Blink! The link between aerobic fitness and cognition
2021-02-03
Tsukuba, Japan - Although exercise is known to enhance cognitive function and improve mental health, the neurological mechanisms of this link are unknown. Now, researchers from Japan have found evidence of the missing link between aerobic fitness and cognitive function.
In a study published in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, researchers from the University of Tsukuba revealed that spontaneous eye blink rate (sEBR), which reflects activity of the dopamine system, could be used to understand the connection between cognitive function and aerobic fitness.
The dopaminergic system is known to be involved in physical activity and exercise, and previous researchers have proposed that exercise-induced changes in cognitive function might be mediated by activity ...
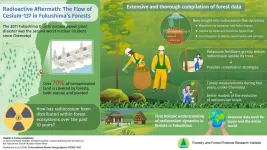
Dynamics of radiocesium in forests after the Fukushima disaster: Concerns and some hope
2021-02-03
After the Chernobyl disaster of 1986, the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant (FDNPP) disaster was the second worst nuclear incident in history. Its consequences were tremendous for the Japanese people and now, almost a decade later, they can still be felt both there and in the rest of the world. One of the main consequences of the event is the release of large amounts of cesium-137 (137Cs)--a radioactive "isotope" of cesium--into the atmosphere, which spread farther away from the power plant through wind and rainfall.
Considering the massive threat posed by 137Cs to the health of both humans and ecosystems, it is essential to understand how it has distributed and how much of it still lingers. This is why the ...
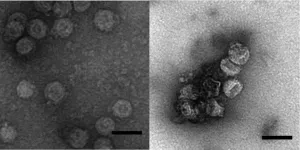
In vitro study helps explain how Zika virus passes from mother to fetus during pregnancy
2021-02-03
Tampa, FL (Feb. 3, 2021) -- A preclinical study by a END ...
Mailing it in: Getting the word out on getting the ballots in
2021-02-03
The coronavirus pandemic forced states across the nation to transform the way their residents voted in 2020, ramping up get-out-the-vote messaging and allowing for more people than ever to vote by mail.
But what's the best way to let residents know about new voting rules? And how much does something like voting by mail increase voter turnout overall?
Political scientists Daniel Hopkins and Marc Meredith looked at these questions during Philadelphia's 2020 primary, and worked with city officials to run an experiment to see whether an inexpensive postcard campaign about mail-in voting would be effective. They partnered with Anjali Chainani, Nathaniel Olin, and Tiffany ...
New research investigates relationship between health literacy and self-care
2021-02-03
It is important for patients to understand the information they need for making health decisions, yet studies have shown that a large segment of the population lacks the health literacy to do so. Health literacy refers to capacity of people to obtain, process, and understand health information needed for making health decisions. A researcher in the School of Information Sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is addressing this topic.
"Many people have inadequate health literacy to support them in understanding health information and/or performing basic self-care activities," said Assistant ...
What impact does Airbnb have on local housing prices and rents?
2021-02-03
Key Takeaways:
Airbnb does have an impact on housing prices and rents.
Impact is stronger in areas with fewer owner-occupiers, such as vacation destination towns.
Airbnb contributes to an increase in the supply of short-term rentals, while decreasing the long-term supply of rentals.
CATONSVILLE, MD, February 2, 2021 - According to new research, the presence of an Airbnb property can actually contribute to an increase in housing prices and rental rates in a local neighborhood. But it depends on where the property is located.
The study sought to assess the impact of home-sharing on residential house prices and ...
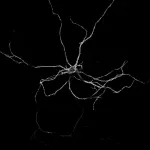
Neurons: 'String of lights' indicates excitation propagation
2021-02-03
A type of novel molecular voltage sensor makes it possible to watch nerve cells at work. The principle of the method has been known for some time. However, researchers at the University of Bonn and the University of California in Los Angeles have now succeeded in significantly improving it. It allows the propagation of electrical signals in living nerve cells to be observed with high temporal and spatial resolution. This enables investigations into completely new questions that were previously closed to research. The study has now been published in the journal PNAS.
When we smell a bottle of suntan lotion, electrical pulses ...
Load-reducing backpack powers electronics by harvesting energy from walking
2021-02-03
Hikers, soldiers and school children all know the burden of a heavy backpack. But now, researchers have developed a prototype that not only makes loads feel about 20% lighter, but also harvests energy from human movements to power small electronics. The new backpack, reported in ACS Nano, could be especially useful for athletes, explorers and disaster rescuers who work in remote areas without electricity, the researchers say.
Backpacks are widely used in everyday life for the hands-free carrying of loads. Over time, however, walking or running with a heavy sack can cause back and neck pain. Also, backpackers ...
Urban agriculture in Chicago does not allow consumers to rely solely on local food
2021-02-03
Environmentally conscious consumers try to "buy local" when food shopping. Now, a study of food raised around Chicago has shown that buying local can't provide all necessary nutrients for area residents, though it could fulfill their needs if some nutrients were supplied as supplements. The researchers report in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology that urban agriculture made little difference in reducing overall land area, and thus distance, required to supply all nutritional needs.
As the U.S. population continues to flow to urban regions, consumers are moving farther from farms and croplands. This limits nutrient recycling and drives up emissions associated with transporting ...
Standard water treatment technique removes and inactivates an enveloped virus
2021-02-03
Enveloped viruses have been detected in raw sewage and sludge, but scientists still don't fully understand the fate and infectivity of these viruses during water purification at treatment plants. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have discovered that a standard water treatment technique, called iron (III) coagulation, and its electrically driven counterpart, iron (0) electrocoagulation, can efficiently remove and inactivate a model enveloped virus.
Enveloped viruses have an outer coating of lipids and proteins that helps protect their genetic material. Typically, disrupting this coat inactivates the virus. Until now, most studies have investigated ...
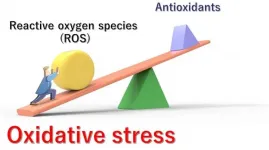
On the dot: Novel quantum sensor provides new approach to early diagnosis via imaging
2021-02-03
Oxygen is essential for human life, but within the body, certain biological environmental conditions can transform oxygen into aggressively reactive molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage DNA, RNA, and proteins. Normally, the body relies on molecules called antioxidants to convert ROS into less dangerous chemical species through a process called reduction. But unhealthy lifestyles, various diseases, stress, and aging can all contribute to an imbalance between the production of ROS and the body's ability to reduce and eliminate them. The resulting excessive levels of ROS cause "oxidative stress," ...
More than half of cancer survivors have underlying medical conditions associated with severe COVID
2021-02-03
ATLANTA - FEBRUARY 3, 2021 - New study finds more than half (56.4%) of cancer survivors in the United States reported having additional underlying medical conditions associated with severe COVID-19 illness. The report appearing in JNCI: The Journal of the National Cancer Institute, suggests that prevalence of these conditions among cancer survivors is nearly 40% higher than that in the general population.
Cancer, and other underlying medical conditions, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, heart diseases, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and obesity, are associated with increased risk of severe COVID-19 illness. For this study, investigators Changchuan (Charles) ...
This is what Germany's eSports athletes eat
2021-02-03
A can of Red Bull next to the computer mouse, a bag of potato chips next to the keyboard - that's how many people imagine nutrition in eSports. "The energy drink is indeed part of the diet for many," says Professor Ingo Froböse, head of the Institute of Movement Therapy and movement-oriented Prevention and Rehabilitation at the German Sport University Cologne, "but overall, eSports players actually eat better than the general population."
This is the result of the third eSport study by the German Sport University Cologne, which was presented in Cologne on February 3, 2021. The two previous eSport studies focused on training ...
Potentially toxic plankton algae may play a crucial role in the future Arctic
2021-02-03
As the sea ice shrinks in the Arctic, the plankton community that produces food for the entire marine food chain is changing. New research shows that a potentially toxic species of plankton algae that lives both by doing photosynthesis and absorbing food may become an important player in the Arctic Ocean as the future sea ice becomes thinner and thinner.
Microscopic plankton algae, invisible to the naked eye, are the foundation of the marine food web, feeding all the ocean´s living creatures from small crustaceans to large whales. Plankton ...
Experiences of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) linked to nutritional health
2021-02-03
A study of factors associated with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) has led to a number of novel findings linking nutrition to experiences of PTSD. Notable among them is the discovery that Canadians, between the ages of 45 and 85, were less likely to exhibit PTSD if they consumed an average of two to three fiber sources daily.
"It is possible that optimal levels of dietary fiber have some type of mental health-related protective effect," says Karen Davison, Director of the Nutrition Informatics Research Group and Health Science Program Faculty Member at Kwantlen Polytechnic University. "This may be due to the communication network that connects the gut and brain via short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are metabolic byproducts of bacterial ...
Study finds childhood diet has lifelong impact
2021-02-03
Eating too much fat and sugar as a child can alter your microbiome for life, even if you later learn to eat healthier, a new study in mice suggests.
The study by UC Riverside researchers is one of the first to show a significant decrease in the total number and diversity of gut bacteria in mature mice fed an unhealthy diet as juveniles.
"We studied mice, but the effect we observed is equivalent to kids having a Western diet, high in fat and sugar and their gut microbiome still being affected up to six years after puberty," explained UCR evolutionary physiologist Theodore Garland.
A paper describing the study has recently been published in the END ...
Brain-related visual problems may affect one in 30 primary school children
2021-02-03
A brain-related visual impairment, which until recently was thought to be rare, may affect one in every 30 children according to new research investigating the prevalence of Cerebral Visual Impairment [CVI]. The University of Bristol-led findings published today [3 February] in Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, aim to raise awareness of CVI among parents and teachers to help them identify signs of the condition earlier.
The brain is just as important as the eyes when it comes to seeing, and many vision problems are caused by areas of the brain that are needed for sight not working properly and cannot be resolved by wearing glasses. Brain-related vision ...
Experts 'scan horizon' to help prepare governments for next major biosecurity threat
2021-02-03
During the summer of 2019, a global team of experts put their heads together to define the key questions facing the UK government when it comes to biological security.
Facilitated by the Centre for Existential Risk (CSER) at the University of Cambridge and the BioRISC project at St Catharine's College, the group of 41 academics and figures from industry and government submitted 450 questions which were then debated, voted on and ranked to define the 80 most urgent.
The final line-up includes major questions on future disease threats, including what role shifts in climate and land use might play, and whether data from social media platforms should be used to help detect the earliest signs of emerging pathogens.
Other ...
Study suggests environmental factors had a role in the evolution of human tolerance
2021-02-03
Environmental pressures may have led humans to become more tolerant and friendly towards each other as the need to share food and raw materials became mutually beneficial, a new study suggests.
This behaviour was not an inevitable natural progression, but subject to ecological pressures, the University of York study concludes.
Humans have a remarkable capacity to care about people well outside their own kin or local group. Whilst most other animals tend to be defensive towards those in other groups our natural tolerance allows us to collaborate today on a global scale, as seen with trade or international relief efforts to provide aid for natural disasters.
Using ...
Alcohol, calories, and obesity: Could labelling make a difference?
2021-02-03
Mandatory calorie labelling of alcoholic drinks could possibly address both alcohol consumption and obesity. An analysis published in Obesity Reviews summaries the results of studies that have examined consumer knowledge of the calorie content of alcoholic drinks, public support for labelling of calorie content on such drinks, and the effect of labelling on consumption.
In the analysis of 18 relevant studies, there was moderate evidence that people were unaware of the calorie content of alcoholic drinks and that they supported labelling. Studies found no evidence that labelling affected consumption levels, but most studies were of low quality and were not conducted in real-world settings.
"The ...
Researchers assess cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer
2021-02-03
A recent analysis of published studies estimates that one-quarter of adults with breast cancer have cognitive impairment before starting therapy. The analysis, which is published in Psycho-Oncology, also found that many patients' cognitive function declines after receiving chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, and/or hormone therapy for breast cancer.
"Our results suggest that cancer-related and personal factors may make a significant contribution to cognitive functioning," said lead author Aicha Dijkshoorn, of the University Medical Center Utrecht, in the Netherlands.
The ...
The pandemic lockdown's psychological impact on pregnant women
2021-02-03
During the lockdown in the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Spain, pregnant women had higher symptoms of depression and anxiety. The finding comes from a study published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, which also revealed that women with higher body mass index and lower social support were most affected.
A total of 204 women accepted to participate in the study, which involved completing questionnaires related to depression, anxiety, and social support.
The study's results "highlight the need to improve mental health care during pregnancy, ...
Sleep deprivation may exacerbate frailty's effects on mental health in older adults
2021-02-03
Previous studies have linked sleep deprivation and frailty with depression. A new study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society that examined their combined effect suggests that short sleep intensifies the impacts of frailty on depressive symptoms.
Among 5,026 community-dwelling older adults in China, participants who were frail at the start of the study were more likely to later develop depressive symptoms. Also, those who experienced worsening frailty throughout the study tended to develop higher levels of depression. Short sleep exacerbated ...
Model predicts likelihood of persistent high-dose opioid use after knee surgery
2021-02-03
A new study published in Arthritis Care & Research has identified 10 readily available clinical factors that may predict which patients will persistently use high doses of opioids in the year following knee replacement surgery.
In the study of 142,089 Medicare patients with osteoarthritis who underwent total knee replacement surgery and had no history of high-dose opioid use, 10.6% became persistent users of high-dose opioids after surgery.
Certain preoperative characteristics including demographics (age, sex, and race), history of substance abuse (opioids, alcohol, and tobacco), and medication use (benzodiazepines, anxiolytics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) were predictors of persistent use of high-dose opioids after surgery. ...
More mammals are being struck by aircraft each year
2021-02-03
Investigators have published a global review of mammal strikes with aircraft, noting that events have been increasing by up to 68% annually. More mammals were struck during the landing phase of an aircraft's rotation than any other phase, according to the article published in Mammal Review.
By analyzing published information and mammal strike data from national aviation authorities in Australia, Canada, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States, researchers found that bats accounted for the greatest proportion of strikes in Australia; rabbits and dog-like carnivores in Canada, Germany, and the United Kingdom; and bats and deer in the United States. Average mammal strikes per year ranged from 1.2 to 38.7 across the countries ...
[1] ... [2682]
[2683]
[2684]
[2685]
[2686]
[2687]
[2688]
[2689]
2690
[2691]
[2692]
[2693]
[2694]
[2695]
[2696]
[2697]
[2698]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.