...
Coral decline -- is sunscreen a scapegoat?
2021-02-02
Many household products contain ingredients to protect them against sun damage. These UV filters are found in plastics, paints and textiles, as well as personal care products such as sunscreens and moisturizers. UV filters are entering the aquatic environment in rivers, lakes and oceans. Consider for a moment a beach goer swimming in the ocean or rain washing over plastic playground equipment and running into a stormwater drain - either directly or indirectly, UV filters end up making their way to a waterway.
UV filters are chemicals that work by either physically blocking or absorbing UV rays. There are two main types of UV filters: inorganic forms, which contain metal particles, ...
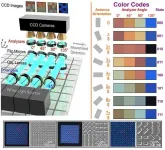
Say goodbye to the dots and dashes to enhance optical storage media
2021-02-02
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Purdue University innovators have created technology aimed at replacing Morse code with colored "digital characters" to modernize optical storage. They are confident the advancement will help with the explosion of remote data storage during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Morse code has been around since the 1830s. The familiar dots and dashes system may seem antiquated given the amount of information needed to be acquired, digitally archived and rapidly accessed every day. But those same basic dots and dashes are still used in many optical media to aid in storage.
A new technology developed at Purdue is aimed at ...
US adults report highest stress level since early days of the COVID-19 pandemic
2021-02-02
As the U.S. confronts a bitter election season, political unrest and violence, a shaky economy, and a soaring death toll due to COVID-19, 84% of U.S. adults say the country has serious societal issues that we need to address, according to a new poll.
At the same time, 9 in 10 adults say they hope that the country moves toward unity, according to Stress in AmericaTM: January 2021 Stress Snapshot, conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of the American Psychological Association.
The survey found that the average reported stress level during the prior month was 5.6, (on a scale from 1 to 10 where ...
In survey of those with uncontrolled asthma, half smoked cannabis
2021-02-02
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, IL (Feb. 2, 2021) - As the number of states increase where medical and recreational cannabis use is legal, so does the importance that physicians discuss with patients the effects of cannabis on those with asthma. A new survey in Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific journal of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, shows that of those who used cannabis, about half smoked it while a third vaped - both "inhalation routes" likely to affect one's lungs.
"It surprised me that over half of the cannabis users in this study who have asthma were smoking it," said Joanna Zeiger, PhD, principal investigator for the study. "And further, of those with uncontrolled asthma, ...
Traffic noise makes mating crickets less picky
2021-02-02
A new study shows that the mating behaviour of crickets is significantly affected by traffic noise and other man-made sounds - a finding that could have implications for the future success of the species.
The research, published in the journal Behavioral Ecology, was carried out at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), and involved studying the mating choices of female field crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus) under different acoustic conditions.
When a female cricket is nearby, male crickets will perform a courtship song by rubbing their wings together. The song is energetically costly to produce and so contains ...
Latest review shows intensive care mortality from COVID-19 continued to fall in 2020, but improvement is slowing
2021-02-02
A meta-analysis of global studies published in Anaesthesia (a journal of the Association of Anaesthetists) shows that intensive care morality from COVID-19 has continued to fall since the start of the pandemic, but the improvement is slowing and may have plateaued. The study is by Professor Tim Cook (Consultant in Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine, Royal United Hospitals Bath NHS Foundation Trust, Bath, UK, and Honorary Professor, School of Medicine, University of Bristol, UK) and colleagues.
A previous meta-analysis* by Cook and colleagues, published in July, 2020, concluded that overall mortality of COVID-19 patients in intensive care units (ICUs) has fallen from almost 60% at the end of March 2020 to 42% at the end of May 2020 -- a relative decrease of around one third. This ...
COVID-19 intensive care mortality in Sweden lower than in many studies from other countries
2021-02-02
New research reveals that the COVID-19 intensive care (ICU) mortality rate in Sweden was lower during the first wave of the pandemic than in many studies from other countries. And while analysis of individual underlying conditions found they were linked to mortality, an analysis looking at all these variables together found COVID-19 mortality in intensive care was not associated with underlying conditions, except for chronic lung disease. This new study did, however, find that, like previous research, mortality was driven by age, severity of COVID-19 disease and the presence and ...
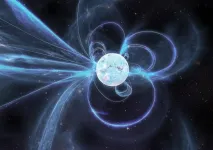
Astronomers spot bizarre activity from one of the strongest magnets in the Universe
2021-02-02
Astronomers from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav) and CSIRO have just observed bizarre, never-seen-before behaviour from a 'radio-loud' magnetar--a rare type of neutron star and one of the strongest magnets in the Universe.
Their new findings, published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS), suggest magnetars have more complex magnetic fields than previously thought - which may challenge theories of how they are born and evolve over time.
Magnetars are a rare type of rotating neutron star with some of the most powerful magnetic fields in the Universe. Astronomers have detected only thirty of these objects in and around the Milky ...
Mathematical method developed to predict cancer and drug-specific immunotherapy efficacy
2021-02-02
HOUSTON-(Feb. 1, 2021) - Houston Methodist researchers have developed a mathematical model to predict how specific cancers will respond to immunotherapy treatments, thus enhancing chances for successful treatments from a wide variety of cancer-immunotherapy drug combinations. The results were published last month in Nature Biomedical Engineering in collaboration with researchers at MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Immunotherapy activates patients' immune systems to recognize and attack their cancers, leading to higher, more targeted kill rates and fewer side effects than chemotherapy, radiation and other therapies. While this technology is a significant advance in fighting cancer, it works only with some cancer ...
February special issue of SLAS Discovery focuses on hit discovery methodologies
2021-02-02
Oak Brook, IL - The February edition of SLAS Discovery is a Special Issue on Hit Discovery Methodologies edited by Mark Wigglesworth, Ph.D., (Medicines Discovery Catapult, Stockport, EN, UK) and Peter Hodder, Ph.D. (Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA, USA).
The focus of this Special Issue is to highlight the use of hit discovery methodologies and technologies and their usage in both small molecule and large molecule drug discovery. The February issue exemplifies how technologies, both new and existing, have been applied successfully to find hits.
Additionally, the issue houses a list of the most downloaded articles from SLAS journals, many of which ...
[1] ... [2678]
[2679]
[2680]
[2681]
[2682]
[2683]
[2684]
[2685]
2686
[2687]
[2688]
[2689]
[2690]
[2691]
[2692]
[2693]
[2694]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.